Rubidium is a chemical element; it has symbol Rb and atomic number 37. It is a very soft, whitish-grey solid in the alkali metal group, similar to potassium and caesium. Rubidium is the first alkali metal in the group to have a density higher than water. On Earth, natural rubidium comprises two isotopes: 72% is a stable isotope 85Rb, and 28% is slightly radioactive 87Rb, with a half-life of 48.8 billion years – more than three times as long as the estimated age of the universe.
Sulfur trioxide (alternative spelling sulphur trioxide) is the chemical compound with the formula SO3. It has been described as "unquestionably the most [economically] important sulfur oxide". It is prepared on an industrial scale as a precursor to sulfuric acid.

Sodium sulfate (also known as sodium sulphate or sulfate of soda) is the inorganic compound with formula Na2SO4 as well as several related hydrates. All forms are white solids that are highly soluble in water. With an annual production of 6 million tonnes, the decahydrate is a major commodity chemical product. It is mainly used as a filler in the manufacture of powdered home laundry detergents and in the Kraft process of paper pulping for making highly alkaline sulfides.

Rubidium perchlorate, RbClO4, is the perchlorate of rubidium. It is an oxidizing agent, as are all perchlorates.
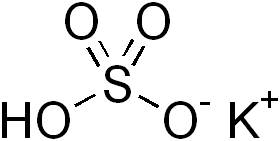
Potassium bisulfate (potassium bisulphate) is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula KHSO4 and is the potassium acid salt of sulfuric acid. It is a white, water-soluble solid.
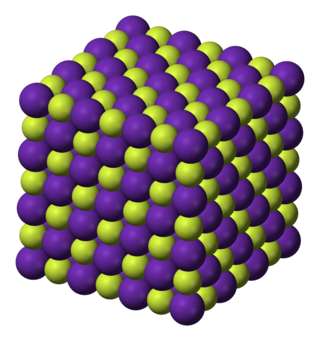
Rubidium fluoride (RbF) is the fluoride salt of rubidium. It is a cubic crystal with rock-salt structure.
Indium(III) sulfate (In2(SO4)3) is a sulfate salt of the metal indium. It is a sesquisulfate, meaning that the sulfate group occurs 11/2 times as much as the metal. It may be formed by the reaction of indium, its oxide, or its carbonate with sulfuric acid. An excess of strong acid is required, otherwise insoluble basic salts are formed. As a solid indium sulfate can be anhydrous, or take the form of a pentahydrate with five water molecules or a nonahydrate with nine molecules of water. Indium sulfate is used in the production of indium or indium containing substances. Indium sulfate also can be found in basic salts, acidic salts or double salts including indium alum.

Potassium pyrosulfate, or potassium disulfate, is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula K2S2O7.

Rubidium iodide is a salt of rubidium and iodine, with the chemical formula RbI. It is a white solid with a melting point of 642 °C.
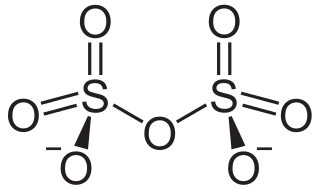
In chemistry, disulfate or pyrosulfate is the anion with the molecular formula S
2O2−
7. Disulfate is the IUPAC name. It has a dichromate-like structure and can be visualised as two corner-sharing SO4 tetrahedra, with a bridging oxygen atom. In this anion, sulfur has an oxidation state of +6. Disulfate is the conjugate base of the hydrogen disulfate (hydrogen pyrosulfate) ion HS
2O−
7, which in turn is the conjugate base of disulfuric acid (pyrosulfuric acid).

Caesium bisulfate or cesium hydrogen sulfate is an inorganic compound with the formula CsHSO4. The caesium salt of bisulfate, it is a colorless solid obtained by combining Cs2SO4 and H2SO4.

Rubidium azide is an inorganic compound with the formula RbN3. It is the rubidium salt of the hydrazoic acid HN3. Like most azides, it is explosive.
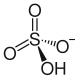
Rubidium sulfate is a sulfate of rubidium. The molecular formula of the compound is Rb2SO4. The molecular weight of this compound is 266.999 g/mol. An acid sulfate of rubidium (rubidium hydrogen sulfate) can be formed. It is soluble in water and is an aqueous solution.

Rubidium sulfide is an inorganic compound and a salt with the chemical formula Rb2S. It is a white solid with similar properties to other alkali metal sulfides.

Cesium sulfide is an inorganic salt with a chemical formula Cs2S. It is a strong alkali in aqueous solution. In the air, cesium sulfide emits rotten egg smelling hydrogen sulfide.
The phosphate sulfates are mixed anion compounds containing both phosphate and sulfate ions. Related compounds include the arsenate sulfates, phosphate selenates, and arsenate selenates.

Rubidium oxalate is a chemical compound with the chemical formula Rb2C2O4. It is a rubidium salt of oxalic acid. It consists of rubidium cations Rb+ and oxalate anions C2O2−4. Rubidium oxalate forms a monohydrate Rb2C2O4·H2O.

Rubidium selenide is an inorganic compound composed of selenium and rubidium. It is a selenide with a chemical formula of Rb2Se. Rubidium selenide is used together with caesium selenide in photovoltaic cells.

Caesium selenide is an inorganic compound of caesium and selenium. It is a selenide, with the chemical formula of Cs2Se. It can be prepared by reacting caesium and selenium. It has an inverse fluorite structure, with space group . There are 4 units per unit cell, and the other selenides from the same group are similar.