
Diatomic molecules are molecules composed of only two atoms, of the same or different chemical elements. If a diatomic molecule consists of two atoms of the same element, such as hydrogen or oxygen, then it is said to be homonuclear. Otherwise, if a diatomic molecule consists of two different atoms, such as carbon monoxide or nitric oxide, the molecule is said to be heteronuclear. The bond in a homonuclear diatomic molecule is non-polar.
In chemistry, a structural isomer of a compound is another compound whose molecule has the same number of atoms of each element, but with logically distinct bonds between them. The term metamer was formerly used for the same concept.

Tellurium is a chemical element; it has symbol Te and atomic number 52. It is a brittle, mildly toxic, rare, silver-white metalloid. Tellurium is chemically related to selenium and sulfur, all three of which are chalcogens. It is occasionally found in its native form as elemental crystals. Tellurium is far more common in the Universe as a whole than on Earth. Its extreme rarity in the Earth's crust, comparable to that of platinum, is due partly to its formation of a volatile hydride that caused tellurium to be lost to space as a gas during the hot nebular formation of Earth.

In chemistry and manufacturing, electrolysis is a technique that uses direct electric current (DC) to drive an otherwise non-spontaneous chemical reaction. Electrolysis is commercially important as a stage in the separation of elements from naturally occurring sources such as ores using an electrolytic cell. The voltage that is needed for electrolysis to occur is called the decomposition potential. The word "lysis" means to separate or break, so in terms, electrolysis would mean "breakdown via electricity."
A timeline of atomic and subatomic physics, including particle physics.

In chemistry, an enantiomer, also known as an optical isomer, antipode, or optical antipode, is one of a pair of molecular entities which are mirror images of each other and non-superposable.
Molecular physics is the study of the physical properties of molecules and molecular dynamics. The field overlaps significantly with physical chemistry, chemical physics, and quantum chemistry. It is often considered as a sub-field of atomic, molecular, and optical physics. Research groups studying molecular physics are typically designated as one of these other fields. Molecular physics addresses phenomena due to both molecular structure and individual atomic processes within molecules. Like atomic physics, it relies on a combination of classical and quantum mechanics to describe interactions between electromagnetic radiation and matter. Experiments in the field often rely heavily on techniques borrowed from atomic physics, such as spectroscopy and scattering.
In physical organic chemistry, a kinetic isotope effect (KIE) is the change in the reaction rate of a chemical reaction when one of the atoms in the reactants is replaced by one of its isotopes. Formally, it is the ratio of rate constants for the reactions involving the light (kL) and the heavy (kH) isotopically substituted reactants (isotopologues): KIE = kL/kH.

In chemistry, a molecule or ion is called chiral if it cannot be superposed on its mirror image by any combination of rotations, translations, and some conformational changes. This geometric property is called chirality. The terms are derived from Ancient Greek χείρ (cheir) 'hand'; which is the canonical example of an object with this property.
In physics, a parity transformation is the flip in the sign of one spatial coordinate. In three dimensions, it can also refer to the simultaneous flip in the sign of all three spatial coordinates :

Sodium tellurite is an inorganic tellurium compound with formula Na2TeO3. It is a water-soluble white solid and a weak reducing agent. Sodium tellurite is an intermediate in the extraction of the element, tellurium; it is a product obtained from anode slimes and is a precursor to tellurium.
In organic chemistry, a ring flip is the interconversion of cyclic conformers that have equivalent ring shapes that results in the exchange of nonequivalent substituent positions. The overall process generally takes place over several steps, involving coupled rotations about several of the molecule's single bonds, in conjunction with minor deformations of bond angles. Most commonly, the term is used to refer to the interconversion of the two chair conformers of cyclohexane derivatives, which is specifically referred to as a chair flip, although other cycloalkanes and inorganic rings undergo similar processes.

In chemistry, molecular symmetry describes the symmetry present in molecules and the classification of these molecules according to their symmetry. Molecular symmetry is a fundamental concept in chemistry, as it can be used to predict or explain many of a molecule's chemical properties, such as whether or not it has a dipole moment, as well as its allowed spectroscopic transitions. To do this it is necessary to use group theory. This involves classifying the states of the molecule using the irreducible representations from the character table of the symmetry group of the molecule. Symmetry is useful in the study of molecular orbitals, with applications to the Hückel method, to ligand field theory, and to the Woodward-Hoffmann rules. Many university level textbooks on physical chemistry, quantum chemistry, spectroscopy and inorganic chemistry discuss symmetry. Another framework on a larger scale is the use of crystal systems to describe crystallographic symmetry in bulk materials.
Physical organic chemistry, a term coined by Louis Hammett in 1940, refers to a discipline of organic chemistry that focuses on the relationship between chemical structures and reactivity, in particular, applying experimental tools of physical chemistry to the study of organic molecules. Specific focal points of study include the rates of organic reactions, the relative chemical stabilities of the starting materials, reactive intermediates, transition states, and products of chemical reactions, and non-covalent aspects of solvation and molecular interactions that influence chemical reactivity. Such studies provide theoretical and practical frameworks to understand how changes in structure in solution or solid-state contexts impact reaction mechanism and rate for each organic reaction of interest.
Triatomic hydrogen or H3 is an unstable triatomic molecule containing only hydrogen. Since this molecule contains only three atoms of hydrogen it is the simplest triatomic molecule and it is relatively simple to numerically solve the quantum mechanics description of the particles. Being unstable the molecule breaks up in under a millionth of a second. Its fleeting lifetime makes it rare, but it is quite commonly formed and destroyed in the universe thanks to the commonness of the trihydrogen cation. The infrared spectrum of H3 due to vibration and rotation is very similar to that of the ion, H+
3. In the early universe this ability to emit infrared light allowed the primordial hydrogen and helium gas to cool down so as to form stars.
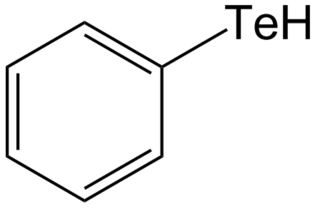
Tellurols are analogues of alcohols and phenols where tellurium replaces oxygen. Tellurols, selenols, and thiols have similar properties, but tellurols are the least stable. Although they are fundamental representatives of organotellurium compounds, tellurols are lightly studied because of their instability. Tellurol derivatives include telluroesters and tellurocyanates (RTeCN).

In chemistry, ethanium or protonated ethane is a highly reactive positive ion with formula C
2H+
7. It can be described as a molecule of ethane with one extra proton, that gives it a +1 electric charge.

Molybdenum(IV) telluride, molybdenum ditelluride or just molybdenum telluride is a compound of molybdenum and tellurium with formula MoTe2, corresponding to a mass percentage of 27.32% molybdenum and 72.68% tellurium.

Bromochlorofluoromethane or fluorochlorobromomethane, is a chemical compound and trihalomethane derivative with the chemical formula CHBrClF. As one of the simplest possible stable chiral compounds, it is useful for fundamental research into this area of chemistry. However, its relative instability to hydrolysis, and lack of suitable functional groups, made separation of the enantiomers of bromochlorofluoromethane especially challenging, and this was not accomplished until almost a century after it was first synthesised, in March 2005, though it has now been done by a variety of methods. More recent research using bromochlorofluoromethane has focused on its potential use for experimental measurement of parity violation, a major unsolved problem in quantum physics. For example, the S enantiomer is predicted to be lower in energy by about 2.356×10−16 eV (56.97 mHz), and the frequency of the C−F vibrational mode should be about 2.4 mHz lower for the R-enantiomer.

Martin Quack is a German physical chemist and spectroscopist; he is a professor at ETH Zürich.














