
Sulfuric acid or sulphuric acid, known in antiquity as oil of vitriol, is a mineral acid composed of the elements sulfur, oxygen, and hydrogen, with the molecular formula H2SO4. It is a colorless, odorless, and viscous liquid that is soluble with water.
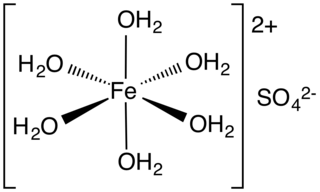
Iron(II) sulfate (British English: iron(II) sulphate) or ferrous sulfate denotes a range of salts with the formula FeSO4·xH2O. These compounds exist most commonly as the heptahydrate (x = 7) but several values for x are known. The hydrated form is used medically to treat or prevent iron deficiency, and also for industrial applications. Known since ancient times as copperas and as green vitriol (vitriol is an archaic name for hydrated sulfate minerals), the blue-green heptahydrate (hydrate with 7 molecules of water) is the most common form of this material. All the iron(II) sulfates dissolve in water to give the same aquo complex [Fe(H2O)6]2+, which has octahedral molecular geometry and is paramagnetic. The name copperas dates from times when the copper(II) sulfate was known as blue copperas, and perhaps in analogy, iron(II) and zinc sulfate were known respectively as green and white copperas.

Copper(II) sulfate is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula CuSO4. It forms hydrates CuSO4·nH2O, where n can range from 1 to 7. The pentahydrate (n = 5), a bright blue crystal, is the most commonly encountered hydrate of copper(II) sulfate, while its anhydrous form is white. Older names for the pentahydrate include blue vitriol, bluestone, vitriol of copper, and Roman vitriol. It exothermically dissolves in water to give the aquo complex [Cu(H2O)6]2+, which has octahedral molecular geometry. The structure of the solid pentahydrate reveals a polymeric structure wherein copper is again octahedral but bound to four water ligands. The Cu(II)(H2O)4 centers are interconnected by sulfate anions to form chains.

Zinc sulfate describes a family of inorganic compounds with the formula ZnSO4(H2O)x. All are colorless solids. The most common form includes water of crystallization as the heptahydrate, with the formula ZnSO4·7H2O. As early as the 16th century it was prepared on the large scale, and was historically known as "white vitriol" (the name was used, for example, in 1620s by the collective writing under the pseudonym of Basil Valentine). Zinc sulfate and its hydrates are colourless solids.

Calcium sulfate (or calcium sulphate) is the inorganic compound with the formula CaSO4 and related hydrates. In the form of γ-anhydrite (the anhydrous form), it is used as a desiccant. One particular hydrate is better known as plaster of Paris, and another occurs naturally as the mineral gypsum. It has many uses in industry. All forms are white solids that are poorly soluble in water. Calcium sulfate causes permanent hardness in water.

Sodium sulfate (also known as sodium sulphate or sulfate of soda) is the inorganic compound with formula Na2SO4 as well as several related hydrates. All forms are white solids that are highly soluble in water. With an annual production of 6 million tonnes, the decahydrate is a major commodity chemical product. It is mainly used as a filler in the manufacture of powdered home laundry detergents and in the Kraft process of paper pulping for making highly alkaline sulfides.

Aluminium sulfate is a salt with the formula Al2(SO4)3. It is soluble in water and is mainly used as a coagulating agent (promoting particle collision by neutralizing charge) in the purification of drinking water and wastewater treatment plants, and also in paper manufacturing.
Permanganic acid (or manganic(VII) acid) is the inorganic compound with the formula HMnO4 and various hydrates. This strong oxoacid has been isolated as its dihydrate. It is the conjugate acid of permanganate salts. It is the subject of few publications and its characterization as well as its uses are very limited.
Uranium(IV) sulfate (U(SO4)2) is a water-soluble salt of uranium. It is a very toxic compound. Uranium sulfate minerals commonly are widespread around uranium bearing mine sites, where they usually form during the evaporation of acid sulfate-rich mine tailings which have been leached by oxygen-bearing waters. Uranium sulfate is a transitional compound in the production of uranium hexafluoride. It was also used to fuel aqueous homogeneous reactors.

Mercury(II) sulfate, commonly called mercuric sulfate, is the chemical compound HgSO4. It is an odorless salt that forms white granules or crystalline powder. In water, it separates into an insoluble basic sulfate with a yellow color and sulfuric acid.
Indium(III) sulfate (In2(SO4)3) is a sulfate salt of the metal indium. It is a sesquisulfate, meaning that the sulfate group occurs 11/2 times as much as the metal. It may be formed by the reaction of indium, its oxide, or its carbonate with sulfuric acid. An excess of strong acid is required, otherwise insoluble basic salts are formed. As a solid indium sulfate can be anhydrous, or take the form of a pentahydrate with five water molecules or a nonahydrate with nine molecules of water. Indium sulfate is used in the production of indium or indium containing substances. Indium sulfate also can be found in basic salts, acidic salts or double salts including indium alum.

Manganese(II) sulfate usually refers to the inorganic compound with the formula MnSO4·H2O. This pale pink deliquescent solid is a commercially significant manganese(II) salt. Approximately 260,000 tonnes of manganese(II) sulfate were produced worldwide in 2005. It is the precursor to manganese metal and many other chemical compounds. Manganese-deficient soil is remediated with this salt.

Chromium(III) sulfate usually refers to the inorganic compounds with the formula Cr2(SO4)3.x(H2O), where x can range from 0 to 18. Additionally, ill-defined but commercially important "basic chromium sulfates" are known. These salts are usually either violet or green solids that are soluble in water. It is commonly used in tanning leather.
Polonium dichloride is a chemical compound of the radioactive metalloid, polonium and chlorine. Its chemical formula is PoCl2. It is an ionic salt.

Concrete degradation may have many different causes. Concrete is mostly damaged by the corrosion of reinforcement bars due to the carbonatation of hardened cement paste or chloride attack under wet conditions. Chemical damage is caused by the formation of expansive products produced by chemical reactions, by aggressive chemical species present in groundwater and seawater, or by microorganisms Other damaging processes can also involve calcium leaching by water infiltration, physical phenomena initiating cracks formation and propagation, fire or radiant heat, aggregate expansion, sea water effects, leaching, and erosion by fast-flowing water.
Polonium tetrachloride (also known as polonium(IV) chloride) is a chemical compound with the formula PoCl4. The salt is a hygroscopic bright yellow crystalline solid at room temperature. Above 200 °C, it tends to decompose into polonium dichloride and excess chlorine, similar to selenium tetrachloride and tellurium tetrachloride.

Polonium dioxide (also known as polonium(IV) oxide) is a chemical compound with the formula PoO2. It is one of three oxides of polonium, the other two being polonium monoxide (PoO) and polonium trioxide (PoO3). It is a pale yellow crystalline solid at room temperature. Under lowered pressure (such as a vacuum), it decomposes into elemental polonium and oxygen at 500 °C. It is the most stable oxide of polonium and is an interchalcogen.
Polonium trioxide (also known as polonium(VI) oxide) is a chemical compound with the formula PoO3. It is one of three oxides of polonium, the other two being polonium monoxide (PoO) and polonium dioxide (PoO2). It is an interchalcogen that has so far only been detected in trace amounts.
A sulfite sulfate is a chemical compound that contains both sulfite and sulfate anions [SO3]2− [SO4]2−. These compounds were discovered in the 1980s as calcium and rare earth element salts. Minerals in this class were later discovered. Minerals may have sulfite as an essential component, or have it substituted for another anion as in alloriite. The related ions [O3SOSO2]2− and [(O2SO)2SO2]2− may be produced in a reaction between sulfur dioxide and sulfate and exist in the solid form as tetramethyl ammonium salts. They have a significant partial pressure of sulfur dioxide.













