
Holmium is a chemical element; it has symbol Ho and atomic number 67. It is a rare-earth element and the eleventh member of the lanthanide series. It is a relatively soft, silvery, fairly corrosion-resistant and malleable metal. Like many other lanthanides, holmium is too reactive to be found in native form, as pure holmium slowly forms a yellowish oxide coating when exposed to air. When isolated, holmium is relatively stable in dry air at room temperature. However, it reacts with water and corrodes readily, and also burns in air when heated.

Holmium(III) oxide, or holmium oxide is a chemical compound of the rare-earth element holmium and oxygen with the formula Ho2O3. Together with dysprosium(III) oxide (Dy2O3), holmium oxide is one of the most powerfully paramagnetic substances known. The oxide, also called holmia, occurs as a component of the related erbium oxide mineral called erbia. Typically, the oxides of the trivalent lanthanides coexist in nature, and separation of these components requires specialized methods. Holmium oxide is used in making specialty colored glasses. Glass containing holmium oxide and holmium oxide solutions have a series of sharp optical absorption peaks in the visible spectral range. They are therefore traditionally used as a convenient calibration standard for optical spectrophotometers.
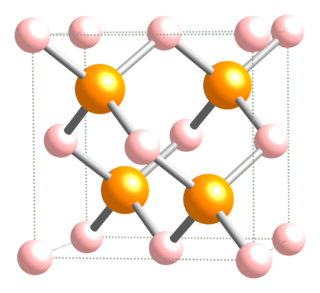
Aluminium arsenide is a semiconductor material with almost the same lattice constant as gallium arsenide and aluminium gallium arsenide and wider band gap than gallium arsenide. (AlAs) can form a superlattice with gallium arsenide (GaAs) which results in its semiconductor properties. Because GaAs and AlAs have almost the same lattice constant, the layers have very little induced strain, which allows them to be grown almost arbitrarily thick. This allows for extremely high performance high electron mobility, HEMT transistors, and other quantum well devices.
Holmium(III) bromide is a crystalline compound made of one holmium atom and three bromine atoms. Holmium bromide is a yellow powder at room temperature. Holmium bromide is hygroscopic. Holmium bromide is odorless.
Neptunium arsenide is a binary inorganic compound of neptunium and arsenic with the chemical formula NpAs. The compound forms crystals.
Lithium phosphide is an inorganic compound of lithium and phosphorus with the chemical formula Li
3P. This dark colored compound is formally the Li+ salt of P3-. It is a hazardous to handle because of its high reactivity toward air.
Lutetium phosphide is an inorganic compound of lutetium and phosphorus with the chemical formula LuP. The compound forms dark crystals, does not dissolve in water.
Neodymium phosphide is an inorganic compound of neodymium and phosphorus with the chemical formula NdP.
Samarium(III) phosphide is an inorganic compound of samarium and phosphorus with the chemical formula SmP.
Ytterbium(III) phosphide is an inorganic compound of ytterbium and phosphorus with the chemical formula YbP. This is one of the phosphides of ytterbium.
Thulium phosphide is an inorganic compound of thulium and phosphorus with the chemical formula TmP.
Holmium phosphide is a binary inorganic compound of holmium and phosphorus with the chemical formula HoP. The compound forms dark crystals and does not dissolve in water.
Erbium phosphide is a binary inorganic compound of erbium and phosphorus with the chemical formula ErP.
Samarium(III) arsenide is a binary inorganic compound of samarium and arsenic with the chemical formula SmAs.
Cobalt arsenide is a binary inorganic compound of cobalt and arsenic with the chemical formula CoAs. The compound occurs naturally as the mineral modderite.

Holmium(III) iodide is an iodide of holmium, with the chemical formula of HoI3. It is used as a component of metal halide lamps.
Erbium compounds are compounds containing the element erbium (Er). These compounds are usually dominated by erbium in the +3 oxidation state, although the +2, +1 and 0 oxidation states have also been reported.
Ytterbium compounds are chemical compounds that contain the element ytterbium (Yb). The chemical behavior of ytterbium is similar to that of the rest of the lanthanides. Most ytterbium compounds are found in the +3 oxidation state, and its salts in this oxidation state are nearly colorless. Like europium, samarium, and thulium, the trihalides of ytterbium can be reduced to the dihalides by hydrogen, zinc dust, or by the addition of metallic ytterbium. The +2 oxidation state occurs only in solid compounds and reacts in some ways similarly to the alkaline earth metal compounds; for example, ytterbium(II) oxide (YbO) shows the same structure as calcium oxide (CaO).
Holmium nitride is a binary inorganic compound of holmium and nitrogen with the chemical formula HoN.

Holmium antimonide is a binary inorganic compound of holmium and antimony with the chemical formula HoSb.





