
Iodine is a chemical element; it has symbol I and atomic number 53. The heaviest of the stable halogens, it exists at standard conditions as a semi-lustrous, non-metallic solid that melts to form a deep violet liquid at 114 °C (237 °F), and boils to a violet gas at 184 °C (363 °F). The element was discovered by the French chemist Bernard Courtois in 1811 and was named two years later by Joseph Louis Gay-Lussac, after the Ancient Greek Ιώδης, meaning 'violet'.
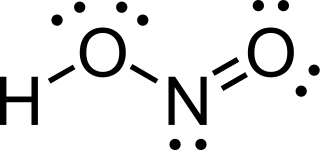
Nitrous acid is a weak and monoprotic acid known only in solution, in the gas phase, and in the form of nitrite salts. It was discovered by Carl Wilhelm Scheele, who called it "phlogisticated acid of niter". Nitrous acid is used to make diazonium salts from amines. The resulting diazonium salts are reagents in azo coupling reactions to give azo dyes.
An iodide ion is the ion I−. Compounds with iodine in formal oxidation state −1 are called iodides. In everyday life, iodide is most commonly encountered as a component of iodized salt, which many governments mandate. Worldwide, iodine deficiency affects two billion people and is the leading preventable cause of intellectual disability.

Hydrazoic acid, also known as hydrogen azide, azic acid or azoimide, is a compound with the chemical formula HN3. It is a colorless, volatile, and explosive liquid at room temperature and pressure. It is a compound of nitrogen and hydrogen, and is therefore a pnictogen hydride. It was first isolated in 1890 by Theodor Curtius. The acid has few applications, but its conjugate base, the azide ion, is useful in specialized processes.

Periodate is an anion composed of iodine and oxygen. It is one of a number of oxyanions of iodine and is the highest in the series, with iodine existing in oxidation state +7. Unlike other perhalogenates, such as perchlorate, it can exist in two forms: metaperiodateIO−
4 and orthoperiodateIO5−
6. In this regard it is comparable to the tellurate ion from the adjacent group. It can combine with a number of counter ions to form periodates, which may also be regarded as the salts of periodic acid.

Iodic acid is a white water-soluble solid with the chemical formula HIO3. Its robustness contrasts with the instability of chloric acid and bromic acid. Iodic acid features iodine in the oxidation state +5 and is one of the most stable oxo-acids of the halogens. When heated, samples dehydrate to give iodine pentoxide. On further heating, the iodine pentoxide further decomposes, giving a mix of iodine, oxygen and lower oxides of iodine.
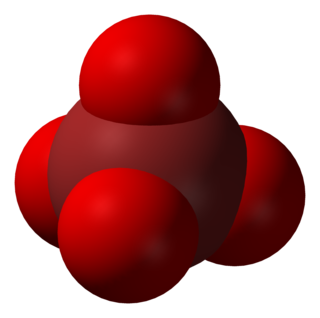
In chemistry, the perbromate ion is the anion having the chemical formula BrO−
4. It is an oxyanion of bromine, the conjugate base of perbromic acid, in which bromine has the oxidation state +7. Unlike its chlorine and iodine analogs, it is difficult to synthesize. It has tetrahedral molecular geometry.

Silver oxide is the chemical compound with the formula Ag2O. It is a fine black or dark brown powder that is used to prepare other silver compounds.
An inorganic nonaqueous solvent is a solvent other than water, that is not an organic compound. These solvents are used in chemical research and industry for reactions that cannot occur in aqueous solutions or require a special environment. Inorganic nonaqueous solvents can be classified into two groups, protic solvents and aprotic solvents. Early studies on inorganic nonaqueous solvents evaluated ammonia, hydrogen fluoride, sulfuric acid, as well as more specialized solvents, hydrazine, and selenium oxychloride.
Bromine compounds are compounds containing the element bromine (Br). These compounds usually form the -1, +1, +3 and +5 oxidation states. Bromine is intermediate in reactivity between chlorine and iodine, and is one of the most reactive elements. Bond energies to bromine tend to be lower than those to chlorine but higher than those to iodine, and bromine is a weaker oxidising agent than chlorine but a stronger one than iodine. This can be seen from the standard electrode potentials of the X2/X− couples (F, +2.866 V; Cl, +1.395 V; Br, +1.087 V; I, +0.615 V; At, approximately +0.3 V). Bromination often leads to higher oxidation states than iodination but lower or equal oxidation states to chlorination. Bromine tends to react with compounds including M–M, M–H, or M–C bonds to form M–Br bonds.
Iodine compounds are compounds containing the element iodine. Iodine can form compounds using multiple oxidation states. Iodine is quite reactive, but it is much less reactive than the other halogens. For example, while chlorine gas will halogenate carbon monoxide, nitric oxide, and sulfur dioxide, iodine will not do so. Furthermore, iodination of metals tends to result in lower oxidation states than chlorination or bromination; for example, rhenium metal reacts with chlorine to form rhenium hexachloride, but with bromine it forms only rhenium pentabromide and iodine can achieve only rhenium tetraiodide. By the same token, however, since iodine has the lowest ionisation energy among the halogens and is the most easily oxidised of them, it has a more significant cationic chemistry and its higher oxidation states are rather more stable than those of bromine and chlorine, for example in iodine heptafluoride.

Thiocyanogen, (SCN)2, is a pseudohalogen derived from the pseudohalide thiocyanate, [SCN]−, with behavior intermediate between dibromine and diiodine. This hexatomic compound exhibits C2 point group symmetry and has the connectivity NCS-SCN.

Magnesium iodide is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula MgI2. It forms various hydrates MgI2·xH2O. Magnesium iodide is a salt of magnesium and hydrogen iodide. These salts are typical ionic halides, being highly soluble in water.

In chemistry, the haloform reaction is a chemical reaction in which a haloform is produced by the exhaustive halogenation of an acetyl group, in the presence of a base. The reaction can be used to transform acetyl groups into carboxyl groups or to produce chloroform, bromoform, or iodoform. Note that fluoroform can't be prepared in this way.
Unlike its lighter congeners, the halogen iodine forms a number of stable organic compounds, in which iodine exhibits higher formal oxidation states than -1 or coordination number exceeding 1. These are the hypervalent organoiodines, often called iodanes after the IUPAC rule used to name them.

Lactoperoxidase is a peroxidase enzyme secreted from mammary, salivary, tears and other mucosal glands including the lungs, bronchii and nose that function as a natural, first line of defense against bacteria and viral agents. Lactoperoxidase is a member of the heme peroxidase family of enzymes. In humans, lactoperoxidase is encoded by the LPO gene.
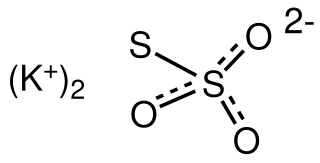
Potassium thiosulfate is an inorganic compound with the formula K2S2O3. This salt can form multiple hydrates, such as the monohydrate, dihydrate, and the pentahydrate, all of which are white or colorless solids. It is used as a fertilizer.

Copper forms a rich variety of compounds, usually with oxidation states +1 and +2, which are often called cuprous and cupric, respectively. Copper compounds, whether organic complexes or organometallics, promote or catalyse numerous chemical and biological processes.
Lutetium compounds are compounds formed by the lanthanide metal lutetium (Lu). In these compounds, lutetium generally exhibits the +3 oxidation state, such as LuCl3, Lu2O3 and Lu2(SO4)3. Aqueous solutions of most lutetium salts are colorless and form white crystalline solids upon drying, with the common exception of the iodide. The soluble salts, such as nitrate, sulfate and acetate form hydrates upon crystallization. The oxide, hydroxide, fluoride, carbonate, phosphate and oxalate are insoluble in water.
Astatine compounds are compounds that contain the element astatine (At). As this element is very radioactive, few compounds have been studied. Less reactive than iodine, astatine is the least reactive of the halogens. Its compounds have been synthesized in nano-scale amounts and studied as intensively as possible before their radioactive disintegration. The reactions involved have been typically tested with dilute solutions of astatine mixed with larger amounts of iodine. Acting as a carrier, the iodine ensures there is sufficient material for laboratory techniques to work. Like iodine, astatine has been shown to adopt odd-numbered oxidation states ranging from −1 to +7.















