The alkali metals consist of the chemical elements lithium (Li), sodium (Na), potassium (K), rubidium (Rb), caesium (Cs), and francium (Fr). Together with hydrogen they constitute group 1, which lies in the s-block of the periodic table. All alkali metals have their outermost electron in an s-orbital: this shared electron configuration results in their having very similar characteristic properties. Indeed, the alkali metals provide the best example of group trends in properties in the periodic table, with elements exhibiting well-characterised homologous behaviour. This family of elements is also known as the lithium family after its leading element.
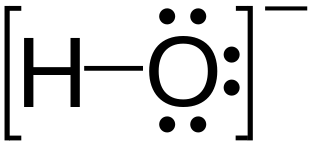
Hydroxide is a diatomic anion with chemical formula OH−. It consists of an oxygen and hydrogen atom held together by a single covalent bond, and carries a negative electric charge. It is an important but usually minor constituent of water. It functions as a base, a ligand, a nucleophile, and a catalyst. The hydroxide ion forms salts, some of which dissociate in aqueous solution, liberating solvated hydroxide ions. Sodium hydroxide is a multi-million-ton per annum commodity chemical. The corresponding electrically neutral compound HO• is the hydroxyl radical. The corresponding covalently bound group –OH of atoms is the hydroxy group. Both the hydroxide ion and hydroxy group are nucleophiles and can act as catalysts in organic chemistry.
Hydrolysis is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water is the nucleophile.

In chemistry, a salt or ionic compound is a chemical compound consisting of an assembly of positively charged ions (cations) and negatively charged ions (anions), which results in a compound with no net electric charge. The constituent ions are held together by electrostatic forces termed ionic bonds.

Thallium is a chemical element; it has symbol Tl and atomic number 81. It is a gray post-transition metal that is not found free in nature. When isolated, thallium resembles tin, but discolors when exposed to air. Chemists William Crookes and Claude-Auguste Lamy discovered thallium independently in 1861, in residues of sulfuric acid production. Both used the newly developed method of flame spectroscopy, in which thallium produces a notable green spectral line. Thallium, from Greek θαλλός, thallós, meaning "green shoot" or "twig", was named by Crookes. It was isolated by both Lamy and Crookes in 1862; Lamy by electrolysis, and Crookes by precipitation and melting of the resultant powder. Crookes exhibited it as a powder precipitated by zinc at the international exhibition, which opened on 1 May that year.

An aqueous solution is a solution in which the solvent is water. It is mostly shown in chemical equations by appending (aq) to the relevant chemical formula. For example, a solution of table salt, also known as sodium chloride (NaCl), in water would be represented as Na+(aq) + Cl−(aq). The word aqueous means pertaining to, related to, similar to, or dissolved in, water. As water is an excellent solvent and is also naturally abundant, it is a ubiquitous solvent in chemistry. Since water is frequently used as the solvent in experiments, the word solution refers to an aqueous solution, unless the solvent is specified.

In chemistry, there are three definitions in common use of the word "base": Arrhenius bases, Brønsted bases, and Lewis bases. All definitions agree that bases are substances that react with acids, as originally proposed by G.-F. Rouelle in the mid-18th century.

Potassium hydroxide is an inorganic compound with the formula KOH, and is commonly called caustic potash.
Thallium(III) hydroxide, Tl(OH)3, also known as thallic hydroxide, is a hydroxide of thallium. It is a white solid.
In chemistry, a strong electrolyte is a solute that completely, or almost completely, ionizes or dissociates in a solution. These ions are good conductors of electric current in the solution.

Thallium(I) sulfate (Tl2SO4) or thallous sulfate is the sulfate salt of thallium in the common +1 oxidation state, as indicated by the Roman numeral I. It is often referred to as simply thallium sulfate.

Tetrafluoroborate is the anion BF−
4. This tetrahedral species is isoelectronic with tetrafluoroberyllate (BeF2−
4), tetrafluoromethane (CF4), and tetrafluoroammonium (NF+
4) and is valence isoelectronic with many stable and important species including the perchlorate anion, ClO−
4, which is used in similar ways in the laboratory. It arises by the reaction of fluoride salts with the Lewis acid BF3, treatment of tetrafluoroboric acid with base, or by treatment of boric acid with hydrofluoric acid.

Sodium hydrosulfide is the chemical compound with the formula NaSH. This compound is the product of the half-neutralization of hydrogen sulfide with sodium hydroxide (NaOH). NaSH and sodium sulfide are used industrially, often for similar purposes. Solid NaSH is colorless. The solid has an odor of H2S owing to hydrolysis by atmospheric moisture. In contrast with sodium sulfide, which is insoluble in organic solvents, NaSH, being a 1:1 electrolyte, is more soluble.
Basic oxides are oxides that show basic properties, in opposition to acidic oxides. A basic oxide can either react with water to form a base, or with an acid to form a salt and water in a neutralization reaction.

Thallium(I) oxide is the inorganic compound of thallium and oxygen with the formula Tl2O in which thallium is in its +1 oxidation state. It is black and produces a basic yellow solution of thallium(I) hydroxide (TlOH) when dissolved in water. It is formed by heating solid TlOH or Tl2CO3 in the absence of air. Thallium oxide is used to make special high refractive index glass. Thallium oxide is a component of several high temperature superconductors. Thallium(I) oxide reacts with acids to make thallium(I) salts.
The thallium halides include monohalides, where thallium has oxidation state +1, trihalides in which thallium generally has oxidation state +3, and some intermediate halides containing thallium with mixed +1 and +3 oxidation states. These salts find use in specialized optical settings, such as focusing elements in research spectrophotometers. Compared to the more common zinc selenide-based optics, materials such as thallium bromoiodide enable transmission at longer wavelengths. In the infrared, this allows for measurements as low as 350 cm−1 (28 μm), whereas zinc selenide is opaque by 21.5 μm, and ZnSe optics are generally only usable to 650 cm−1 (15 μm).

Barium ferrate is the chemical compound of formula BaFeO4. This is a rare compound containing iron in the +6 oxidation state. The ferrate(VI) ion has two unpaired electrons, making it paramagnetic. It is isostructural with BaSO4, and contains the tetrahedral [FeO4]2− anion.
A metal ion in aqueous solution or aqua ion is a cation, dissolved in water, of chemical formula [M(H2O)n]z+. The solvation number, n, determined by a variety of experimental methods is 4 for Li+ and Be2+ and 6 for most elements in periods 3 and 4 of the periodic table. Lanthanide and actinide aqua ions have higher solvation numbers (often 8 to 9), with the highest known being 11 for Ac3+. The strength of the bonds between the metal ion and water molecules in the primary solvation shell increases with the electrical charge, z, on the metal ion and decreases as its ionic radius, r, increases. Aqua ions are subject to hydrolysis. The logarithm of the first hydrolysis constant is proportional to z2/r for most aqua ions.

Aluminium (British and IUPAC spellings) or aluminum (North American spelling) combines characteristics of pre- and post-transition metals. Since it has few available electrons for metallic bonding, like its heavier group 13 congeners, it has the characteristic physical properties of a post-transition metal, with longer-than-expected interatomic distances. Furthermore, as Al3+ is a small and highly charged cation, it is strongly polarizing and aluminium compounds tend towards covalency; this behaviour is similar to that of beryllium (Be2+), an example of a diagonal relationship. However, unlike all other post-transition metals, the underlying core under aluminium's valence shell is that of the preceding noble gas, whereas for gallium and indium it is that of the preceding noble gas plus a filled d-subshell, and for thallium and nihonium it is that of the preceding noble gas plus filled d- and f-subshells. Hence, aluminium does not suffer the effects of incomplete shielding of valence electrons by inner electrons from the nucleus that its heavier congeners do. Aluminium's electropositive behavior, high affinity for oxygen, and highly negative standard electrode potential are all more similar to those of scandium, yttrium, lanthanum, and actinium, which have ds2 configurations of three valence electrons outside a noble gas core: aluminium is the most electropositive metal in its group. Aluminium also bears minor similarities to the metalloid boron in the same group; AlX3 compounds are valence isoelectronic to BX3 compounds (they have the same valence electronic structure), and both behave as Lewis acids and readily form adducts. Additionally, one of the main motifs of boron chemistry is regular icosahedral structures, and aluminium forms an important part of many icosahedral quasicrystal alloys, including the Al–Zn–Mg class.