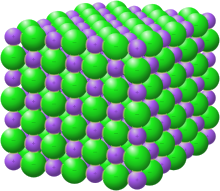
Lanthanum is a chemical element; it has symbol La and atomic number 57. It is a soft, ductile, silvery-white metal that tarnishes slowly when exposed to air. It is the eponym of the lanthanide series, a group of 15 similar elements between lanthanum and lutetium in the periodic table, of which lanthanum is the first and the prototype. Lanthanum is traditionally counted among the rare earth elements. Like most other rare earth elements, its usual oxidation state is +3, although some compounds are known with an oxidation state of +2. Lanthanum has no biological role in humans but is essential to some bacteria. It is not particularly toxic to humans but does show some antimicrobial activity.
The lanthanide or lanthanoid series of chemical elements comprises at least the 14 metallic chemical elements with atomic numbers 57–70, from lanthanum through ytterbium. In the periodic table, they fill the 4f orbitals. Lutetium is also sometimes considered a lanthanide, despite being a d-block element and a transition metal.

Lead(II) sulfate (PbSO4) is a white solid, which appears white in microcrystalline form. It is also known as fast white, milk white, sulfuric acid lead salt or anglesite.

Ammonium hydrosulfide is the chemical compound with the formula [NH4]SH.

Copper monosulfide is a chemical compound of copper and sulfur. It was initially thought to occur in nature as the dark indigo blue mineral covellite. However, it was later shown to be rather a cuprous compound, formula Cu+3S(S2). CuS is a moderate conductor of electricity. A black colloidal precipitate of CuS is formed when hydrogen sulfide, H2S, is bubbled through solutions of Cu(II) salts. It is one of a number of binary compounds of copper and sulfur (see copper sulfide for an overview of this subject), and has attracted interest because of its potential uses in catalysis and photovoltaics.

Lanthanum chloride is the inorganic compound with the formula LaCl3. It is a common salt of lanthanum which is mainly used in research. It is a white solid that is highly soluble in water and alcohols.

Titanium(II) sulfide (TiS) is an inorganic chemical compound of titanium and sulfur.

Copper(I) sulfide is a copper sulfide, a chemical compound of copper and sulfur. It has the chemical compound Cu2S. It is found in nature as the mineral chalcocite. It has a narrow range of stoichiometry ranging from Cu1.997S to Cu2.000S. Samples are typically black.

Samarium monosulfide is a binary inorganic chemical compound of samarium metal and sulfur with the chemical formula SmS.

Silicon monosulfide is a chemical compound of silicon and sulfur. The chemical formula is SiS. Molecular SiS has been detected at high temperature in the gas phase. The gas phase molecule has an Si-S bondlength of 192.93 pm, this compares to the normal single bond length of 216 pm, and is shorter than the Si=S bond length of around 201 pm reported in an organosilanethione. Historically a pale yellow-red amorphous solid compound has been reported. The behavior of silicon can be contrasted with germanium which forms a stable solid monosulfide.
Praseodymium compounds are compounds formed by the lanthanide metal praseodymium (Pr). In these compounds, praseodymium generally exhibits the +3 oxidation state, such as PrCl3, Pr(NO3)3 and Pr(CH3COO)3. However, compounds with praseodymium in the +2 and +4 oxidation states, and unlike other lanthanides, the +5 oxidation state, are also known.
Neodymium(III) sulfide is a inorganic chemical compound with the formula Nd2S3 composed of a two neodymium atoms in the +3 oxidation state and three sulfur atoms in the -2 oxidation state. Like other rare earth sulfides, neodymium(III) sulfide is used as a high-performance inorganic pigment.

Lanthanum(III) iodide is an inorganic compound containing lanthanum and iodine with the chemical formula LaI
3.
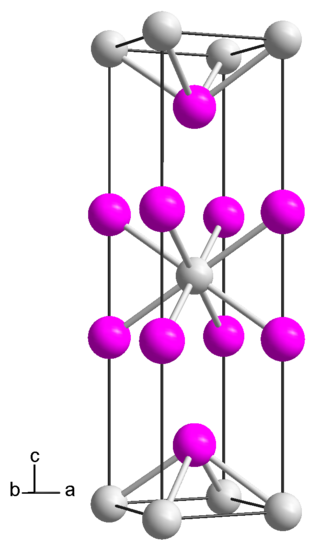
Cerium diiodide is an iodide of cerium, with the chemical formula of CeI2.
Cerium monosulfide is a binary inorganic compound of cerium and sulfur with the chemical formula CeS. This is the simplest of cerium sulfides.

Lithium hexafluorotungstate is an inorganic chemical compound with the chemical formula LiWF6.
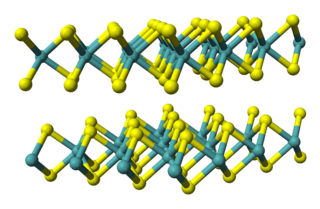
Technetium disulphide is a binary inorganic chemical compound of technetium metal and sulfur with the chemical formula TcS2.
Lanthanum(III) sulfide is a binary inorganic chemical compound of lanthanum metal and sulfur with the chemical formula La2S3.

Holmium monosulfide is a binary inorganic compound of holmium and sulfur with the chemical formula HoS.

Dysprosium monosulfide is a binary inorganic compound of dysprosium and sulfur with the chemical formula DyS.