
Europium is a chemical element with the symbol Eu and atomic number 63. Europium is the most reactive lanthanide by far, having to be stored under an inert fluid to protect it from atmospheric oxygen or moisture. Europium is also the softest lanthanide, as it can be dented with a fingernail and easily cut with a knife. When oxidation is removed a shiny-white metal is visible. Europium was isolated in 1901 and is named after the continent of Europe. Being a typical member of the lanthanide series, europium usually assumes the oxidation state +3, but the oxidation state +2 is also common. All europium compounds with oxidation state +2 are slightly reducing. Europium has no significant biological role and is relatively non-toxic as compared to other heavy metals. Most applications of europium exploit the phosphorescence of europium compounds. Europium is one of the rarest of the rare-earth elements on Earth.

Sodium hydroxide, also known as lye and caustic soda, is an inorganic compound with the formula NaOH. It is a white solid ionic compound consisting of sodium cations Na+ and hydroxide anions OH−.

Europium(III) chloride is an inorganic compound with the formula EuCl3. The anhydrous compound is a yellow solid. Being hygroscopic it rapidly absorbs water to form a white crystalline hexahydrate, EuCl3·6H2O, which is colourless. The compound is used in research.
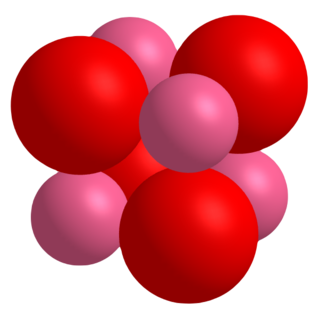
Cobalt(II) oxide is an inorganic compound that has been described as an olive-green or gray solid. It is used extensively in the ceramics industry as an additive to create blue colored glazes and enamels as well as in the chemical industry for producing cobalt(II) salts. A related material is cobalt(II,III) oxide, a black solid with the formula Co3O4.
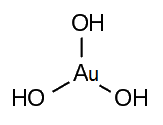
Gold(III) hydroxide, gold trihydroxide, or gold hydroxide is an inorganic compound, a hydroxide of gold, with formula Au(OH)3. It is also called auric acid with formula H3AuO3. It is easily dehydrated above 140 °C to gold(III) oxide. Salts of auric acid are termed aurates.

Lanthanum hydroxide is La(OH)
3, a hydroxide of the rare-earth element lanthanum.
Americium(III) hydroxide is a radioactive inorganic compound with the chemical formula Am(OH)3. It consists of one americium atom and three hydroxide groups. It was first discovered in 1944, closely related to the Manhattan Project. However, these results were confidential and were only released to the public in 1945. It was the first isolated sample of americium, and the first americium compound discovered.
Europium(III) fluoride is an inorganic compound with a chemical formula EuF3.
Thorium(IV) hydroxide is an inorganic compound with a chemical formula Th(OH)4.
Europium hydride is the most common hydride of europium with a chemical formula EuH2. In this compound, europium atom is in the +2 oxidation state and the hydrogen atoms are -1. It is a ferromagnetic semiconductor.
Cerium(IV) hydroxide, also known as ceric hydroxide, is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Ce(OH)4. It is a yellowish powder that is insoluble in water but soluble in concentrated acids.
Praseodymium(III) hydroxide is an inorganic compound with a chemical formula Pr(OH)3.

Neodymium(III) hydroxide is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Nd(OH)3.

Samarium(III) hydroxide is an inorganic compound with chemical formula Sm(OH)3.
Erbium(III) hydroxide is an inorganic compound with chemical formula Er(OH)3.

Dysprosium(III) hydroxide is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Dy(OH)3.
Yttrium(III) hydroxide is an inorganic compound and an alkali with the chemical formula Y(OH)3.

Thulium(III) hydroxide is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Tm(OH)3.
Terbium(III) hydroxide is an inorganic compound with chemical formula Tb(OH)3.

Europium acetate is an inorganic salt of europium and acetic acid with the chemical formula of Eu(CH3COO)3. In this compound, europium exhibits the +3 oxidation state. It can exist in the form of anhydrous, sesquihydrate and tetrahydrate. Its hydrate molecule is a dimer.













