 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
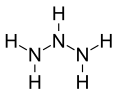
| Systematic IUPAC name Triazane [1] | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| N3H5 | |
| Molar mass | 47.061 g·mol−1 |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Triazane is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula NH2NHNH2 or N3H5. [2] Triazane is the third simplest acyclic azane after ammonia and hydrazine. It can be synthesized from hydrazine but is unstable and cannot be isolated in the free base form, only as salt forms such as triazanium sulfate. [3] Attempts to convert triazanium salts to the free base release only diazene and ammonia. [4] Triazane was first synthesized as a ligand of the silver complex ion: tris(μ2-triazane-κ2N1,N3)disilver(2+).[ clarification needed ] Triazane has also been synthesized in electron-irradiated ammonia ices and detected as a stable gas-phase product after sublimation. [5]