
Zinc acetate is a salt with the formula Zn(CH3CO2)2, which commonly occurs as the dihydrate Zn(CH3CO2)2·2H2O. Both the hydrate and the anhydrous forms are colorless solids that are used as dietary supplements. When used as a food additive, it has the E number E650.

Lanthanum(III) oxide, also known as lanthana, chemical formula La2O3, is an inorganic compound containing the rare earth element lanthanum and oxygen. It is used in some ferroelectric materials, as a component of optical materials, and is a feedstock for certain catalysts, among other uses.

Iron(II) acetate is a coordination complex with formula Fe(CH3COO)2. It is a white solid, although impure samples can be slightly colored. A light green tetrahydrate is also known, which is highly soluble in water.
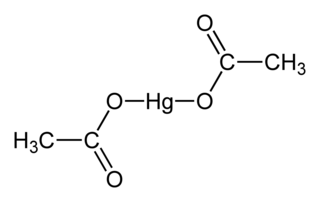
Mercury(II) acetate, also known as mercuric acetate is a chemical compound, the mercury(II) salt of acetic acid, with the formula Hg(O2CCH3)2. Commonly abbreviated Hg(OAc)2, this compound is employed as a reagent to generate organomercury compounds from unsaturated organic precursors. It is a white, water-soluble solid, but some samples can appear yellowish with time owing to decomposition.

Lanthanum chloride is the inorganic compound with the formula LaCl3. It is a common salt of lanthanum which is mainly used in research. It is a white solid that is highly soluble in water and alcohols.

Cobalt(II) acetate is the cobalt salt of acetic acid. It is commonly found as the tetrahydrate Co(CH3CO2)2·4 H2O, abbreviated Co(OAc)2·4 H2O. It is used as a catalyst.

Acetic acid, systematically named ethanoic acid, is an acidic, colourless liquid and organic compound with the chemical formula CH3COOH. Vinegar is at least 4% acetic acid by volume, making acetic acid the main component of vinegar apart from water. It has been used, as a component of vinegar, throughout history from at least the third century BC.
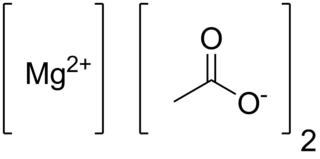
Anhydrous magnesium acetate has the chemical formula Mg(C2H3O2)2 and in its hydrated form, magnesium acetate tetrahydrate, it has the chemical formula Mg(CH3COO)2 • 4H2O. In this compound magnesium has an oxidation state of 2+. Magnesium acetate is the magnesium salt of acetic acid. It is deliquescent and upon heating, it decomposes to form magnesium oxide. Magnesium acetate is commonly used as a source of magnesium in biological reactions.

Lanthanum hydroxide is La(OH)
3, a hydroxide of the rare-earth element lanthanum.

Neodymium(III) acetate is an inorganic salt composed of a neodymium atom trication and three acetate groups as anions where neodymium exhibits the +3 oxidation state. It has a chemical formula of Nd(CH3COO)3 although it can be informally referred to as NdAc because Ac is an informal symbol for acetate. It commonly occurs as a light purple powder.

Praseodymium(III) acetate is an inorganic salt composed of a Praseodymium atom trication and three acetate groups as anions. This compound commonly forms the dihydrate, Pr(O2C2H3)3·2H2O.

Neodymium compounds are compounds formed by the lanthanide metal neodymium (Nd). In these compounds, neodymium generally exhibits the +3 oxidation state, such as NdCl3, Nd2(SO4)3 and Nd(CH3COO)3. Compounds with neodymium in the +2 oxidation state are also known, such as NdCl2 and NdI2. Some neodymium compounds have colors that vary based upon the type of lighting.
Praseodymium compounds are compounds formed by the lanthanide metal praseodymium (Pr). In these compounds, praseodymium generally exhibits the +3 oxidation state, such as PrCl3, Pr(NO3)3 and Pr(CH3COO)3. However, compounds with praseodymium in the +2 and +4 oxidation states, and unlike other lanthanides, the +5 oxidation state, are also known.

Europium(III) acetate is an inorganic salt of europium and acetic acid with the chemical formula of Eu(CH3COO)3. In this compound, europium exhibits the +3 oxidation state. It can exist in the anhydrous form, sesquihydrate and tetrahydrate. Its hydrate molecule is a dimer.

Ytterbium(III) acetate is an inorganic salt of ytterbium and acetic acid, with a chemical formula of Yb(CH3COO)3. It has colorless crystals that are soluble in water and can form hydrates.

Lutetium(III) acetate is the acetate salt of lutetium with the chemical formula of Lu(CH3COO)3.

Holmium acetate is the acetate salt of holmium, with a chemical formula of Ho(CH3COO)3.
Erbium compounds are compounds containing the element erbium (Er). These compounds are usually dominated by erbium in the +3 oxidation state, although the +2, +1 and 0 oxidation states have also been reported.

Scandium acetate is an compound, with the chemical formula of Sc(CH3COO)3. It exists in the anhydrous and the hydrate forms. It can be obtained by reacting scandium hydroxide or scandium oxide with acetic acid. It is a colorless, water-soluble solid. It decomposes into scandium oxide at high temperature. It can be used to prepare other scandium-containing materials.
Lanthanum oxalate is an inorganic compound, a salt of lanthanum metal and oxalic acid with the chemical formula La
2(C
2O
4)
3.



















