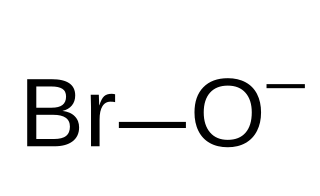Bromine is a chemical element; it has symbol Br and atomic number 35. It is a volatile red-brown liquid at room temperature that evaporates readily to form a similarly coloured vapour. Its properties are intermediate between those of chlorine and iodine. Isolated independently by two chemists, Carl Jacob Löwig and Antoine Jérôme Balard, its name was derived from Ancient Greek βρῶμος (bromos) 'stench', referring to its sharp and pungent smell.
Hydrobromic acid is an aqueous solution of hydrogen bromide. It is a strong acid formed by dissolving the diatomic molecule hydrogen bromide (HBr) in water. "Constant boiling" hydrobromic acid is an aqueous solution that distills at 124.3 °C (255.7 °F) and contains 47.6% HBr by mass, which is 8.77 mol/L. Hydrobromic acid is one of the strongest mineral acids known.

Hydrogen bromide is the inorganic compound with the formula HBr. It is a hydrogen halide consisting of hydrogen and bromine. A colorless gas, it dissolves in water, forming hydrobromic acid, which is saturated at 68.85% HBr by weight at room temperature. Aqueous solutions that are 47.6% HBr by mass form a constant-boiling azeotrope mixture that boils at 124.3 °C (255.7 °F). Boiling less concentrated solutions releases H2O until the constant-boiling mixture composition is reached.

A single-displacement reaction, also known as single replacement reaction or exchange reaction, is an archaic concept in chemistry. It describes the stoichiometry of some chemical reactions in which one element or ligand is replaced by atom or group.
A bromide ion is the negatively charged form (Br−) of the element bromine, a member of the halogens group on the periodic table. Most bromides are colorless. Bromides have many practical roles, being found in anticonvulsants, flame-retardant materials, and cell stains. Although uncommon, chronic toxicity from bromide can result in bromism, a syndrome with multiple neurological symptoms. Bromide toxicity can also cause a type of skin eruption, see potassium bromide. The bromide ion has an ionic radius of 196 pm.

Hydrogen iodide (HI) is a diatomic molecule and hydrogen halide. Aqueous solutions of HI are known as hydroiodic acid or hydriodic acid, a strong acid. Hydrogen iodide and hydroiodic acid are, however, different in that the former is a gas under standard conditions, whereas the other is an aqueous solution of the gas. They are interconvertible. HI is used in organic and inorganic synthesis as one of the primary sources of iodine and as a reducing agent.
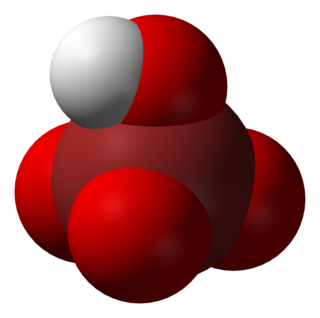
Perbromic acid is the inorganic compound with the formula HBrO4. Perbromic acid is characterized as a colorless liquid which has no characteristic scent. It is an oxoacid of bromine, with an oxidation state of +7. Perbromic acid is a strong acid and strongly oxidizing, though dilute perbromic acid solutions are slow oxidizing agents. It is the most unstable of the halogen(VII) oxoacids. It decomposes rapidly on standing to bromic acid and oxygen, which releases toxic brown bromine vapors. It can be used in the synthesis of perbromate salts, by reacting with a base.

1-Bromo-3-chloro-5,5-dimethylhydantoin is a chemical structurally related to hydantoin. It is a white crystalline compound with a slight bromine and acetone odor and is insoluble in water, but soluble in acetone.

DBDMH is an organic compound derived from the heterocycle called dimethylhydantoin. This white crystalline compound with a slight bromine odor is widely used as a disinfectant used for drinking water purification, recreational water treatment, as a bleaching agent in pulp and paper mills, and for treating industrial/commercial water cooling systems. Its action does not involve the use of hypochlorous acid.
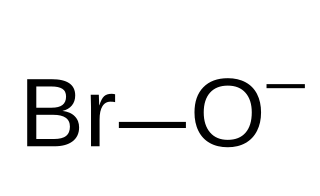
The hypobromite ion, also called alkaline bromine water, is BrO−. Bromine is in the +1 oxidation state. The Br–O bond length is 1.82 Å. Hypobromite is the bromine compound analogous to hypochlorites found in common bleaches, and in immune cells. In many ways, hypobromite functions in the same manner as hypochlorite, and is also used as a germicide and antiparasitic in both industrial applications, and in the immune system.
Bromine compounds are compounds containing the element bromine (Br). These compounds usually form the -1, +1, +3 and +5 oxidation states. Bromine is intermediate in reactivity between chlorine and iodine, and is one of the most reactive elements. Bond energies to bromine tend to be lower than those to chlorine but higher than those to iodine, and bromine is a weaker oxidising agent than chlorine but a stronger one than iodine. This can be seen from the standard electrode potentials of the X2/X− couples (F, +2.866 V; Cl, +1.395 V; Br, +1.087 V; I, +0.615 V; At, approximately +0.3 V). Bromination often leads to higher oxidation states than iodination but lower or equal oxidation states to chlorination. Bromine tends to react with compounds including M–M, M–H, or M–C bonds to form M–Br bonds.

Hypoiodous acid is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula HIO. It forms when an aqueous solution of iodine is treated with mercuric or silver salts. It rapidly decomposes by disproportionation:

Barium bromide is the chemical compound with the formula BaBr2. It is ionic and hygroscopic in nature.

Bromous acid is the inorganic compound with the formula of HBrO2. It is an unstable compound, although salts of its conjugate base – bromites – have been isolated. In acidic solution, bromites decompose to bromine.
Haloperoxidases are peroxidases that are able to mediate the oxidation of halides by hydrogen peroxide. Both halides and hydrogen peroxide are widely available in the environment.
Organobromine chemistry is the study of the synthesis and properties of organobromine compounds, also called organobromides, which are organic compounds that contain carbon bonded to bromine. The most pervasive is the naturally produced bromomethane.

Bromide peroxidase (EC 1.11.1.18, bromoperoxidase, haloperoxidase (ambiguous), eosinophil peroxidase) is a family of enzymes with systematic name bromide:hydrogen-peroxide oxidoreductase. These enzymes catalyse the following chemical reaction:

Eosinophil peroxidase is an enzyme found within the eosinophil granulocytes, innate immune cells of humans and mammals. This oxidoreductase protein is encoded by the gene EPX, expressed within these myeloid cells. EPO shares many similarities with its orthologous peroxidases, myeloperoxidase (MPO), lactoperoxidase (LPO), and thyroid peroxidase (TPO). The protein is concentrated in secretory granules within eosinophils. Eosinophil peroxidase is a heme peroxidase, its activities including the oxidation of halide ions to bacteriocidal reactive oxygen species, the cationic disruption of bacterial cell walls, and the post-translational modification of protein amino acid residues.
A hypohalous acid is an oxyacid consisting of a hydroxyl group single-bonded to any halogen. Examples include hypofluorous acid, hypochlorous acid, hypobromous acid, and hypoiodous acid. The conjugate base is a hypohalite. They can be formed by reacting the corresponding diatomic halogen molecule with water in the reaction:
A halous acid, also known as a halogenous acid, is an oxyacid consisting of a halogen atom in the +3 oxidation state single-bonded to a hydroxyl group and double-bonded to an oxygen atom. Examples include chlorous acid, bromous acid, and iodous acid. The conjugate base is a halite.