
Ytterbium is a chemical element; it has symbol Yb and atomic number 70. It is a metal, the fourteenth and penultimate element in the lanthanide series, which is the basis of the relative stability of its +2 oxidation state. Like the other lanthanides, its most common oxidation state is +3, as in its oxide, halides, and other compounds. In aqueous solution, like compounds of other late lanthanides, soluble ytterbium compounds form complexes with nine water molecules. Because of its closed-shell electron configuration, its density, melting point and boiling point are much lower than those of most other lanthanides.

Sodium hydroxide, also known as lye and caustic soda, is an inorganic compound with the formula NaOH. It is a white solid ionic compound consisting of sodium cations Na+ and hydroxide anions OH−.

Ytterbium(III) oxide is the chemical compound with the formula Yb2O3. It is one of the more commonly encountered compounds of ytterbium. It occurs naturally in trace amounts in the mineral gadolinite. It was first isolated from this in 1878 by Jean Charles Galissard de Marignac.

Ytterbium(III) chloride (YbCl3) is an inorganic chemical compound. It reacts with NiCl2 to form a very effective catalyst for the reductive dehalogenation of aryl halides. It is poisonous if injected, and mildly toxic by ingestion. It is an experimental teratogen, known to irritate the skin and eyes.
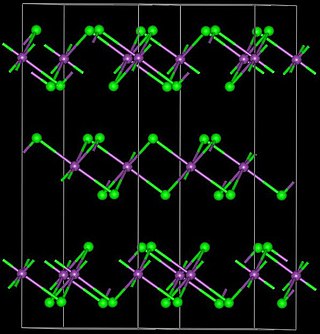
Ytterbium(III) bromide (YbBr3) is an inorganic chemical compound.
Lanthanum ytterbium oxide is a solid inorganic compound of lanthanum, ytterbium and oxygen with the chemical formula of LaYbO3. This compound adopts the perovskite structure.

Ytterbium(III) nitrate is an inorganic compound, a salt of ytterbium and nitric acid with the chemical formula Yb(NO3)3. The compound forms colorless crystals, dissolves in water, and also forms crystalline hydrates.
Ytterbium(III) phosphide is an inorganic compound of ytterbium and phosphorus with the chemical formula YbP. This is one of the phosphides of ytterbium.

Praseodymium(III) acetate is an inorganic salt composed of a Praseodymium atom trication and three acetate groups as anions. This compound commonly forms the dihydrate, Pr(O2C2H3)3·2H2O.

Ytterbium(III) acetate is an inorganic salt of ytterbium and acetic acid, with a chemical formula of Yb(CH3COO)3. It has colorless crystals that are soluble in water and can form hydrates.

Europium compounds are compounds formed by the lanthanide metal europium (Eu). In these compounds, europium generally exhibits the +3 oxidation state, such as EuCl3, Eu(NO3)3 and Eu(CH3COO)3. Compounds with europium in the +2 oxidation state are also known. The +2 ion of europium is the most stable divalent ion of lanthanide metals in aqueous solution. Many europium compounds fluoresce under ultraviolet light due to the excitation of electrons to higher energy levels. Lipophilic europium complexes often feature acetylacetonate-like ligands, e.g., Eufod.
Erbium compounds are compounds containing the element erbium (Er). These compounds are usually dominated by erbium in the +3 oxidation state, although the +2, +1 and 0 oxidation states have also been reported.
Ytterbium compounds are chemical compounds that contain the element ytterbium (Yb). The chemical behavior of ytterbium is similar to that of the rest of the lanthanides. Most ytterbium compounds are found in the +3 oxidation state, and its salts in this oxidation state are nearly colorless. Like europium, samarium, and thulium, the trihalides of ytterbium can be reduced to the dihalides by hydrogen, zinc dust, or by the addition of metallic ytterbium. The +2 oxidation state occurs only in solid compounds and reacts in some ways similarly to the alkaline earth metal compounds; for example, ytterbium(II) oxide (YbO) shows the same structure as calcium oxide (CaO).

Ytterbium(II) iodide is an iodide of ytterbium, with the chemical formula of YbI2. It is a yellow solid.

Ytterbium(III) iodide is one of ytterbium's iodides, with the chemical formula of YbI3.
Ytterbium(II) sulfide is a binary inorganic compound of ytterbium and sulfur with the chemical formula YbS.

Ytterbium(II) fluoride is a binary inorganic compound of ytterbium and fluorine with the chemical formula YbF2.
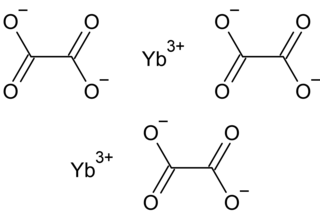
Ytterbium(III) oxalate is the oxalate of ytterbium, with the chemical formula Yb2(C2O4)3.

Ytterbium(II) bromide is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula YbBr2.














