Samarium(II) iodide is an inorganic compound with the formula SmI2. When employed as a solution for organic synthesis, it is known as Kagan's reagent. SmI2 is a green solid and forms a dark blue solution in THF. It is a strong one-electron reducing agent that is used in organic synthesis.

Iron pentacarbonyl, also known as iron carbonyl, is the compound with formula Fe(CO)5. Under standard conditions Fe(CO)5 is a free-flowing, straw-colored liquid with a pungent odour. Older samples appear darker. This compound is a common precursor to diverse iron compounds, including many that are useful in small scale organic synthesis.

Metal carbonyls are coordination complexes of transition metals with carbon monoxide ligands. Metal carbonyls are useful in organic synthesis and as catalysts or catalyst precursors in homogeneous catalysis, such as hydroformylation and Reppe chemistry. In the Mond process, nickel tetracarbonyl is used to produce pure nickel. In organometallic chemistry, metal carbonyls serve as precursors for the preparation of other organometallic complexes.
Iron shows the characteristic chemical properties of the transition metals, namely the ability to form variable oxidation states differing by steps of one and a very large coordination and organometallic chemistry: indeed, it was the discovery of an iron compound, ferrocene, that revolutionalized the latter field in the 1950s. Iron is sometimes considered as a prototype for the entire block of transition metals, due to its abundance and the immense role it has played in the technological progress of humanity. Its 26 electrons are arranged in the configuration [Ar]3d64s2, of which the 3d and 4s electrons are relatively close in energy, and thus it can lose a variable number of electrons and there is no clear point where further ionization becomes unprofitable.

Triiron dodecacarbonyl is the organoiron compound with the formula Fe3(CO)12. It is a dark green solid that sublimes under vacuum. It is soluble in nonpolar organic solvents to give intensely green solutions. Most low-nuclearity clusters are pale yellow or orange. Hot solutions of Fe3(CO)12 decompose to an iron mirror, which can be pyrophoric in air. The solid decomposes slowly in air, and thus samples are typically stored cold under an inert atmosphere. It is a more reactive source of iron(0) than iron pentacarbonyl.
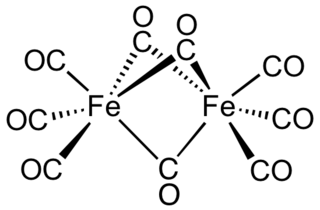
Diiron nonacarbonyl is an organometallic compound with the formula Fe2(CO)9. This metal carbonyl is an important reagent in organometallic chemistry and of occasional use in organic synthesis. It is a more reactive source of Fe(0) than Fe(CO)5. This micaceous orange solid is virtually insoluble in all common solvents.

Dicobalt octacarbonyl is an organocobalt compound with composition Co2(CO)8. This metal carbonyl is used as a reagent and catalyst in organometallic chemistry and organic synthesis, and is central to much known organocobalt chemistry. It is the parent member of a family of hydroformylation catalysts. Each molecule consists of two cobalt atoms bound to eight carbon monoxide ligands, although multiple structural isomers are known. Some of the carbonyl ligands are labile.

Triruthenium dodecacarbonyl is the chemical compound with the formula Ru3(CO)12. Classified as metal carbonyl cluster, it is a dark orange-colored solid that is soluble in nonpolar organic solvents. The compound serves as a precursor to other organoruthenium compounds.

Hexadecacarbonylhexarhodium is a metal carbonyl cluster with the formula Rh6(CO)16. It exists as purple-brown crystals that are slightly soluble in dichloromethane and chloroform. It is the principal binary carbonyl of rhodium.
Organoiron chemistry is the chemistry of iron compounds containing a carbon-to-iron chemical bond. Organoiron compounds are relevant in organic synthesis as reagents such as iron pentacarbonyl, diiron nonacarbonyl and disodium tetracarbonylferrate. Although iron is generally less active in many catalytic applications, it is less expensive and "greener" than other metals. Organoiron compounds feature a wide range of ligands that support the Fe-C bond; as with other organometals, these supporting ligands prominently include phosphines, carbon monoxide, and cyclopentadienyl, but hard ligands such as amines are employed as well.

Cobalt tetracarbonyl hydride is an organometallic compound with the formula HCo(CO)4. It is a volatile, yellow liquid that forms a colorless vapor and has an intolerable odor. The compound readily decomposes upon melt and in absentia of high CO partial pressures forms Co2(CO)8. Despite operational challenges associated with its handling, the compound has received considerable attention for its ability to function as a catalyst in hydroformylation. In this respect, HCo(CO)4 and related derivatives have received significant academic interest for their ability to mediate a variety of carbonylation (introduction of CO into inorganic compounds) reactions.

Iron tetracarbonyl dihydride is the organometallic compound with the formula H2Fe(CO)4. This compound was the first transition metal hydride discovered. The complex is stable at low temperatures but decomposes rapidly at temperatures above –20 °C.
A metallacarboxylic acid is a metal complex with the ligand CO2H. These compounds are intermediates in reactions that involve carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide, these species are intermediates in the water gas shift reaction. Metallacarboxylic acids are also called hydroxycarbonyls.

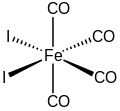
Cyclopentadienyliron dicarbonyl iodide is an organoiron compound with the formula (C5H5)Fe(CO)2I. It is a dark brown solid that is soluble in common organic solvents. (C5H5)Fe(CO)2I, or FpI as it is often known, is an intermediate for the preparation of other organoiron compounds such as in ferraboranes.

Metal carbonyl hydrides are complexes of transition metals with carbon monoxide and hydride as ligands. These complexes are useful in organic synthesis as catalysts in homogeneous catalysis, such as hydroformylation.
Iron(II) hydride, systematically named iron dihydride and poly(dihydridoiron) is solid inorganic compound with the chemical formula (FeH
2)
n (also written ([FeH
2])n or FeH
2). ). It is kinetically unstable at ambient temperature, and as such, little is known about its bulk properties. However, it is known as a black, amorphous powder, which was synthesised for the first time in 2014.

In chemistry, a metal carbonyl cluster is a compound that contains two or more metal atoms linked in part by metal–metal bonds and containing carbon monoxide (CO) as the exclusive or predominant ligand. The area is a subfield of metal carbonyl chemistry, and many metal carbonyl clusters are in fact prepared from simple metal carbonyls. Simple examples include Fe2(CO)9, Fe3(CO)12, and Mn2(CO)10. High nuclearity clusters include [Rh13(CO)24H3]2− and the stacked Pt3 triangules [Pt3n(CO)6n]2− (n = 2–6).
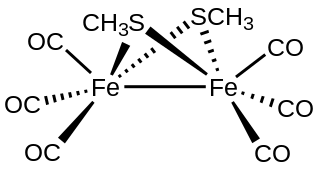
Methylthioirontricarbonyl dimer, also known as methanethiolatoirontricarbonyl dimer, is an organometallic compound with the formula Fe2(SCH3)2(CO)6. It is a red volatile solid that is classified as a transition metal thiolate complex. It exists as air-stable red crystals with two isomers, where the methyl groups are either anti (isomer A) or syn (isomer B) with respect to each other.

Rhodium carbonyl chloride is an organorhodium compound with the formula Rh2Cl2(CO)4. It is a red-brown volatile solid that is soluble in nonpolar organic solvents. It is a precursor to other rhodium carbonyl complexes, some of which are useful in homogeneous catalysis.
Iron(III) iodide is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula FeI3. It is a thermodynamically unstable compound that is difficult to prepare. Nevertheless, iron(III) iodide has been synthesised in small quantities in the absence of air and water.