
Nitrogen is a chemical element; it has symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a nonmetal and the lightest member of group 15 of the periodic table, often called the pnictogens. It is a common element in the universe, estimated at seventh in total abundance in the Milky Way and the Solar System. At standard temperature and pressure, two atoms of the element bond to form N2, a colorless and odorless diatomic gas. N2 forms about 78% of Earth's atmosphere, making it the most abundant uncombined element in air. Because of the volatility of nitrogen compounds, nitrogen is relatively rare in the solid parts of the Earth.

Praseodymium(III) chloride is the inorganic compound with the formula PrCl3. Like other lanthanide trichlorides, it exists both in the anhydrous and hydrated forms. It is a blue-green solid that rapidly absorbs water on exposure to moist air to form a light green heptahydrate.

Lithium nitride is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Li3N. It is the only stable alkali metal nitride. It is a reddish-pink solid. It has high melting point.

Zinc nitride (Zn3N2) is an inorganic compound of zinc and nitrogen, usually obtained as (blue)grey crystals. It is a semiconductor. In pure form, it has the anti-bixbyite structure.
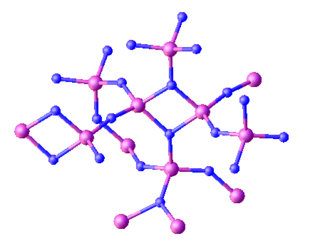
Triphosphorus pentanitride is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula P3N5. Containing only phosphorus and nitrogen, this material is classified as a binary nitride. While it has been investigated for various applications this has not led to any significant industrial uses. It is a white solid, although samples often appear colored owing to impurities.
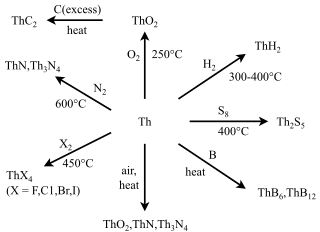
Many compounds of thorium are known: this is because thorium and uranium are the most stable and accessible actinides and are the only actinides that can be studied safely and legally in bulk in a normal laboratory. As such, they have the best-known chemistry of the actinides, along with that of plutonium, as the self-heating and radiation from them is not enough to cause radiolysis of chemical bonds as it is for the other actinides. While the later actinides from americium onwards are predominantly trivalent and behave more similarly to the corresponding lanthanides, as one would expect from periodic trends, the early actinides up to plutonium have relativistically destabilised and hence delocalised 5f and 6d electrons that participate in chemistry in a similar way to the early transition metals of group 3 through 8: thus, all their valence electrons can participate in chemical reactions, although this is not common for neptunium and plutonium.
Praseodymium(III) fluoride is an inorganic compound with the formula PrF3, being the most stable fluoride of praseodymium.
Praseodymium(III) oxalate is an inorganic compound, a salt of praseodymium metal and oxalic acid, with the chemical formula C6O12Pr2. The compound forms light green crystals that are insoluble in water. It also forms crystalline hydrates.

Praseodymium(IV) fluoride (also praseodymium tetrafluoride) is a binary inorganic compound, a highly oxidised metal salt of praseodymium and fluoride with the chemical formula PrF4.
Praseodymium monophosphide is an inorganic compound of praseodymium and phosphorus with the chemical formula PrP. The compound forms crystals.
Praseodymium compounds are compounds formed by the lanthanide metal praseodymium (Pr). In these compounds, praseodymium generally exhibits the +3 oxidation state, such as PrCl3, Pr(NO3)3 and Pr(CH3COO)3. However, compounds with praseodymium in the +2 and +4 oxidation states, and unlike other lanthanides, the +5 oxidation state, are also known.

Neodymium(II) iodide or neodymium diiodide is an inorganic salt of iodine and neodymium the formula NdI2. Neodymium uses the +2 oxidation state in the compound.
Neodymium(III) nitride is a chemical compound of neodymium and nitrogen with the formula NdN in which neodymium exhibits the +3 oxidation state and nitrogen exhibits the -3 oxidation state. It is ferromagnetic, like gadolinium(III) nitride, terbium(III) nitride and dysprosium(III) nitride. Neodymium(III) nitride is not usually stoichiometric, and it is very hard to create pure stoichiometric neodymium nitride.

Praseodymium(III) iodide is an inorganic salt, consisting of the rare-earth metal praseodymium and iodine, with the chemical formula PrI3. It forms green crystals. It is soluble in water.

Europium compounds are compounds formed by the lanthanide metal europium (Eu). In these compounds, europium generally exhibits the +3 oxidation state, such as EuCl3, Eu(NO3)3 and Eu(CH3COO)3. Compounds with europium in the +2 oxidation state are also known. The +2 ion of europium is the most stable divalent ion of lanthanide metals in aqueous solution. Many europium compounds fluoresce under ultraviolet light due to the excitation of electrons to higher energy levels. Lipophilic europium complexes often feature acetylacetonate-like ligands, e.g., Eufod.

Praseodymium(V) oxide nitride is a compound of praseodymium in the oxidation state of +5 with the chemical formula PrNO. It was first reported in 2000. However, the compound was not verified to have an oxidation state of +5 until 2017. This compound is produced by the reaction of praseodymium metal and nitric oxide in 4K and solid neon. The crystal structure is linear with the praseodymium forming a triple bond with the nitrogen and a double bond with the oxygen. Calculation shows a significant level of f-orbital covalence of Pr-X bonds.

Terbium compounds are compounds formed by the lanthanide metal terbium (Tb). Terbium generally exhibits the +3 oxidation state in these compounds, such as in TbCl3, Tb(NO3)3 and Tb(CH3COO)3. Compounds with terbium in the +4 oxidation state are also known, such as TbO2 and BaTbF6. Terbium can also form compounds in the 0, +1 and +2 oxidation states.
Protactinium compounds are compounds containing the element protactinium. These compounds usually have protactinium in the +5 oxidation state, although these compounds can also exist in the +2, +3 and +4 oxidation states.
Lanthanum nitride is a binary inorganic compound of lanthanum and nitride with the chemical formula LaN.
Thulium nitride is a binary inorganic compound of thulium and nitrogen with the chemical formula TmN. It can be prepared by reacting thulium amalgam with nitrogen at high temperature.
 [1]
[1] 










