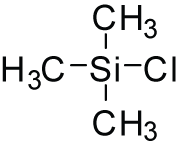Pyrrole is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound, a five-membered ring with the formula C4H4NH. It is a colorless volatile liquid that darkens readily upon exposure to air. Substituted derivatives are also called pyrroles, e.g., N-methylpyrrole, C4H4NCH3. Porphobilinogen, a trisubstituted pyrrole, is the biosynthetic precursor to many natural products such as heme.
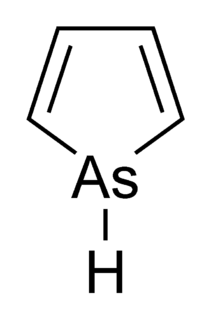
Arsole, also called arsenole or arsacyclopentadiene, is an organoarsenic compound with the formula C4H4AsH. It is classified as a metallole and is isoelectronic to and related to pyrrole except that an arsenic atom is substituted for the nitrogen atom. Whereas the pyrrole molecule is planar, the arsole molecule is not, and the hydrogen atom bonded to arsenic extends out of the molecular plane. Arsole is only moderately aromatic, with about 40% the aromaticity of pyrrole. Arsole itself has not been reported in pure form, but several substituted analogs called arsoles exist. Arsoles and more complex arsole derivatives have similar structure and chemical properties to those of phosphole derivatives. When arsole is fused to a benzene ring, this molecule is called arsindole, or benzarsole.
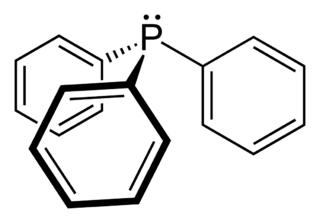
Triphenylphosphine (IUPAC name: triphenylphosphane) is a common organophosphorus compound with the formula P(C6H5)3 and often abbreviated to PPh3 or Ph3P. It is widely used in the synthesis of organic and organometallic compounds. PPh3 exists as relatively air stable, colorless crystals at room temperature. It dissolves in non-polar organic solvents such as benzene and diethyl ether.

A trimethylsilyl group (abbreviated TMS) is a functional group in organic chemistry. This group consists of three methyl groups bonded to a silicon atom [−Si(CH3)3], which is in turn bonded to the rest of a molecule. This structural group is characterized by chemical inertness and a large molecular volume, which makes it useful in a number of applications.
Organosulfur compounds are organic compounds that contain sulfur. They are often associated with foul odors, but many of the sweetest compounds known are organosulfur derivatives, e.g., saccharin. Nature abounds with organosulfur compounds—sulfur is essential for life. Of the 20 common amino acids, two are organosulfur compounds, and the antibiotics penicillin and sulfa drugs both contain sulfur. While sulfur-containing antibiotics save many lives, sulfur mustard is a deadly chemical warfare agent. Fossil fuels, coal, petroleum, and natural gas, which are derived from ancient organisms, necessarily contain organosulfur compounds, the removal of which is a major focus of oil refineries.

A sulfoxide is a chemical compound containing a sulfinyl (SO) functional group attached to two carbon atoms. It is a polar functional group. Sulfoxides are the oxidized derivatives of sulfides. Examples of important sulfoxides are alliin, a precursor to the compound that gives freshly crushed garlic its aroma, and dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), a common solvent.
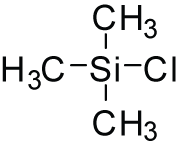
Trimethylsilyl chloride, also known as chlorotrimethylsilane is an organosilicon compound (silyl halide), with the formula (CH3)3SiCl, often abbreviated Me3SiCl or TMSCl. It is a colourless volatile liquid that is stable in the absence of water. It is widely used in organic chemistry.

Organosilicon compounds are organometallic compounds containing carbon–silicon bonds. Organosilicon chemistry is the corresponding science of their preparation and properties. Most organosilicon compounds are similar to the ordinary organic compounds, being colourless, flammable, hydrophobic, and stable to air. Silicon carbide is an inorganic compound.
Silyl enol ethers in organic chemistry are a class of organic compounds that share a common functional group composed of an enolate bonded through its oxygen end to an organosilicon group. They are important intermediates in organic synthesis.

Bismuth chloride (or butter of bismuth) is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula BiCl3. It is a covalent compound and is the common source of the Bi3+ ion. In the gas phase and in the crystal, the species adopts a pyramidal structure, in accord with VSEPR theory.

Isoindole in heterocyclic chemistry is a benzo-fused pyrrole. The compound is an isomer of indole. Its reduced form is isoindoline. The parent isoindole is a rarely encountered in the technical literature, but substituted derivatives are useful commercially and occur naturally. Isoindoles units occur in phthalocyanines, an important family of dyes. Some alkaloids containing isoindole have been isolated and characterized.
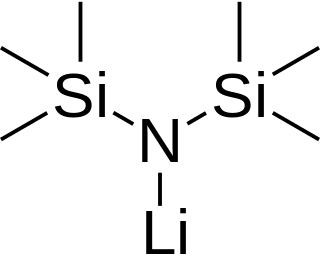
Lithium bis(trimethylsilyl)amide is a lithiated organosilicon compound with the formula LiN(SiMe3)2. It is commonly abbreviated as LiHMDS (lithium hexamethyldisilazide - a reference to its conjugate acid HMDS) and is primarily used as a strong non-nucleophilic base and as a ligand. Like many lithium reagents, it has a tendency to aggregate and will form a cyclic trimer in the absence of coordinating species.
Organoarsenic chemistry is the chemistry of compounds containing a chemical bond between arsenic and carbon. A few organoarsenic compounds, also called "organoarsenicals," are produced industrially with uses as insecticides, herbicides, and fungicides. In general these applications are declining in step with growing concerns about their impact on the environment and human health. The parent compounds are arsine and arsenic acid. Despite their toxicity, organoarsenic biomolecules are well known.

Bismuth is a chemical element with the symbol Bi and atomic number 83. It is a post-transition metal and one of the pnictogens with chemical properties resembling its lighter group 15 siblings arsenic and antimony. Elemental bismuth may occur naturally, although its sulfide and oxide form important commercial ores. The free element is 86% as dense as lead. It is a brittle metal with a silvery-white color when freshly produced, but surface oxidation can give it an iridescent tinge in numerous colours. Bismuth is the most naturally diamagnetic element and has one of the lowest values of thermal conductivity among metals.

Organobismuth chemistry is the chemistry of organometallic compounds containing a carbon to bismuth chemical bond. Applications are few. The main bismuth oxidation states are Bi(III) and Bi(V) as in all higher group 15 elements. The energy of a bond to carbon in this group decreases in the order P > As > Sb > Bi. The first reported use of bismuth in organic chemistry was in oxidation of alcohols by Challenger in 1934 (using Ph3Bi(OH)2). Knowledge about methylated species of bismuth in environmental and biological media is limited.
Organosodium chemistry is the chemistry of organometallic compounds containing a carbon to sodium chemical bond. The application of organosodium compounds in chemistry is limited in part due to competition from organolithium compounds, which are commercially available and exhibit more convenient reactivity.

Stibole is a theoretical heterocyclic organic compound, a five-membered ring with the formula C4H4SbH. It is classified as a metallole. It can be viewed as a structural analog of pyrrole, with antimony replacing the nitrogen atom of pyrrole. Substituted derivatives, which have been synthesized, are called stiboles.

Metal bis(trimethylsilyl)amides are coordination complexes composed of a cationic metal with anionic bis(trimethylsilyl)amide ligands and are part of a broader category of metal amides.

Bismuth(III) nitrate is a salt composed of bismuth in its cationic +3 oxidation state and nitrate anions. The most common solid form is the pentahydrate. It is used in the synthesis of other bismuth compounds. It is available commercially. It is the only nitrate salt formed by a group 15 element, indicative of bismuth's metallic nature.

Pentamethylbismuth (or pentamethylbismuthorane) is an organometalllic compound containing five methyl groups bound to a bismuth atom with formula Bi(CH3)5. It is an example of a hypervalent compound. The molecular shape is trigonal bipyramid.