
Sodium hydroxide, also known as lye and caustic soda, is an inorganic compound with the formula NaOH. It is a white solid ionic compound consisting of sodium cations Na+ and hydroxide anions OH−.

Calcium hydroxide (traditionally called slaked lime) is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Ca(OH)2. It is a colorless crystal or white powder and is produced when quicklime (calcium oxide) is mixed with water. Annually, approximately 125 million tons of calcium hydroxide are produced worldwide.
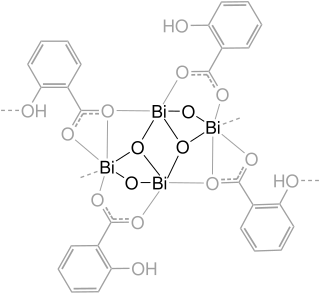
Bismuth subsalicylate, sold generically as pink bismuth and under brand names including Pepto-Bismol, Pepti-Calm and BisBacter, is a medication used to treat temporary discomfort of the stomach and gastrointestinal tract. This includes an upset stomach, heartburn or other similar symptoms.

Sodium aluminate is an inorganic chemical that is used as an effective source of aluminium hydroxide for many industrial and technical applications. Pure sodium aluminate (anhydrous) is a white crystalline solid having a formula variously given as NaAlO2, NaAl(OH)4 (hydrated), Na2O·Al2O3, or Na2Al2O4. Commercial sodium aluminate is available as a solution or a solid.
Other related compounds, sometimes called sodium aluminate, prepared by reaction of Na2O and Al2O3 are Na5AlO4 which contains discrete AlO45− anions, Na7Al3O8 and Na17Al5O16 which contain complex polymeric anions, and NaAl11O17, once mistakenly believed to be β-alumina, a phase of aluminium oxide.
In chemistry, a plumbate often refers to compounds that can be viewed as derivatives of the hypothetical PbO2−3 anion.
Lead(II) hydroxide,, is a hydroxide of lead, with lead in oxidation state +2.

Lithium bromide (LiBr) is a chemical compound of lithium and bromine. Its extreme hygroscopic character makes LiBr useful as a desiccant in certain air conditioning systems.

Tetrasodium EDTA is the salt resulting from the neutralization of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid with four equivalents of sodium hydroxide (or an equivalent sodium base). It is a white solid that is highly soluble in water. Commercial samples are often hydrated, e.g. Na4EDTA.4H2O. The properties of solutions produced from the anhydrous and hydrated forms are the same, provided they are at the same pH.

Bismuth chloride (or butter of bismuth) is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula BiCl3. It is a covalent compound and is the common source of the Bi3+ ion. In the gas phase and in the crystal, the species adopts a pyramidal structure, in accord with VSEPR theory.

White lead is the basic lead carbonate 2PbCO3·Pb(OH)2. It is a complex salt, containing both carbonate and hydroxide ions. White lead occurs naturally as a mineral, in which context it is known as hydrocerussite, a hydrate of cerussite. It was formerly used as an ingredient for lead paint and a cosmetic called Venetian ceruse, because of its opacity and the satiny smooth mixture it made with dryable oils. However, it tended to cause lead poisoning, and its use has been banned in most countries.

Barium ferrate is the chemical compound of formula BaFeO4. This is a rare compound containing iron in the +6 oxidation state. The ferrate(VI) ion has two unpaired electrons, making it paramagnetic. It is isostructural with BaSO4, and contains the tetrahedral [FeO4]2− anion.

Bismuth is a chemical element with the symbol Bi and atomic number 83. It is a post-transition metal and one of the pnictogens, with chemical properties resembling its lighter group 15 siblings arsenic and antimony. Elemental bismuth occurs naturally, and its sulfide and oxide forms are important commercial ores. The free element is 86% as dense as lead. It is a brittle metal with a silvery-white color when freshly produced. Surface oxidation generally gives samples of the metal a somewhat rosy cast. Further oxidation under heat can give bismuth a vividly iridescent appearance due to thin-film interference. Bismuth is both the most diamagnetic element and one of the least thermally conductive metals known.
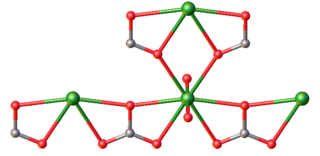
Uranyl carbonate refers to the inorganic compound with the formula UO2CO3. Also known by its mineral name rutherfordine, this material consists of uranyl (UO22+) and carbonate (CO32-). Like most uranyl salts, the compound is a polymeric, each uranium(VI) center being bonded to eight O atoms. Hydrolysis products of rutherfordine are also found in both the mineral and organic fractions of coal and its fly ash and is the main component of uranium in mine tailing seepage water.
Bismuth pentafluoride is an inorganic compound with the formula BiF5. It is a white solid that is highly reactive. The compound is of interest to researchers but not of particular value.
Polonium dichloride is a chemical compound of the radioactive metalloid, polonium and chlorine. Its chemical formula is PoCl2. It is an ionic salt.

Polonium dioxide (also known as polonium(IV) oxide) is a chemical compound with the formula PoO2. It is one of three oxides of polonium, the other two being polonium monoxide (PoO) and polonium trioxide (PoO3). It is a pale yellow crystalline solid at room temperature. Under lowered pressure (such as a vacuum), it decomposes into elemental polonium and oxygen at 500 °C. It is the most stable oxide of polonium and is an interchalcogen.

Bismuth oxynitrate is the name applied to a number of compounds that contain Bi3+, nitrate ions and oxide ions and which can be considered as compounds formed from Bi2O3, N2O5 and H2O. Other names for bismuth oxynitrate include bismuth subnitrate and bismuthyl nitrate. In older texts bismuth oxynitrate is often simply described as BiONO3 or basic bismuth nitrate. Bismuth oxynitrate was once called magisterium bismuti or bismutum subnitricum, and was used as a white pigment, in beauty care, and as a gentle disinfectant for internal and external use. It is also used to form Dragendorff's reagent, which is used as a TLC stain.

The metallic elements in the periodic table located between the transition metals to their left and the chemically weak nonmetallic metalloids to their right have received many names in the literature, such as post-transition metals, poor metals, other metals, p-block metals, basic metals, and chemically weak metals. The most common name, post-transition metals, is generally used in this article.

Bismuthyl is an inorganic oxygen-containing singly charged ion with the chemical formula BiO+, and is an oxycation of bismuth in the +3 oxidation state. Most often it is formed during the hydrolysis of trivalent bismuth salts, primarily nitrate, chloride and other halides. In chemical compounds, bismuthyl plays the role of a monovalent cation.

















