
Dysprosium is the chemical element with the symbol Dy and atomic number 66. It is a rare-earth element in the lanthanide series with a metallic silver luster. Dysprosium is never found in nature as a free element, though, like other lanthanides, it is found in various minerals, such as xenotime. Naturally occurring dysprosium is composed of seven isotopes, the most abundant of which is 164Dy.

Dysprosium(III) chloride (DyCl3), also known as dysprosium trichloride, is a compound of dysprosium and chlorine. It is a white to yellow solid which rapidly absorbs water on exposure to moist air to form a hexahydrate, DyCl3·6H2O. Simple rapid heating of the hydrate causes partial hydrolysis to an oxychloride, DyOCl.
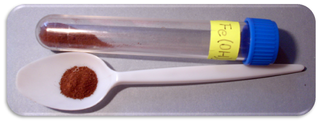
Iron(III) oxide-hydroxide or ferric oxyhydroxide is the chemical compound of iron, oxygen, and hydrogen with formula FeO(OH).

Dysprosium oxide (Dy2O3) is a sesquioxide compound of the rare earth metal dysprosium. It is a pastel yellowish-greenish, slightly hygroscopic powder having specialized uses in ceramics, glass, phosphors, lasers, as a Faraday rotator and dysprosium metal halide lamps.
Dysprosium(III) fluoride is an inorganic compound of dysprosium with a chemical formula DyF3.

Cerium(IV) hydroxide, also known as ceric hydroxide, is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Ce(OH)4. It is a yellowish powder that is insoluble in water but soluble in concentrated acids.
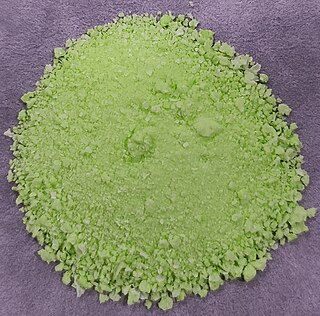
Praseodymium(III) hydroxide is an inorganic compound with a chemical formula Pr(OH)3.

Neodymium(III) hydroxide is an insoluble inorganic compound with the chemical formula Nd(OH)3.

Samarium(III) hydroxide is an inorganic compound with chemical formula Sm(OH)3.

Europium(III) hydroxide is an inorganic compound with a chemical formula Eu(OH)3.

Erbium(III) hydroxide is an inorganic compound with chemical formula Er(OH)3.
Yttrium(III) hydroxide is an inorganic compound and an alkali with the chemical formula Y(OH)3.

Thulium(III) hydroxide is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Tm(OH)3.

Terbium(III) hydroxide is an inorganic compound with chemical formula Tb(OH)3.

Dysprosium acetate is a hypothetical salt of dysprosium and acetate. Its proposed chemical formula is Dy(CH3COO)3.

Europium compounds are compounds formed by the lanthanide metal europium (Eu). In these compounds, europium generally exhibits the +3 oxidation state, such as EuCl3, Eu(NO3)3 and Eu(CH3COO)3. Compounds with europium in the +2 oxidation state are also known. The +2 ion of europium is the most stable divalent ion of lanthanide metals in aqueous solution. Many europium compounds fluoresce under ultraviolet light due to the excitation of electrons to higher energy levels. Lipophilic europium complexes often feature acetylacetonate-like ligands, e.g., Eufod.

Terbium compounds are compounds formed by the lanthanide metal terbium (Tb). Terbium generally exhibits the +3 oxidation state in these compounds, such as in TbCl3, Tb(NO3)3 and Tb(CH3COO)3. Compounds with terbium in the +4 oxidation state are also known, such as TbO2 and BaTbF6. Terbium can also form compounds in the 0, +1 and +2 oxidation states.

Dysprosium(III) bromide is an inorganic compound of bromine and dysprosium, with the chemical formula of DyBr3.

Europium(II) hydroxide is an inorganic compound, with the chemical formula of Eu(OH)2. It can exist as the dihydrate Eu(OH)2·H2O.

Holmium(III) hydroxide is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Ho(OH)3.


















