 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names Neodymium(III) bismuthide | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| BiNd | |
| Molar mass | 352.22 g/mol |
| Density | 8.8 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 1775°C; [1] 1900°C [2] |
| Critical point (T, P) | −111 kJ/mol [3] |
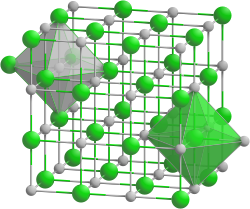
| Structure | |
| cubic | |
| Fm3m | |
a = 6.4222 Å | |
Formula units (Z) | 4 |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions | Neodymium(III) nitride Neodymium(III) arsenide Neodymium(III) phosphide Neodymium(III) antimonide Neodymium(III) oxide |
Other cations | PrBi |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Neodymium bismuthide or Bismuth-Neodymium [4] is a binary inorganic compound of neodymium and bismuth with the formula NdBi. It forms crystals.