
Neodymium is a chemical element; it has symbol Nd and atomic number 60. It is the fourth member of the lanthanide series and is considered to be one of the rare-earth metals. It is a hard, slightly malleable, silvery metal that quickly tarnishes in air and moisture. When oxidized, neodymium reacts quickly producing pink, purple/blue and yellow compounds in the +2, +3 and +4 oxidation states. It is generally regarded as having one of the most complex spectra of the elements. Neodymium was discovered in 1885 by the Austrian chemist Carl Auer von Welsbach, who also discovered praseodymium. Neodymium is present in significant quantities in the minerals monazite and bastnäsite. Neodymium is not found naturally in metallic form or unmixed with other lanthanides, and it is usually refined for general use. Neodymium is fairly common—about as common as cobalt, nickel, or copper—and is widely distributed in the Earth's crust. Most of the world's commercial neodymium is mined in China, as is the case with many other rare-earth metals.
Strontium phosphide is an inorganic compound of strontium and phosphorus with the chemical formula Sr
3P
2. The compound looks like black crystalline material.
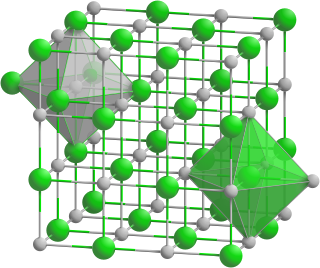
Yttrium phosphide is an inorganic compound of yttrium and phosphorus with the chemical formula YP. The compound may be also classified as yttrium(III) phosphide.
Lithium phosphide is an inorganic compound of lithium and phosphorus with the chemical formula Li3P. This dark colored compound is formally the lithium salt of phosphine, consisting of lithium cations Li+ and phosphide anions P3−. It is hazardous to handle because of its high reactivity toward air.

Scandium phosphide is an inorganic compound of scandium and phosphorus with the chemical formula ScP.
Lutetium phosphide is an inorganic compound of lutetium and phosphorus with the chemical formula LuP. The compound forms dark crystals, does not dissolve in water.
Praseodymium monophosphide is an inorganic compound of praseodymium and phosphorus with the chemical formula PrP. The compound forms crystals.
Europium phosphide is an inorganic compound of europium and phosphorus with the chemical formula EuP. Other phosphides are also known.
Samarium(III) phosphide is an inorganic compound of samarium and phosphorus with the chemical formula SmP.

Lanthanum phosphide is an inorganic compound of lanthanum and phosphorus with the chemical formula LaP.
Ytterbium(III) phosphide is an inorganic compound of ytterbium and phosphorus with the chemical formula YbP. This is one of the phosphides of ytterbium.
Thulium phosphide is an inorganic compound of thulium and phosphorus with the chemical formula TmP.
Holmium phosphide is a binary inorganic compound of holmium and phosphorus with the chemical formula HoP. The compound forms dark crystals, is stable in air, and does not dissolve in water.
Erbium phosphide is a binary inorganic compound of erbium and phosphorus with the chemical formula ErP.

Dysprosium phosphide is an inorganic compound of dysprosium and phosphorus with the chemical formula DyP.

Terbium phosphide is an inorganic compound of terbium and phosphorus with the chemical formula TbP.

Gadolinium phosphide is an inorganic compound of gadolinium and phosphorus with the chemical formula GdP.

Neodymium(III) vanadate is an inorganic compound, a salt of neodymium and vanadic acid with the chemical formula of NdVO4. It forms pale-blue, hydrated crystals.
Erbium compounds are compounds containing the element erbium (Er). These compounds are usually dominated by erbium in the +3 oxidation state, although the +2, +1 and 0 oxidation states have also been reported.
Ytterbium compounds are chemical compounds that contain the element ytterbium (Yb). The chemical behavior of ytterbium is similar to that of the rest of the lanthanides. Most ytterbium compounds are found in the +3 oxidation state, and its salts in this oxidation state are nearly colorless. Like europium, samarium, and thulium, the trihalides of ytterbium can be reduced to the dihalides by hydrogen, zinc dust, or by the addition of metallic ytterbium. The +2 oxidation state occurs only in solid compounds and reacts in some ways similarly to the alkaline earth metal compounds; for example, ytterbium(II) oxide (YbO) shows the same structure as calcium oxide (CaO).



