
Chlorine is a chemical element; it has symbol Cl and atomic number 17. The second-lightest of the halogens, it appears between fluorine and bromine in the periodic table and its properties are mostly intermediate between them. Chlorine is a yellow-green gas at room temperature. It is an extremely reactive element and a strong oxidising agent: among the elements, it has the highest electron affinity and the third-highest electronegativity on the revised Pauling scale, behind only oxygen and fluorine.

Perchloric acid is a mineral acid with the formula HClO4. It is an oxoacid of chlorine. Usually found as an aqueous solution, this colorless compound is a stronger acid than sulfuric acid, nitric acid and hydrochloric acid. It is a powerful oxidizer when hot, but aqueous solutions up to approximately 70% by weight at room temperature are generally safe, only showing strong acid features and no oxidizing properties. Perchloric acid is useful for preparing perchlorate salts, especially ammonium perchlorate, an important rocket fuel component. Perchloric acid is dangerously corrosive and readily forms potentially explosive mixtures.

An oxidizing agent is a substance in a redox chemical reaction that gains or "accepts"/"receives" an electron from a reducing agent. In other words, an oxidizer is any substance that oxidizes another substance. The oxidation state, which describes the degree of loss of electrons, of the oxidizer decreases while that of the reductant increases; this is expressed by saying that oxidizers "undergo reduction" and "are reduced" while reducers "undergo oxidation" and "are oxidized". Common oxidizing agents are oxygen, hydrogen peroxide, and the halogens.
In chemistry, an interhalogen compound is a molecule which contains two or more different halogen atoms and no atoms of elements from any other group.
Dichlorine heptoxide is the chemical compound with the formula Cl2O7. This chlorine oxide is the anhydride of perchloric acid. It is produced by the careful distillation of perchloric acid in the presence of the dehydrating agent phosphorus pentoxide:

Sodium perchlorate is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula NaClO4. It consists of sodium cations Na+ and perchlorate anions ClO−4. It is a white crystalline, hygroscopic solid that is highly soluble in water and ethanol. It is usually encountered as sodium perchlorate monohydrate NaClO4·H2O. The compound is noteworthy as the most water-soluble of the common perchlorate salts.

Lithium perchlorate is the inorganic compound with the formula LiClO4. This white or colourless crystalline salt is noteworthy for its high solubility in many solvents. It exists both in anhydrous form and as a trihydrate.
Perchloryl fluoride is a reactive gas with the chemical formula ClO
3F. It has a characteristic sweet odor that resembles gasoline and kerosene. It is toxic and is a powerful oxidizing and fluorinating agent. It is the acid fluoride of perchloric acid.
Organofluorine chemistry describes the chemistry of organofluorine compounds, organic compounds that contain a carbon–fluorine bond. Organofluorine compounds find diverse applications ranging from oil and water repellents to pharmaceuticals, refrigerants, and reagents in catalysis. In addition to these applications, some organofluorine compounds are pollutants because of their contributions to ozone depletion, global warming, bioaccumulation, and toxicity. The area of organofluorine chemistry often requires special techniques associated with the handling of fluorinating agents.

Chloryl fluoride is the chemical compound with the formula ClO2F. It is commonly encountered as side-product in reactions of chlorine fluorides with oxygen sources. It is the acyl fluoride of chloric acid.

Hypofluorous acid, chemical formula HOF, is the only known oxyacid of fluorine and the only known oxoacid in which the main atom gains electrons from oxygen to create a negative oxidation state. The oxidation state of the oxygen in this acid is 0, while its valence is 2. It is also the only hypohalous acid that can be isolated as a solid. HOF is an intermediate in the oxidation of water by fluorine, which produces hydrogen fluoride, oxygen difluoride, hydrogen peroxide, ozone and oxygen. HOF is explosive at room temperature, forming HF and O2:

The carbon–fluorine bond is a polar covalent bond between carbon and fluorine that is a component of all organofluorine compounds. It is one of the strongest single bonds in chemistry, and relatively short, due to its partial ionic character. The bond also strengthens and shortens as more fluorines are added to the same carbon on a chemical compound. As such, fluoroalkanes like tetrafluoromethane are some of the most unreactive organic compounds.

Dichlorine hexoxide is the chemical compound with the molecular formula Cl
2O
6, which is correct for its gaseous state. However, in liquid or solid form, this chlorine oxide ionizes into the dark red ionic compound chloryl perchlorate [ClO
2]+
[ClO
4]−
, which may be thought of as the mixed anhydride of chloric and perchloric acids. This compound is a notable perchlorating agent.

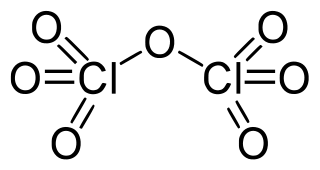
Chlorine perchlorate is a chemical compound with the formula Cl2O4. This chlorine oxide is an asymmetric oxide, with one chlorine atom in +1 oxidation state and the other +7, with proper formula ClOClO3. It is produced by the photodimerization of chlorine dioxide (ClO2) at room temperature by 436 nm ultraviolet light:

In chemistry, chloryl refers to a triatomic cation with chemical formula ClO+
2. This species has the same general structure as chlorite (ClO−
2) but it is electronically different, with chlorine having a +5 oxidation state (rather than the +3 of chlorite). This makes it a rare example of a positively charged oxychloride. Chloryl compounds, such as FClO
2 and [ClO2][RuF6], are all highly reactive and react violently with water and most organic compounds.
Perchloratoborate is an anion of the form [B(ClO4)4]−. It can form partly stable solid salts with heavy alkali metals. They are more stable than nitratoborate salts. K[B(ClO4)4] decomposes at 35 °C, Rb[B(ClO4)4] is stable to 50 °C, and Cs[B(ClO4)4] can exist up to 80 °C.
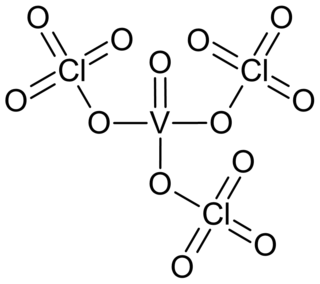
Vanadyl perchlorate or vanadyl triperchlorate is a golden yellow coloured liquid or crystalline compound of vanadium, oxygen and perchlorate group. The substance consists of molecules covalently bound and is quite volatile; it ignites organic solvents on contact and explodes at temperatures above 80 °C.

Zirconium perchlorate is an inorganic compound with the formula Zr(ClO4)4. It is a hygroscopic colorless solid that sublimes in a vacuum at 70 °C. These properties show that the compound is covalently bonded molecule, rather than a salt. It is an example of a transition metal perchlorate complex.

Chlorine oxide trifluoride or chlorine trifluoride oxide is a corrosive liquid molecular compound with formula ClOF3. It was developed secretly as a rocket fuel oxidiser.

Bromine perchlorate is an inorganic chemical compound with the formula BrOClO3. It is a shock and light-sensitive red liquid which decomposes above -20 °C.

















