Neodymium(III) chloride or neodymium trichloride is a chemical compound of neodymium and chlorine with the formula NdCl3. This anhydrous compound is a mauve-colored solid that rapidly absorbs water on exposure to air to form a purple-colored hexahydrate, NdCl3·6H2O. Neodymium(III) chloride is produced from minerals monazite and bastnäsite using a complex multistage extraction process. The chloride has several important applications as an intermediate chemical for production of neodymium metal and neodymium-based lasers and optical fibers. Other applications include a catalyst in organic synthesis and in decomposition of waste water contamination, corrosion protection of aluminium and its alloys, and fluorescent labeling of organic molecules (DNA).
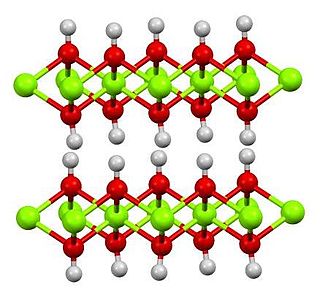
Cadmium hydroxide is an inorganic compound with the formula Cd(OH)2. It is a white crystalline ionic compound that is a key component of nickel–cadmium battery.
Thorium(IV) hydroxide is an inorganic compound with a chemical formula Th(OH)4.

Cerium(IV) hydroxide, also known as ceric hydroxide, is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Ce(OH)4. It is a yellowish powder that is insoluble in water but soluble in concentrated acids.
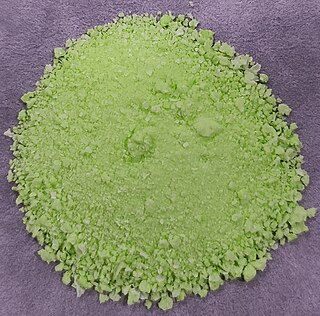
Praseodymium(III) hydroxide is an inorganic compound with a chemical formula Pr(OH)3.

Samarium(III) hydroxide is an inorganic compound with chemical formula Sm(OH)3.

Europium(III) hydroxide is an inorganic compound with a chemical formula Eu(OH)3.

Erbium(III) hydroxide is an inorganic compound with chemical formula Er(OH)3.

Dysprosium(III) hydroxide is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Dy(OH)3.
Yttrium(III) hydroxide is an inorganic compound and an alkali with the chemical formula Y(OH)3.

Thulium(III) hydroxide is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Tm(OH)3.

Terbium(III) hydroxide is an inorganic compound with chemical formula Tb(OH)3.

Neodymium compounds are compounds formed by the lanthanide metal neodymium (Nd). In these compounds, neodymium generally exhibits the +3 oxidation state, such as NdCl3, Nd2(SO4)3 and Nd(CH3COO)3. Compounds with neodymium in the +2 oxidation state are also known, such as NdCl2 and NdI2. Some neodymium compounds have colors that vary based upon the type of lighting.
Neodymium(III) carbonate is an inorganic compound, a salt, where neodymium is in the +3 oxidation state and the carbonate ion has charge -2. It has a chemical formula of Nd2(CO3)3. The anhydrous form is purple-red, while the octahydrate is a pink solid. Both of these salts are insoluble in water.

Europium compounds are compounds formed by the lanthanide metal europium (Eu). In these compounds, europium generally exhibits the +3 oxidation state, such as EuCl3, Eu(NO3)3 and Eu(CH3COO)3. Compounds with europium in the +2 oxidation state are also known. The +2 ion of europium is the most stable divalent ion of lanthanide metals in aqueous solution. Many europium compounds fluoresce under ultraviolet light due to the excitation of electrons to higher energy levels. Lipophilic europium complexes often feature acetylacetonate-like ligands, e.g., Eufod.

Terbium compounds are compounds formed by the lanthanide metal terbium (Tb). Terbium generally exhibits the +3 oxidation state in these compounds, such as in TbCl3, Tb(NO3)3 and Tb(CH3COO)3. Compounds with terbium in the +4 oxidation state are also known, such as TbO2 and BaTbF6. Terbium can also form compounds in the 0, +1 and +2 oxidation states.

Cerium acetate is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula of Ce(CH3COO)3. It is a white powder that is soluble in water. Its 1.5 hydrate loses water at 133°C to obtain an amorphous anhydrous form, and the amorphous phase changes to crystal at 212°C, and phase changes again at 286°C.
Cobalt compounds are chemical compounds formed by cobalt with other elements.

Holmium(III) hydroxide is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Ho(OH)3.

Ytterbium(III) hydroxide is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Yb(OH)3.















