
An enamine is an unsaturated compound derived by the condensation of an aldehyde or ketone with a secondary amine. Enamines are versatile intermediates.

In organic chemistry, an imine is a functional group or organic compound containing a carbon–nitrogen double bond. The nitrogen atom can be attached to a hydrogen or an organic group (R). The carbon atom has two additional single bonds. Imines are common in synthetic and naturally occurring compounds and they participate in many reactions.
Organopalladium chemistry is a branch of organometallic chemistry that deals with organic palladium compounds and their reactions. Palladium is often used as a catalyst in the reduction of alkenes and alkynes with hydrogen. This process involves the formation of a palladium-carbon covalent bond. Palladium is also prominent in carbon-carbon coupling reactions, as demonstrated in tandem reactions.

Crabtree's catalyst is an organoiridium compound with the formula [C8H12IrP(C6H11)3C5H5N]PF6. It is a homogeneous catalyst for hydrogenation and hydrogen-transfer reactions, developed by Robert H. Crabtree. This air stable orange solid is commercially available and known for its directed hydrogenation to give trans stereoselectivity with respective of directing group.
In organic chemistry and organometallic chemistry, carbon–hydrogen bond activation is a type of organic reaction in which a carbon–hydrogen bond is cleaved and replaced with a C−X bond. Some authors further restrict the term C–H activation to reactions in which a C–H bond, one that is typically considered to be "unreactive", interacts with a transition metal center M, resulting in its cleavage and the generation of an organometallic species with an M–C bond. The intermediate of this step could then undergo subsequent reactions with other reagents, either in situ or in a separate step, to produce the functionalized product.
In organic chemistry, the Buchwald–Hartwig amination is a chemical reaction for the synthesis of carbon–nitrogen bonds via the palladium-catalyzed coupling reactions of amines with aryl halides. Although Pd-catalyzed C–N couplings were reported as early as 1983, Stephen L. Buchwald and John F. Hartwig have been credited, whose publications between 1994 and the late 2000s established the scope of the transformation. The reaction's synthetic utility stems primarily from the shortcomings of typical methods for the synthesis of aromatic C−N bonds, with most methods suffering from limited substrate scope and functional group tolerance. The development of the Buchwald–Hartwig reaction allowed for the facile synthesis of aryl amines, replacing to an extent harsher methods while significantly expanding the repertoire of possible C−N bond formations.

Cyclooctadiene rhodium chloride dimer is the organorhodium compound with the formula Rh2Cl2(C8H12)2, commonly abbreviated [RhCl(COD)]2 or Rh2Cl2(COD)2. This yellow-orange, air-stable compound is a widely used precursor to homogeneous catalysts.
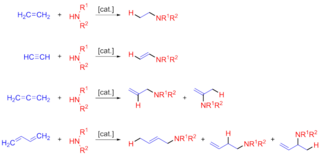
In organic chemistry, hydroamination is the addition of an N−H bond of an amine across a carbon-carbon multiple bond of an alkene, alkyne, diene, or allene. In the ideal case, hydroamination is atom economical and green. Amines are common in fine-chemical, pharmaceutical, and agricultural industries. Hydroamination can be used intramolecularly to create heterocycles or intermolecularly with a separate amine and unsaturated compound. The development of catalysts for hydroamination remains an active area, especially for alkenes. Although practical hydroamination reactions can be effected for dienes and electrophilic alkenes, the term hydroamination often implies reactions metal-catalyzed processes.

cis-Cyclooctene is a cycloalkene with the formula (CH2)6(CH)2. It is a colorless liquid that is used industrially to produce a polymer. It is also a ligand in organometallic chemistry.
Asymmetric hydrogenation is a chemical reaction that adds two atoms of hydrogen to a target (substrate) molecule with three-dimensional spatial selectivity. Critically, this selectivity does not come from the target molecule itself, but from other reagents or catalysts present in the reaction. This allows spatial information to transfer from one molecule to the target, forming the product as a single enantiomer. The chiral information is most commonly contained in a catalyst and, in this case, the information in a single molecule of catalyst may be transferred to many substrate molecules, amplifying the amount of chiral information present. Similar processes occur in nature, where a chiral molecule like an enzyme can catalyse the introduction of a chiral centre to give a product as a single enantiomer, such as amino acids, that a cell needs to function. By imitating this process, chemists can generate many novel synthetic molecules that interact with biological systems in specific ways, leading to new pharmaceutical agents and agrochemicals. The importance of asymmetric hydrogenation in both academia and industry contributed to two of its pioneers — William Standish Knowles and Ryōji Noyori — being collectively awarded one half of the 2001 Nobel Prize in Chemistry.

Carbene C−H insertion in organic chemistry concerns the insertion reaction of a carbene into a carbon–hydrogen bond. This organic reaction is of some importance in the synthesis of new organic compounds.
Hydroacylation is a type of organic reaction in which an electron-rich unsaturated hydrocarbon inserts into a formyl C-H bond. With alkenes, the product is a ketone:

The Shvo catalyst is an organoruthenium compound that catalyzes the hydrogenation of polar functional groups including aldehydes, ketones and imines. The compound is of academic interest as an early example of a catalyst for transfer hydrogenation that operates by an "outer sphere mechanism". Related derivatives are known where p-tolyl replaces some of the phenyl groups. Shvo's catalyst represents a subset of homogeneous hydrogenation catalysts that involves both metal and ligand in its mechanism.

Organorhodium chemistry is the chemistry of organometallic compounds containing a rhodium-carbon chemical bond, and the study of rhodium and rhodium compounds as catalysts in organic reactions.
The Buchner ring expansion is a two-step organic C-C bond forming reaction used to access 7-membered rings. The first step involves formation of a carbene from ethyl diazoacetate, which cyclopropanates an aromatic ring. The ring expansion occurs in the second step, with an electrocyclic reaction opening the cyclopropane ring to form the 7-membered ring.

Hydrogen-bond catalysis is a type of organocatalysis that relies on use of hydrogen bonding interactions to accelerate and control organic reactions. In biological systems, hydrogen bonding plays a key role in many enzymatic reactions, both in orienting the substrate molecules and lowering barriers to reaction. The field is relatively undeveloped compared to research in Lewis acid catalysis.
In organometallic chemistry, a transition metal alkene complex is a coordination compound containing one or more alkene ligands. The inventory is large. Such compounds are intermediates in many catalytic reactions that convert alkenes to other organic products.

Chlorobis(cyclooctene)iridium dimer is an organoiridium compound with the formula Ir2Cl2(C8H14)4, where C8H14 is cis-cyclooctene. Sometimes abbreviated Ir2Cl2(coe)4, it is a yellow, air-sensitive solid that is used as a precursor to many other organoiridium compounds and catalysts.

Chlorobis(ethylene)rhodium dimer is an organorhodium compound with the formula Rh2Cl2(C2H4)4. It is a red-orange solid that is soluble in nonpolar organic solvents. The molecule consists of two bridging chloride ligands and four ethylene ligands. The ethylene ligands are labile and readily displaced even by other alkenes. A variety of homogeneous catalysts have been prepared from this complex.

In organometallic chemistry, the activation of cyclopropanes by transition metals is a research theme with implications for organic synthesis and homogeneous catalysis. Being highly strained, cyclopropanes are prone to oxidative addition to transition metal complexes. The resulting metallacycles are susceptible to a variety of reactions. These reactions are rare examples of C-C bond activation. The rarity of C-C activation processes has been attributed to Steric effects that protect C-C bonds. Furthermore, the directionality of C-C bonds as compared to C-H bonds makes orbital interaction with transition metals less favorable. Thermodynamically, C-C bond activation is more favored than C-H bond activation as the strength of a typical C-C bond is around 90 kcal per mole while the strength of a typical unactivated C-H bond is around 104 kcal per mole.

















