| |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name Nitrosylsulfuric acid | |
| Other names nitrosonium bisulfate, chamber crystals | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.029.058 |
PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| HSO4NO | |
| Molar mass | 127.08 g/mol |
| Appearance | Pale yellow crystals [1] |
| Density | 1.865 g/mL in 40% sulfuric acid soln [2] |
| Melting point | 70 °C (158 °F; 343 K) [1] |
| Boiling point | Decomposes |
| Decomposes | |
| Solubility | Soluble in H2SO4 [1] |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards | Oxidizer |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions | NOCl |
Other cations | NaHSO4 |
Related compounds | NOBF4 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
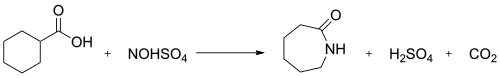
Nitrosylsulfuric acid is the chemical compound with the formula HSO4NO. It is a colourless solid that is used industrially in the production of caprolactam, [3] and was formerly part of the lead chamber process for producing sulfuric acid. The compound is the mixed anhydride of sulfuric acid and nitrous acid.
Contents
In organic chemistry, it is used as a reagent for nitrosating, as a diazotizing agent, and as an oxidizing agent. [1]