
In crystallography, the cubiccrystal system is a crystal system where the unit cell is in the shape of a cube. This is one of the most common and simplest shapes found in crystals and minerals.

Cadmium arsenide (Cd3As2) is an inorganic semimetal in the II-V family. It exhibits the Nernst effect.

Cadmium sulfide is the inorganic compound with the formula CdS. Cadmium sulfide is a yellow solid. It occurs in nature with two different crystal structures as the rare minerals greenockite and hawleyite, but is more prevalent as an impurity substituent in the similarly structured zinc ores sphalerite and wurtzite, which are the major economic sources of cadmium. As a compound that is easy to isolate and purify, it is the principal source of cadmium for all commercial applications. Its vivid yellow color led to its adoption as a pigment for the yellow paint "cadmium yellow" in the 18th century.
In chemistry, an arsenide is a compound of arsenic with a less electronegative element or elements. Many metals form binary compounds containing arsenic, and these are called arsenides. They exist with many stoichiometries, and in this respect arsenides are similar to phosphides.
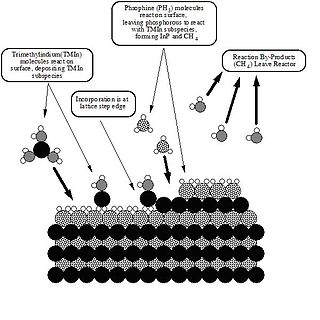
Metalorganic vapour-phase epitaxy (MOVPE), also known as organometallic vapour-phase epitaxy (OMVPE) or metalorganic chemical vapour deposition (MOCVD), is a chemical vapour deposition method used to produce single- or polycrystalline thin films. It is a process for growing crystalline layers to create complex semiconductor multilayer structures. In contrast to molecular-beam epitaxy (MBE), the growth of crystals is by chemical reaction and not physical deposition. This takes place not in vacuum, but from the gas phase at moderate pressures. As such, this technique is preferred for the formation of devices incorporating thermodynamically metastable alloys, and it has become a major process in the manufacture of optoelectronics, such as Light-emitting diodes. It was invented in 1968 at North American Aviation Science Center by Harold M. Manasevit.
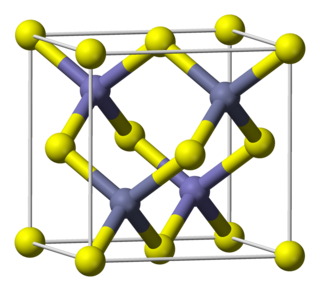
Indium arsenide, InAs, or indium monoarsenide, is a narrow-bandgap semiconductor composed of indium and arsenic. It has the appearance of grey cubic crystals with a melting point of 942 °C.

Cadmium oxide is an inorganic compound with the formula CdO. It is one of the main precursors to other cadmium compounds. It crystallizes in a cubic rocksalt lattice like sodium chloride, with octahedral cation and anion centers. It occurs naturally as the rare mineral monteponite. Cadmium oxide can be found as a colorless amorphous powder or as brown or red crystals. Cadmium oxide is an n-type semiconductor with a band gap of 2.18 eV at room temperature.

Zinc phosphide (Zn3P2) is an inorganic chemical compound. It is a grey solid, although commercial samples are often dark or even black. It is used as a rodenticide. Zn3P2 is a II-V semiconductor with a direct band gap of 1.5 eV and may have applications in photovoltaic cells. A second compound exists in the zinc-phosphorus system, zinc diphosphide (ZnP2).
In chemistry, the Grimm–Sommerfeld rule predicts that binary compounds with covalent character that have an average of 4 electrons per atom will have structures where both atoms are tetrahedrally coordinated. Examples are silicon carbide, the III-V semiconductors indium phosphide and gallium arsenide, the II-VI semiconductors, cadmium sulfide, cadmium selenide.
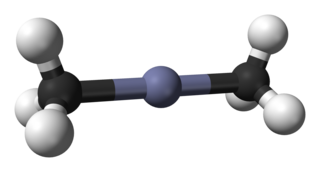
Dimethylzinc, also known as Zinc methyl, DMZ, or DMZn is a colorless volatile liquid Zn(CH3)2, formed by the action of methyl iodide on zinc at elevated temperature or on zinc sodium alloy.
Compounds of zinc are chemical compounds containing the element zinc which is a member of the group 12 of the periodic table. The oxidation state of zinc in most compounds is the group oxidation state of +2. Zinc may be classified as a post-transition main group element with zinc(II). Zinc compounds are noteworthy for their nondescript behavior, they are generally colorless, do not readily engage in redox reactions, and generally adopt symmetrical structures.

In crystallography, the hexagonal crystal family is one of the six crystal families, which includes two crystal systems and two lattice systems. While commonly confused, the trigonal crystal system and the rhombohedral lattice system are not equivalent. In particular, there are crystals that have trigonal symmetry but belong to the hexagonal lattice.
Zinc diphosphide (ZnP2) is an inorganic chemical compound. It is a red semiconductor solid with a band gap of 2.1 eV. It is one of the two compounds in the zinc-phosphorus system, the other being zinc phosphide (Zn3P2).
Zinc cadmium phosphide arsenide (Zn-Cd-P-As) is a quaternary system of group II (IUPAC group 12) and group V (IUPAC group 15) elements. Many of the inorganic compounds in the system are II-V semiconductor materials. The quaternary system of II3V2 compounds, (Zn1−xCdx)3(P1−yAsy)2, has been shown to allow solid solution continuously over the whole compositional range. This material system and its subsets have applications in electronics, optoelectronics, including photovoltaics, and thermoelectrics.
Cadmium phosphide (Cd3P2) is an inorganic chemical compound. It is a grey or white bluish solid semiconductor material with a bandgap of 0.5 eV. It has applications as a pesticide, material for laser diodes and for high-power-high-frequency electronics.
Phosphide iodides or iodide phosphides are compounds containing anions composed of iodide (I−) and phosphide (P3−). They can be considered as mixed anion compounds. They are in the category of pnictidehalides. Related compounds include the phosphide chlorides, arsenide iodides antimonide iodides and phosphide bromides.
Phosphide bromides or bromide phosphides are compounds containing anions composed of bromide (Br−) and phosphide (P3−) anions. Usually phosphorus is covalently connected into more complex structures. They can be considered as mixed anion compounds. They are in the category of pnictidehalides. Related compounds include the phosphide chlorides, phosphide iodides, nitride bromides, arsenide bromides, and antimonide bromides.
Arsenide bromides or bromide arsenides are compounds containing anions composed of bromide (Br−) and arsenide (As3−). They can be considered as mixed anion compounds. They are in the category of pnictidehalides. Related compounds include the arsenide chlorides, arsenide iodides, phosphide bromides, and antimonide bromides.
Arsenide iodides or iodide arsenides are compounds containing anions composed of iodide (I−) and arsenide (As3−). They can be considered as mixed anion compounds. They are in the category of pnictidehalides. Related compounds include the arsenide chlorides, arsenide bromides, phosphide iodides, and antimonide iodides.












