
Perchloric acid is a mineral acid with the formula HClO4. Usually found as an aqueous solution, this colorless compound is a stronger acid than sulfuric acid, nitric acid and hydrochloric acid. It is a powerful oxidizer when hot, but aqueous solutions up to approximately 70% by weight at room temperature are generally safe, only showing strong acid features and no oxidizing properties. Perchloric acid is useful for preparing perchlorate salts, especially ammonium perchlorate, an important rocket fuel component. Perchloric acid is dangerously corrosive and readily forms potentially explosive mixtures.

Dysprosium(III) chloride (DyCl3), also known as dysprosium trichloride, is a compound of dysprosium and chlorine. It is a white to yellow solid which rapidly absorbs water on exposure to moist air to form a hexahydrate, DyCl3·6H2O. Simple rapid heating of the hydrate causes partial hydrolysis to an oxychloride, DyOCl.
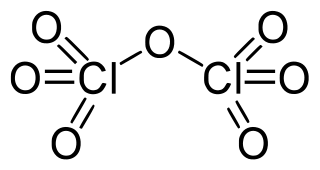
Dichlorine heptoxide is the chemical compound with the formula Cl2O7. This chlorine oxide is the anhydride of perchloric acid. It is produced by the careful distillation of perchloric acid in the presence of the dehydrating agent phosphorus pentoxide:

Rhodium(III) chloride refers to inorganic compounds with the formula RhCl3(H2O)n, where n varies from 0 to 3. These are diamagnetic solids featuring octahedral Rh(III) centres. Depending on the value of n, the material is either a dense brown solid or a soluble reddish salt. The soluble trihydrated (n = 3) salt is widely used to prepare compounds used in homogeneous catalysis, notably for the industrial production of acetic acid and hydroformylation.

Sodium perchlorate is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula NaClO4. It consists of sodium cations Na+ and perchlorate anions ClO−4. It is a white crystalline, hygroscopic solid that is highly soluble in water and ethanol. It is usually encountered as sodium perchlorate monohydrate NaClO4·H2O. The compound is noteworthy as the most water-soluble of the common perchlorate salts.
A solubility chart is a chart describing whether the ionic compounds formed from different combinations of cations and anions dissolve in or precipitate from solution.

Iron(III) nitrate, or ferric nitrate, is the name used for a series of inorganic compounds with the formula Fe(NO3)3.(H2O)n. Most common is the nonahydrate Fe(NO3)3.(H2O)9. The hydrates are all pale colored, water-soluble paramagnetic salts.

Fluorine perchlorate, also called perchloryl hypofluorite is the rarely encountered chemical compound of fluorine, chlorine, and oxygen with the chemical formula ClO
4F or FOClO
3. It is an extremely unstable gas that explodes spontaneously and has a penetrating odor.

Copper(II) perchlorate is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Cu(ClO4)2. It is a salt of copper and perchloric acid. It is a hygroscopic crystalline blue solid. It is commonly encountered as copper(II) perchlorate hexahydrate, According to X-ray crystallography, the salt is the aquo complex [Cu(H2O)6]2+ together with the weakly coordinating anion ClO−4.
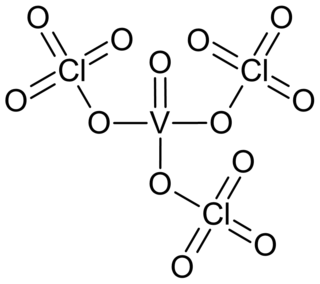
Vanadyl perchlorate or vanadyl triperchlorate is a golden yellow coloured liquid or crystalline compound of vanadium, oxygen and perchlorate group. The substance consists of molecules covalently bound and is quite volatile; it ignites organic solvents on contact and explodes at temperatures above 80 °C.
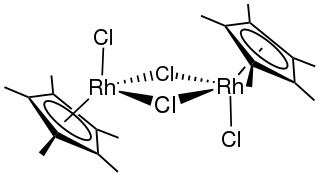
Pentamethylcyclopentadienyl rhodium dichloride dimer is an organometallic compound with the formula [(C5(CH3)5RhCl2)]2, commonly abbreviated [Cp*RhCl2]2 This dark red air-stable diamagnetic solid is a reagent in organometallic chemistry.
Hydronium perchlorate is an inorganic chemical compound with the chemical formula [H3O]ClO4. It is an unusual salt due to it being a solid and stable hydronium salt. It consists of hydronium cations [H3O]+ and perchlorate anions ClO−4.
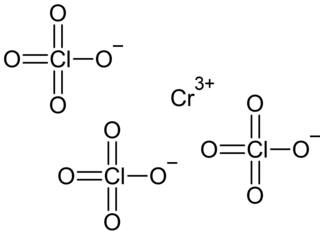
Chromium(III) perchlorate is an inorganic compound, a salt with the chemical formula Cr(ClO4)3. It's hexahydrate Cr(ClO4)3·6H2O is a cyan solid that dissolves in water.

Nickel(II) perchlorate is a inorganic compound with the chemical formula of Ni(ClO4)2, and it is a strong oxidizing agent. Its colours are different depending on water. For example, the hydrate forms cyan crystals, the pentahydrate forms green crystals, but the hexahydrate (Ni(ClO4)2·6H2O) forms blue crystals.

Neodymium(III) perchlorate is an inorganic compound. It is a salt of neodymium and perchloric acid with the chemical formula of Nd(ClO4)3 – it is soluble in water, forming purple-pink, hydrated crystals.

Lead(II) perchlorate is a chemical compound with the formula Pb(ClO4)2·xH2O, where is x is 0,1, or 3. It is an extremely hygroscopic white solid that is very soluble in water.

Zinc perchlorate is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula Zn(ClO4)2 which forms the hexahydrate.
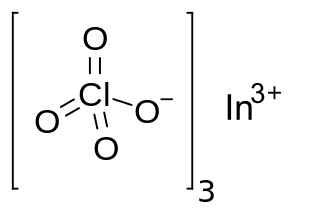
Indium perchlorate is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula In(ClO
4)
3. The compound is an indium salt of perchloric acid.

Nitrosyl perchlorate is the inorganic compound with the formula NO(ClO4). A hygroscopic white solid, it is the salt of the nitrosonium cation with the perchlorate anion. It is an oxidant and strong electrophile, but has fallen out of use with the availability of the closely related salt nitrosonium tetrafluoroborate NO(BF4).
Niobium perchlorate is a chemical compound with the formula Nb(ClO4)5. It is a hygroscopic, white crystalline solid that readily reacts with moist air or water to produce niobium(V) oxide.

















