The alkali metals consist of the chemical elements lithium (Li), sodium (Na), potassium (K), rubidium (Rb), caesium (Cs), and francium (Fr). Together with hydrogen they constitute group 1, which lies in the s-block of the periodic table. All alkali metals have their outermost electron in an s-orbital: this shared electron configuration results in their having very similar characteristic properties. Indeed, the alkali metals provide the best example of group trends in properties in the periodic table, with elements exhibiting well-characterised homologous behaviour. This family of elements is also known as the lithium family after its leading element.

Caesium is a chemical element; it has symbol Cs and atomic number 55. It is a soft, silvery-golden alkali metal with a melting point of 28.5 °C, which makes it one of only five elemental metals that are liquid at or near room temperature. Caesium has physical and chemical properties similar to those of rubidium and potassium. It is pyrophoric and reacts with water even at −116 °C (−177 °F). It is the least electronegative element, with a value of 0.79 on the Pauling scale. It has only one stable isotope, caesium-133. Caesium is mined mostly from pollucite. Caesium-137, a fission product, is extracted from waste produced by nuclear reactors. It has the largest atomic radius of all elements whose radii have been measured or calculated, at about 260 picometers.

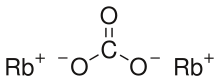
A carbonate is a salt of carbonic acid, H2CO3, characterized by the presence of the carbonate ion, a polyatomic ion with the formula CO2−3. The word "carbonate" may also refer to a carbonate ester, an organic compound containing the carbonate groupO=C(−O−)2.

Rubidium is a chemical element; it has symbol Rb and atomic number 37. It is a very soft, whitish-grey solid in the alkali metal group, similar to potassium and caesium. Rubidium is the first alkali metal in the group to have a density higher than water. On Earth, natural rubidium comprises two isotopes: 72% is a stable isotope 85Rb, and 28% is slightly radioactive 87Rb, with a half-life of 48.8 billion years—more than three times as long as the estimated age of the universe.
The rubidium-strontium dating method (Rb-Sr) is a radiometric dating technique, used by scientists to determine the age of rocks and minerals from their content of specific isotopes of rubidium (87Rb) and strontium. One of the two naturally occurring isotopes of rubidium, 87Rb, decays to 87Sr with a half-life of 49.23 billion years. The radiogenic daughter, 87Sr, produced in this decay process is the only one of the four naturally occurring strontium isotopes that was not produced exclusively by stellar nucleosynthesis predating the formation of the Solar System. Over time, decay of 87Rb increases the amount of radiogenic 87Sr while the amount of other Sr isotopes remains unchanged.

Sodium carbonate is the inorganic compound with the formula Na2CO3 and its various hydrates. All forms are white, odourless, water-soluble salts that yield alkaline solutions in water. Historically, it was extracted from the ashes of plants grown in sodium-rich soils, and because the ashes of these sodium-rich plants were noticeably different from ashes of wood, sodium carbonate became known as "soda ash". It is produced in large quantities from sodium chloride and limestone by the Solvay process, as well as by carbonating sodium hydroxide which is made using the Chlor-alkali process.
Rubidium (37Rb) has 36 isotopes, with naturally occurring rubidium being composed of just two isotopes; 85Rb (72.2%) and the radioactive 87Rb (27.8%).
Rubidium nitrate is an inorganic compound with the formula RbNO3. This alkali metal nitrate salt is white and highly soluble in water.

Rubidium oxide is the chemical compound with the formula Rb2O. Rubidium oxide is highly reactive towards water, and therefore it would not be expected to occur naturally. The rubidium content in minerals is often calculated and quoted in terms of Rb2O. In reality, the rubidium is typically present as a component of (actually, an impurity in) silicate or aluminosilicate. A major source of rubidium is lepidolite, KLi2Al(Al,Si)3O10(F,OH)2, wherein Rb sometimes replaces K.

Rubidium chloride is the chemical compound with the formula RbCl. This alkali metal halide salt is composed of rubidium and chlorine, and finds diverse uses ranging from electrochemistry to molecular biology.
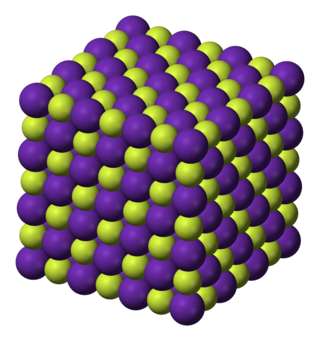
Rubidium fluoride (RbF) is the fluoride salt of rubidium. It is a cubic crystal with rock-salt structure.
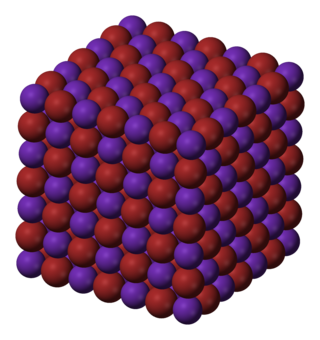
Rubidium bromide is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula RbBr. It is a salt of hydrogen bromide. It consists of bromide anions Br− and rubidium cations Rb+. It has a NaCl crystal structure, with a lattice constant of 685 picometres.

Uranyl zinc acetate (ZnUO2(CH3COO)4) is a compound of uranium.
Rubidium telluride is the inorganic compound with the formula Rb2Te. It is a yellow-green powder that melts at either 775 °C or 880 °C (two different values have been reported). It is an obscure material of minor academic interest.

Caesium chromate or cesium chromate is an inorganic compound with the formula Cs2CrO4. It is a yellow crystalline solid that is the caesium salt of chromic acid, and it crystallises in the orthorhombic system.

Rubidium iodide is a salt of rubidium and iodine, with the chemical formula RbI. It is a white solid with a melting point of 642 °C.

In chemistry, peroxydicarbonate is a divalent anion with the chemical formula C
2O2−
6. It is one of the oxocarbon anions, which consist solely of carbon and oxygen. Its molecular structure can be viewed as two carbonate anions joined so as to form a peroxide bridge –O–O–.
Yttrium(III) sulfate is an inorganic compound with the formula Y2(SO4)3. The most common form is the anhydrate and octahydrate.
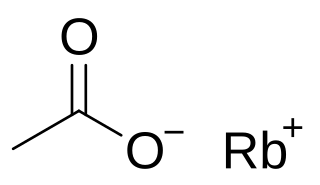
Rubidium acetate is a rubidium salt that is the result of reacting rubidium metal, rubidium carbonate, or rubidium hydroxide with acetic acid. It is soluble in water like other acetates.