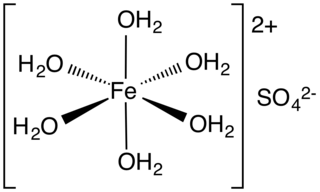
Iron(II) sulfate (British English: iron(II) sulphate) or ferrous sulfate denotes a range of salts with the formula FeSO4·xH2O. These compounds exist most commonly as the heptahydrate (x = 7) but several values for x are known. The hydrated form is used medically to treat or prevent iron deficiency, and also for industrial applications. Known since ancient times as copperas and as green vitriol (vitriol is an archaic name for hydrated sulfate minerals), the blue-green heptahydrate (hydrate with 7 molecules of water) is the most common form of this material. All the iron(II) sulfates dissolve in water to give the same aquo complex [Fe(H2O)6]2+, which has octahedral molecular geometry and is paramagnetic. The name copperas dates from times when the copper(II) sulfate was known as blue copperas, and perhaps in analogy, iron(II) and zinc sulfate were known respectively as green and white copperas.
Iron(III) chloride describes the inorganic compounds with the formula FeCl3(H2O)x. Also called ferric chloride, these compounds are some of the most important and commonplace compounds of iron. They are available both in anhydrous and in hydrated forms which are both hygroscopic. They feature iron in its +3 oxidation state. The anhydrous derivative is a Lewis acid, while all forms are mild oxidizing agents. It is used as a water cleaner and as an etchant for metals.
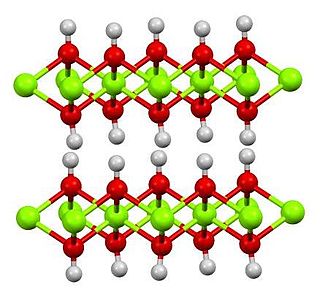
In chemistry, water(s) of crystallization or water(s) of hydration are water molecules that are present inside crystals. Water is often incorporated in the formation of crystals from aqueous solutions. In some contexts, water of crystallization is the total mass of water in a substance at a given temperature and is mostly present in a definite (stoichiometric) ratio. Classically, "water of crystallization" refers to water that is found in the crystalline framework of a metal complex or a salt, which is not directly bonded to the metal cation.

Acetic anhydride, or ethanoic anhydride, is the chemical compound with the formula (CH3CO)2O. Commonly abbreviated Ac2O, it is the simplest isolable anhydride of a carboxylic acid and is widely used as a reagent in organic synthesis. It is a colorless liquid that smells strongly of acetic acid, which is formed by its reaction with moisture in the air.
Iron(II) chloride, also known as ferrous chloride, is the chemical compound of formula FeCl2. It is a paramagnetic solid with a high melting point. The compound is white, but typical samples are often off-white. FeCl2 crystallizes from water as the greenish tetrahydrate, which is the form that is most commonly encountered in commerce and the laboratory. There is also a dihydrate. The compound is highly soluble in water, giving pale green solutions.

Cadmium chloride is a white crystalline compound of cadmium and chloride, with the formula CdCl2. This salt is a hygroscopic solid that is highly soluble in water and slightly soluble in alcohol. The crystal structure of cadmium chloride (described below), is a reference for describing other crystal structures. Also known are CdCl2•H2O and the hemipentahydrate CdCl2•2.5H2O.

Zinc acetate is a salt with the formula Zn(CH3CO2)2, which commonly occurs as the dihydrate Zn(CH3CO2)2·2H2O. Both the hydrate and the anhydrous forms are colorless solids that are used as dietary supplements. When used as a food additive, it has the E number E650.
Iron (II) hydroxide or ferrous hydroxide is an inorganic compound with the formula Fe(OH)2. It is produced when iron (II) salts, from a compound such as iron(II) sulfate, are treated with hydroxide ions. Iron(II) hydroxide is a white solid, but even traces of oxygen impart a greenish tinge. The air-oxidised solid is sometimes known as "green rust".

Iron(II) fluoride or ferrous fluoride is an inorganic compound with the molecular formula FeF2. It forms a tetrahydrate FeF2·4H2O that is often referred to by the same names. The anhydrous and hydrated forms are white crystalline solids.

Iron(II) bromide refers to inorganic compounds with the chemical formula FeBr2(H2O)x. The anhydrous compound (x = 0) is a yellow or brownish-colored paramagnetic solid. The tetrahydrate is also known, all being pale colored solids. They are common precursor to other iron compounds.

Ferric acetate is the acetate salt of the coordination complex [Fe3O(OAc)6(H2O)3]+ (OAc− is CH3CO2−). Commonly the salt is known as "basic iron acetate". The formation of the red-brown complex was once used as a test for ferric ions.

Calcium sulfite, or calcium sulphite, is a chemical compound, the calcium salt of sulfite with the formula CaSO3·x(H2O). Two crystalline forms are known, the hemihydrate and the tetrahydrate, respectively CaSO3·½(H2O) and CaSO3·4(H2O). All forms are white solids. It is most notable as the product of flue-gas desulfurization.

Cobalt(II) acetate is the cobalt salt of acetic acid. It is commonly found as the tetrahydrate Co(CH3CO2)2·4 H2O, abbreviated Co(OAc)2·4 H2O. It is used as a catalyst.
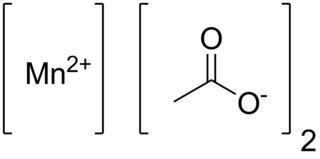
Manganese(II) acetate are chemical compounds with the formula Mn(CH3CO2)2·(H2O)n where n = 0, 2, 4. These materials are white or pale pink solids. Some of these compounds are used as a catalyst and as fertilizer.

Nickel(II) acetate is the name for the coordination compounds with the formula Ni(CH3CO2)2·x H2O where x can be 0, 2, and 4. The green tetrahydrate Ni(CH3CO2)2·4 H2O is most common. It is used for electroplating.
Aluminium triacetate, formally named aluminium acetate, is a chemical compound with composition Al(CH
3CO
2)
3. Under standard conditions it appears as a white, water-soluble solid that decomposes on heating at around 200 °C. The triacetate hydrolyses to a mixture of basic hydroxide / acetate salts, and multiple species co-exist in chemical equilibrium, particularly in aqueous solutions of the acetate ion; the name aluminium acetate is commonly used for this mixed system.
The nickel organic acid salts are organic acid salts of nickel. In many of these the ionised organic acid acts as a ligand.

Transition metal carboxylate complexes are coordination complexes with carboxylate (RCO2−) ligands. Reflecting the diversity of carboxylic acids, the inventory of metal carboxylates is large. Many are useful commercially, and many have attracted intense scholarly scrutiny. Carboxylates exhibit a variety of coordination modes, most common are κ1- (O-monodentate), κ2 (O,O-bidentate), and bridging.

Europium(III) acetate is an inorganic salt of europium and acetic acid with the chemical formula of Eu(CH3COO)3. In this compound, europium exhibits the +3 oxidation state. It can exist in the anhydrous form, sesquihydrate and tetrahydrate. Its hydrate molecule is a dimer.

Holmium acetate is the acetate salt of holmium, with a chemical formula of Ho(CH3COO)3 as well as at least one hydrate.
 [3]
[3] 














