
Phosphorus is a chemical element; it has symbol P and atomic number 15. Elemental phosphorus exists in two major forms, white phosphorus and red phosphorus, but because it is highly reactive, phosphorus is never found as a free element on Earth. It has a concentration in the Earth's crust of about one gram per kilogram. In minerals, phosphorus generally occurs as phosphate.

Phosphoric acid is a colorless, odorless phosphorus-containing solid, and inorganic compound with the chemical formula H3PO4. It is commonly encountered as an 85% aqueous solution, which is a colourless, odourless, and non-volatile syrupy liquid. It is a major industrial chemical, being a component of many fertilizers.
The iron–sulfur world hypothesis is a set of proposals for the origin of life and the early evolution of life advanced in a series of articles between 1988 and 1992 by Günter Wächtershäuser, a Munich patent lawyer with a degree in chemistry, who had been encouraged and supported by philosopher Karl R. Popper to publish his ideas. The hypothesis proposes that early life may have formed on the surface of iron sulfide minerals, hence the name. It was developed by retrodiction from extant biochemistry in conjunction with chemical experiments.

Phosphorus trichloride is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula PCl3. A colorless liquid when pure, it is an important industrial chemical, being used for the manufacture of phosphites and other organophosphorus compounds. It is toxic and reacts readily with water to release hydrogen chloride.

Boron trioxide or diboron trioxide is the oxide of boron with the formula B2O3. It is a colorless transparent solid, almost always glassy (amorphous), which can be crystallized only with great difficulty. It is also called boric oxide or boria. It has many important industrial applications, chiefly in ceramics as a flux for glazes and enamels and in the production of glasses.
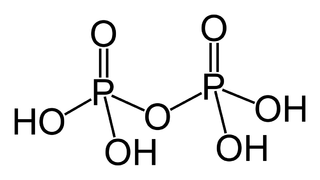
In chemistry, a phosphoric acid, in the general sense, is a phosphorus oxoacid in which each phosphorus (P) atom is in the oxidation state +5, and is bonded to four oxygen (O) atoms, one of them through a double bond, arranged as the corners of a tetrahedron. Two or more of these PO4 tetrahedra may be connected by shared single-bonded oxygens, forming linear or branched chains, cycles, or more complex structures. The single-bonded oxygen atoms that are not shared are completed with acidic hydrogen atoms. The general formula of a phosphoric acid is Hn+2−2xPnO3n+1−x, where n is the number of phosphorus atoms and x is the number of fundamental cycles in the molecule's structure, between 0 and n + 2/2.

Phosphorus pentoxide is a chemical compound with molecular formula P4O10 (with its common name derived from its empirical formula, P2O5). This white crystalline solid is the anhydride of phosphoric acid. It is a powerful desiccant and dehydrating agent.

Phosphoryl chloride is a colourless liquid with the formula POCl3. It hydrolyses in moist air releasing phosphoric acid and fumes of hydrogen chloride. It is manufactured industrially on a large scale from phosphorus trichloride and oxygen or phosphorus pentoxide. It is mainly used to make phosphate esters such as tricresyl phosphate.
Extreme pressure additives, or EP additives, are additives for lubricants with a role to decrease wear of the parts of the gears exposed to very high pressures. They are also added to cutting fluids for machining of metals.
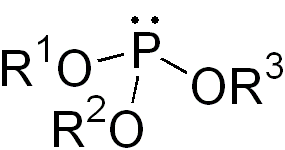
In organic chemistry, a phosphite ester or organophosphite usually refers to an organophosphorous compound with the formula P(OR)3. They can be considered as esters of an unobserved tautomer phosphorous acid, H3PO3, with the simplest example being trimethylphosphite, P(OCH3)3. Some phosphites can be considered esters of the dominant tautomer of phosphorous acid (HP(O)(OH)2). The simplest representative is dimethylphosphite with the formula HP(O)(OCH3)2. Both classes of phosphites are usually colorless liquids.
Organophosphorus chemistry is the scientific study of the synthesis and properties of organophosphorus compounds, which are organic compounds containing phosphorus. They are used primarily in pest control as an alternative to chlorinated hydrocarbons that persist in the environment. Some organophosphorus compounds are highly effective insecticides, although some are extremely toxic to humans, including sarin and VX nerve agents.
Silver molybdate (Ag2MoO4), a chemical compound, is a yellow, cubic crystalline substance often used in glass. Its crystals present two types of electronic structure, depending on the pressure conditions to which the crystal is subjected. At room temperature, Ag2MoO4 exhibits a spinel-type cubic structure, known as β-Ag2MoO4, which is more stable in nature. However, when exposed to high hydrostatic pressure, the tetragonal α-Ag2MoO4 forms as a metastable phase.
Aluminium phosphate is a chemical compound. In nature it occurs as the mineral berlinite. Many synthetic forms of aluminium phosphate are known. They have framework structures similar to zeolites and some are used as catalysts, ion-exchangers or molecular sieves. Commercial aluminium phosphate gel is available.

Triethyl phosphite is an organophosphorus compound, specifically a phosphite ester, with the formula P(OCH2CH3)3, often abbreviated P(OEt)3. It is a colorless, malodorous liquid. It is used as a ligand in organometallic chemistry and as a reagent in organic synthesis.

Ammonium dihydrogen phosphate (ADP), also known as monoammonium phosphate (MAP) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula (NH4)(H2PO4). ADP is a major ingredient of agricultural fertilizers and dry chemical fire extinguishers. It also has significant uses in optics and electronics.
Triphosphorus pentanitride is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula P3N5. Containing only phosphorus and nitrogen, this material is classified as a binary nitride. While it has been investigated for various applications this has not led to any significant industrial uses. It is a white solid, although samples often appear colored owing to impurities.

Chromium(III) phosphate describes inorganic compounds with the chemical formula CrPO4·(H2O)n, where n = 0, 4, or 6. All are deeply colored solids. Anhydrous CrPO4 is green. The hexahydrate CrPO4·6H2O is violet.

Peroxymonophosphoric acid is an oxyacid of phosphorus. It is a colorless viscous oil. Its salts are called peroxymonophosphates. Another peroxyphosphoric acid is peroxydiphosphoric acid, H4P2O8.

Borocarbonitrides are two-dimensional compounds that contain boron, nitrogen, and carbon atoms in a ratio BxCyNz. Borocarbonitrides are distinct from B,N co-doped graphene in that the former contains separate boron nitride and graphene domains as well as rings with B-C, B-N, C-N, and C-C bonds. These compounds generally have a high surface area, but borocarbonitrides synthesized from a high surface area carbon material, urea, and boric acid tend to have the highest surface areas. This high surface area coupled with the presence of Stone-Wales defects in the structure of borocarbonitrides also allows for high absorption of CO2 and CH4, which may make borocarbonitride compounds a useful material in sequestering these gases.
Neptunium compounds are compounds containg the element neptunium (Np). Neptunium has five ionic oxidation states ranging from +3 to +7 when forming chemical compounds, which can be simultaneously observed in solutions. It is the heaviest actinide that can lose all its valence electrons in a stable compound. The most stable state in solution is +5, but the valence +4 is preferred in solid neptunium compounds. Neptunium metal is very reactive. Ions of neptunium are prone to hydrolysis and formation of coordination compounds.
















