Synthesis
The reaction of sodium phosphide and bismuth trichloride in toluene (0 °C): [3]
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names Phosphanylidynebismuth | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
PubChem CID | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| BiP | |
| Molar mass | 239.9 |
| Appearance | Black solid |
| Density | g/cm3 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Bismuth phosphide is an inorganic compound of bismuth and phosphorus with the chemical formula BiP. [1] [2]
The reaction of sodium phosphide and bismuth trichloride in toluene (0 °C): [3]
When heated in air, bismuth phosphide burns.
When heated in an atmosphere of carbon dioxide, a gradual volatilization of phosphorus is observed.
This compound is oxidized when boiled in water.
All strong acids dissolve it.
The compound is a semiconductor used in high power, high frequency applications and in laser diodes. [1]

A pnictogen is any of the chemical elements in group 15 of the periodic table. Group (V) is also known as the nitrogen group or nitrogen family. Group (V) consists of the elements nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), arsenic (As), antimony (Sb), bismuth (Bi), and moscovium (Mc).

In chemistry, a phosphide is a compound containing the P3− ion or its equivalent. Many different phosphides are known, with widely differing structures. Most commonly encountered on the binary phosphides, i.e. those materials consisting only of phosphorus and a less electronegative element. Numerous are polyphosphides, which are solids consisting of anionic chains or clusters of phosphorus. Phosphides are known with the majority of less electronegative elements with the exception of Hg, Pb, Sb, Bi, Te, and Po. Finally, some phosphides are molecular.

Sodium phosphide is the inorganic compound with the formula Na3P. It is a black solid. It is often described as Na+ salt of the P3− anion. Na3P is a source of the highly reactive phosphide anion. It should not be confused with sodium phosphate, Na3PO4.

Bismuth chloride (or butter of bismuth) is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula BiCl3. It is a covalent compound and is the common source of the Bi3+ ion. In the gas phase and in the crystal, the species adopts a pyramidal structure, in accord with VSEPR theory.
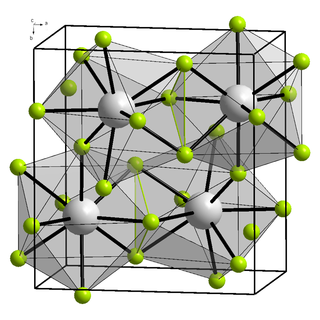
Bismuth(III) fluoride or bismuth trifluoride is a chemical compound of bismuth and fluorine. The chemical formula is BiF3. It is a grey-white powder melting at 649 °C.

Bismuth(III) iodide is the inorganic compound with the formula BiI3. This gray-black salt is the product of the reaction of bismuth and iodine, which once was of interest in qualitative inorganic analysis.

Bismuth is a chemical element with the symbol Bi and atomic number 83. It is a post-transition metal and one of the pnictogens, with chemical properties resembling its lighter group 15 siblings arsenic and antimony. Elemental bismuth occurs naturally, and its sulfide and oxide forms are important commercial ores. The free element is 86% as dense as lead. It is a brittle metal with a silvery-white color when freshly produced. Surface oxidation generally gives samples of the metal a somewhat rosy cast. Further oxidation under heat can give bismuth a vividly iridescent appearance due to thin-film interference. Bismuth is both the most diamagnetic element and one of the least thermally conductive metals known.

Bismuth oxychloride is an inorganic compound of bismuth with the formula BiOCl. It is a lustrous white solid used since antiquity, notably in ancient Egypt. Light wave interference from its plate-like structure gives a pearly iridescent light reflectivity similar to nacre. It is also known as pearl white.
Strontium phosphide is an inorganic compound of strontium and phosphorus with the chemical formula Sr
3P
2. The compound looks like black crystalline material.
Claire Jane Carmalt is a British chemist who is a Professor of Inorganic Chemistry and Head of the Department of Chemistry at University College London. Her research considers the synthesis of molecular precursors and the development of thin film deposition techniques.
Phosphide silicides or silicide phosphides or silicophosphides are compounds containing anions composed of silicide (Si4−) and phosphide (P3−). They can be considered as mixed anion compounds. They are distinct from the phosphidosilicates, which have the phosphorus bonded to the silicon. Related compounds include the phosphide carbides, germanide phosphides, nitride silicides, and antimonide silicides.
Praseodymium phosphide is an inorganic compound of praseodymium and phosphorus with the chemical formula PrP. The compound forms crystals.
Samarium phosphide is an inorganic compound of samarium and phosphorus with the chemical formula SmP.
Thulium phosphide is an inorganic compound of thulium and phosphorus with the chemical formula TmP.
Dysprosium phosphide is an inorganic compound of dysprosium and phosphorus with the chemical formula DyP.
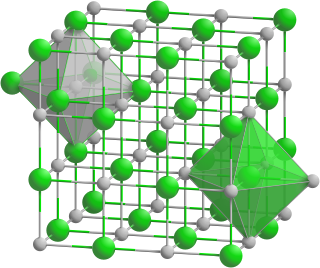
Terbium phosphide is an inorganic compound of terbium and phosphorus with the chemical formula TbP.
Gadolinium phosphide is an inorganic compound of gadolinium and phosphorus with the chemical formula GdP.
Phosphide iodides or iodide phosphides are compounds containing anions composed of iodide (I−) and phosphide (P3−). They can be considered as mixed anion compounds. They are in the category of pnictidehalides. Related compounds include the phosphide chlorides, arsenide iodides antimonide iodides and phosphide bromides.
Cobalt compounds are chemical compounds formed by cobalt with other elements.

Bismuth compounds are compounds containing the element bismuth (Bi). Bismuth forms trivalent and pentavalent compounds, the trivalent ones being more common. Many of its chemical properties are similar to those of arsenic and antimony, although they are less toxic than derivatives of those lighter elements.