In organic chemistry, an alkene, or olefin, is a hydrocarbon containing a carbon–carbon double bond. The double bond may be internal or in the terminal position. Terminal alkenes are also known as α-olefins.

1,4-Cyclohexadiene is an organic compound with the formula C6H8. It is a colourless, flammable liquid that is of academic interest as a prototype of a large class of related compounds called terpenoids, an example being γ-terpinene. An isomer of this compound is 1,3-cyclohexadiene.
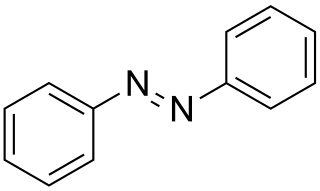
Azobenzene is a photoswitchable chemical compound composed of two phenyl rings linked by a N=N double bond. It is the simplest example of an aryl azo compound. The term 'azobenzene' or simply 'azo' is often used to refer to a wide class of similar compounds. These azo compounds are considered as derivatives of diazene (diimide), and are sometimes referred to as 'diazenes'. The diazenes absorb light strongly and are common dyes. Different classes of azo dyes exist, most notably the ones substituted with heteroaryl rings.
Diarylethene is the general name of a class of chemical compounds that have aromatic functional groups bonded to each end of a carbon–carbon double bond. The simplest example is stilbene, which has two geometric isomers, E and Z.
In chemistry, linkage isomerism or ambidentate isomerism is a form of isomerism in which certain coordination compounds have the same composition but differ in their metal atom's connectivity to a ligand.

In coordination chemistry, metal ammine complexes are metal complexes containing at least one ammonia ligand. "Ammine" is spelled this way for historical reasons; in contrast, alkyl or aryl bearing ligands are spelt with a single "m". Almost all metal ions bind ammonia as a ligand, but the most prevalent examples of ammine complexes are for Cr(III), Co(III), Ni(II), Cu(II) as well as several platinum group metals.

(E)-Stilbene, commonly known as trans-stilbene, is an organic compound represented by the condensed structural formula C6H5CH=CHC6H5. Classified as a diarylethene, it features a central ethylene moiety with one phenyl group substituent on each end of the carbon–carbon double bond. It has an (E) stereochemistry, meaning that the phenyl groups are located on opposite sides of the double bond, the opposite of its geometric isomer, cis-stilbene. Trans-stilbene occurs as a white crystalline solid at room temperature and is highly soluble in organic solvents. It can be converted to cis-stilbene photochemically, and further reacted to produce phenanthrene.
A triazole is a heterocyclic compound featuring a five-membered ring of two carbon atoms and three nitrogen atoms with molecular formula C2H3N3. Triazoles exhibit substantial isomerism, depending on the positioning of the nitrogen atoms within the ring.

Glycolaldehyde is the organic compound with the formula HOCH2−CHO. It is the smallest possible molecule that contains both an aldehyde group and a hydroxyl group. It is a highly reactive molecule that occurs both in the biosphere and in the interstellar medium. It is normally supplied as a white solid. Although it conforms to the general formula for carbohydrates, Cn(H2O)n, it is not generally considered to be a saccharide.

Azines are a functional class of organic compounds with the connectivity RR'C=N-N=CRR'. These compounds are the product of the condensation of hydrazine with ketones and aldehydes, although in practice they are often made by alternative routes. Ketazines are azines derived from ketones. For example, acetone azine is the simplest ketazine. Aldazines are azines derived from aldehydes.
A photoswitch is a type of molecule that can change its structural geometry and chemical properties upon irradiation with electromagnetic radiation. Although often used interchangeably with the term molecular machine, a switch does not perform work upon a change in its shape whereas a machine does. However, photochromic compounds are the necessary building blocks for light driven molecular motors and machines. Upon irradiation with light, photoisomerization about double bonds in the molecule can lead to changes in the cis- or trans- configuration. These photochromic molecules are being considered for a range of applications.
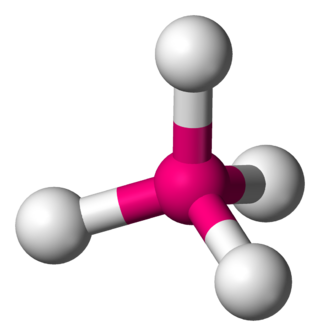
In a tetrahedral molecular geometry, a central atom is located at the center with four substituents that are located at the corners of a tetrahedron. The bond angles are cos−1(−1⁄3) = 109.4712206...° ≈ 109.5° when all four substituents are the same, as in methane as well as its heavier analogues. Methane and other perfectly symmetrical tetrahedral molecules belong to point group Td, but most tetrahedral molecules have lower symmetry. Tetrahedral molecules can be chiral.

Carbon trioxide (CO3) is an unstable oxide of carbon (an oxocarbon). The possible isomers of carbon trioxide include ones with molecular symmetry point groups Cs, D3h, and C2v. The C2v state, consisting of a dioxirane, has been shown to be the ground state of the molecule. Carbon trioxide should not be confused with the stable carbonate ion (CO2−
3).
Carbamic acid, which might also be called aminoformic acid or aminocarboxylic acid, is the chemical compound with the formula H2NCOOH. It can be obtained by the reaction of ammonia NH3 and carbon dioxide CO2 at very low temperatures, which also yields ammonium carbamate [NH4]+[NH2CO2]−. The compound is stable only up to about 250 K (−23 °C); at higher temperatures it decomposes into those two gases. The solid apparently consists of dimers, with the two molecules connected by hydrogen bonds between the two carboxyl groups –COOH.
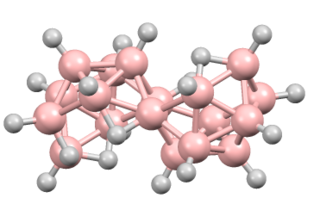
Octadecaborane is an inorganic compound, a borane with chemical formula B18H22. It is a colorless flammable solid, like many higher boron hydrides. Although the compound has no practical applications, its structure is of theoretical and pedagogical interest.
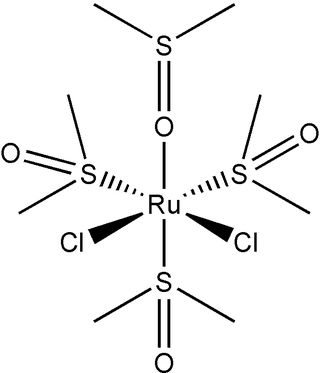
Dichlorotetrakis(dimethyl sulfoxide) ruthenium(II) describes coordination compounds with the formula RuCl2(dmso)4, where DMSO is dimethylsulfoxide. Both cis and trans isomers are known, but the cis isomer is more common. The cis isomer is a yellow, air-stable solid that is soluble in some organic solvents. These sulfoxide complexes are used in the synthesis of various ruthenium(ii) complexes. They have also attracted attention as possible anti-cancer drugs.

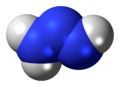
Triazane is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula NH2NHNH2 or N3H5. Triazane is the third simplest acyclic azane after ammonia and hydrazine. It can be synthesized from hydrazine but is unstable and cannot be isolated in the free base form, only as salt forms such as triazanium sulfate. Attempts to convert triazanium salts to the free base release only diazene and ammonia. Triazane was first synthesized as a ligand of the silver complex ion: tris(μ2-triazane-κ2N1,N3)disilver(2+). Triazane has also been synthesized in electron-irradiated ammonia ices and detected as a stable gas-phase product after sublimation.
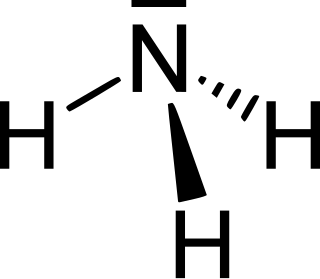
Azanes are acyclic, saturated hydronitrogens, which means that they consist only of hydrogen and nitrogen atoms and all bonds are single bonds. They are therefore pnictogen hydrides. Because cyclic hydronitrogens are excluded by definition, the azanes comprise a homologous series of inorganic compounds with the general chemical formula N
nH
n+2.
Formamide-based prebiotic chemistry is a reconstruction of the beginnings of life on Earth, assuming that formamide could accumulate in sufficiently high amounts to serve as the building block and reaction medium for the synthesis of the first biogenic molecules.
The Hantzsch pyridine synthesis or Hantzsch dihydropyridine synthesis is a multi-component organic reaction between an aldehyde such as formaldehyde, 2 equivalents of a β-keto ester such as ethyl acetoacetate and a nitrogen donor such as ammonium acetate or ammonia. The initial reaction product is a dihydropyridine which can be oxidized in a subsequent step to a pyridine. The driving force for this second reaction step is aromatization. This reaction was reported in 1881 by Arthur Rudolf Hantzsch.