A covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electrons to form electron pairs between atoms. These electron pairs are known as shared pairs or bonding pairs. The stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atoms, when they share electrons, is known as covalent bonding. For many molecules, the sharing of electrons allows each atom to attain the equivalent of a full valence shell, corresponding to a stable electronic configuration. In organic chemistry, covalent bonding is much more common than ionic bonding.

Boranes is the name given to compounds with the formula BxHy and related anions. Many such boranes are known. Most common are those with 1 to 12 boron atoms. Although they have few practical applications, the boranes exhibit structures and bonding that differs strongly from the patterns seen in hydrocarbons. Hybrids of boranes and hydrocarbons, the carboranes are also well developed.

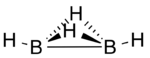
Diborane(6), commonly known as diborane, is the chemical compound with the formula B2H6. It is a toxic, colorless, and pyrophoric gas with a repulsively sweet odor. Diborane is a key boron compound with a variety of applications. It has attracted wide attention for its electronic structure. Several of its derivatives are useful reagents.
A three-center two-electron (3c–2e) bond is an electron-deficient chemical bond where three atoms share two electrons. The combination of three atomic orbitals form three molecular orbitals: one bonding, one non-bonding, and one anti-bonding. The two electrons go into the bonding orbital, resulting in a net bonding effect and constituting a chemical bond among all three atoms. In many common bonds of this type, the bonding orbital is shifted towards two of the three atoms instead of being spread equally among all three. Example molecules with 3c–2e bonds are the trihydrogen cation and diborane. In these two structures, the three atoms in each 3c-2e bond form an angular geometry, leading to a bent bond.

Organoboron chemistry or organoborane chemistry is the chemistry of organoboron compounds or organoboranes, which are chemical compounds of boron and carbon that are organic derivatives of borane (BH3), for example trialkyl boranes..

Borazine, also known as borazole, is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula B3H6N3. In this cyclic compound, the three BH units and three NH units alternate. The compound is isoelectronic and isostructural with benzene. For this reason borazine is sometimes referred to as “inorganic benzene”. Like benzene, borazine is a colourless liquid with an aromatic odor.

Ammonia borane (also systematically named amminetrihydridoboron), also called borazane, is the chemical compound with the formula H3NBH3. The colourless or white solid is the simplest molecular boron-nitrogen-hydride compound. It has attracted attention as a source of hydrogen fuel, but is otherwise primarily of academic interest.
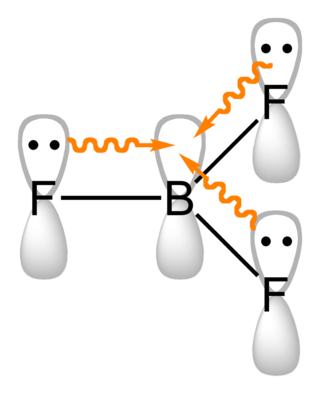
Boron compounds are compounds containing the element boron. In the most familiar compounds, boron has the formal oxidation state +3. These include oxides, sulfides, nitrides, and halides.

Borohydride refers to the anion [BH4]−, which is also called tetrahydroborate, and its salts. Borohydride or hydroborate is also the term used for compounds containing [BH4−nXn]−, where n is an integer from 0 to 3, for example cyanoborohydride or cyanotrihydroborate [BH3(CN)]− and triethylborohydride or triethylhydroborate [BH(CH2CH3)3]−. Borohydrides find wide use as reducing agents in organic synthesis. The most important borohydrides are lithium borohydride and sodium borohydride, but other salts are well known. Tetrahydroborates are also of academic and industrial interest in inorganic chemistry.

Digallane is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula GaH
2(H)
2GaH
2. It is the dimer of the monomeric compound gallane. The eventual preparation of the pure compound, reported in 1989, was hailed as a "tour de force." Digallane had been reported as early as 1941 by Wiberg; however, this claim could not be verified by later work by Greenwood and others. This compound is a colorless gas that decomposes above 0 °C.
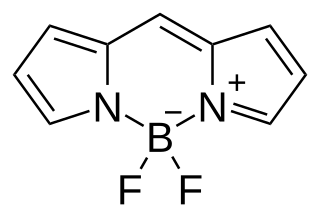
BODIPY is the technical common name of a chemical compound with formula C
9H
7BN
2F
2, whose molecule consists of a boron difluoride group BF
2 joined to a dipyrromethene group C
9H
7N
2; specifically, the compound 4,4-difluoro-4-bora-3a,4a-diaza-s-indacene in the IUPAC nomenclature. The common name is an abbreviation for "boron-dipyrromethene". It is a red crystalline solid, stable at ambient temperature, soluble in methanol.
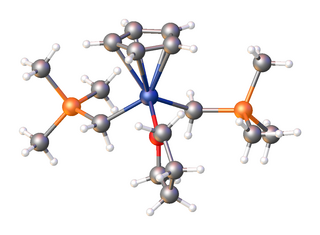
Organoscandium chemistry is an area with organometallic compounds focused on compounds with at least one carbon to scandium chemical bond. The interest in organoscandium compounds is mostly academic but motivated by potential practical applications in catalysis, especially in polymerization. A common precursor is scandium chloride, especially its THF complex.
Boron monofluoride or fluoroborylene is a chemical compound with formula BF, one atom of boron and one of fluorine. It was discovered as an unstable gas and only in 2009 found to be a stable ligand combining with transition metals, in the same way as carbon monoxide. It is a subhalide, containing fewer than the normal number of fluorine atoms, compared with boron trifluoride. It can also be called a borylene, as it contains boron with two unshared electrons. BF is isoelectronic with carbon monoxide and dinitrogen; each molecule has 14 electrons.
Borane, also known as borine, is an unstable and highly reactive molecule with the chemical formula BH
3. The preparation of borane carbonyl, BH3(CO), played an important role in exploring the chemistry of boranes, as it indicated the likely existence of the borane molecule. However, the molecular species BH3 is a very strong Lewis acid. Consequently, it is highly reactive and can only be observed directly as a continuously produced, transitory, product in a flow system or from the reaction of laser ablated atomic boron with hydrogen. It normally dimerizes to diborane in the absence of other chemicals.

1,2-Dimethyldiborane is an organoboron compound with the formula [(CH3)BH2]2. Structurally, it is related to diborane, but with methyl groups replacing terminal hydrides on each boron. It is the dimer of methylborane, CH3BH2, the simplest alkylborane. 1,2-Dimethyldiborane can exist in a cis- and a trans arrangement. 1,2-Dimethyldiborane is an easily condensed, colorless gas that ignites spontaneously in air.
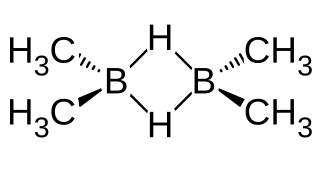
Dimethylborane, (CH3)2BH is the simplest dialkylborane, consisting of a methyl group substituted for a hydrogen in borane. As for other boranes it normally exists in the form of a dimer called tetramethyldiborane or tetramethylbisborane or TMDB ((CH3)2BH)2. Other combinations of methylation occur on diborane, including monomethyldiborane, trimethyldiborane, 1,2-dimethylborane, 1,1-dimethylborane and trimethylborane. At room temperature the substance is at equilibrium between these forms. The methylboranes were first prepared by H. I. Schlesinger and A. O. Walker in the 1930s.

Trimethyldiborane, (CH3)3B2H3 is a molecule containing boron carbon and hydrogen. It is an alkylborane, consisting of three methyl group substituted for a hydrogen in diborane. It can be considered a mixed dimer: (CH3)2BH2BH(CH3) or dimethylborane and methylborane. called 1,2-dimethyldiborane. Other combinations of methylation occur on diborane, including monomethyldiborane, 1,2-dimethyldiborane, tetramethyldiborane, 1,1-dimethylborane and trimethylborane. At room temperature the substance is at equilibrium between these forms, so it is difficult to keep it pure. The methylboranes were first prepared by H. I. Schlesinger and A. O. Walker in the 1930s.
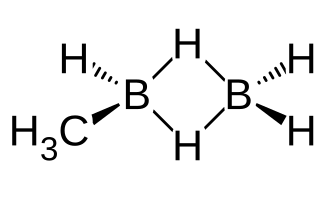
Methyldiborane, CH3B2H5, or monomethyldiborane is the simplest of alkyldiboranes, consisting of a methyl group substituted for a hydrogen in diborane. As with other boranes it exists in the form of a dimer with a twin hydrogen bridge that uses three-center two-electron bonding between the two boron atoms, and can be imagined as methyl borane (CH3BH2) bound to borane (BH3). Other combinations of methylation occur on diborane, including 1,1-dimethylborane, 1,2-dimethyldiborane, trimethyldiborane, tetramethyldiborane, and trimethylborane (which is not a dimer). At room temperature the substance is at equilibrium between these molecules.
Diborane(2), also known as diborene, is an inorganic compound with the formula B2H2. The number 2 in diborane(2) indicates the number of hydrogen atoms bonded to the boron complex. There are other forms of diborane with different numbers of hydrogen atoms, including diborane(4) and diborane(6).

An N-heterocyclic carbene boryl anion is an isoelectronic structure of an N-heterocyclic carbene (NHC), where the carbene carbon is replaced with a boron atom that has a -1 charge. NHC boryl anions have a planar geometry, and the boron atom is considered to be sp2-hybridized. They serve as extremely strong bases, as they are very nucleophilic. They also have a very strong trans influence, due to the σ-donation coming from the boron atom. NHC boryl anions have stronger electron-releasing character when compared to normal NHCs. These characteristics make NHC boryl anions key ligands in many applications, such as polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, and more commonly low oxidation state main group element bonding.