
Ozone depletion consists of two related events observed since the late 1970s: a steady lowering of about four percent in the total amount of ozone in Earth's atmosphere, and a much larger springtime decrease in stratospheric ozone around Earth's polar regions. The latter phenomenon is referred to as the ozone hole. There are also springtime polar tropospheric ozone depletion events in addition to these stratospheric events.
The haloalkanes are alkanes containing one or more halogen substituents. They are a subset of the general class of halocarbons, although the distinction is not often made. Haloalkanes are widely used commercially. They are used as flame retardants, fire extinguishants, refrigerants, propellants, solvents, and pharmaceuticals. Subsequent to the widespread use in commerce, many halocarbons have also been shown to be serious pollutants and toxins. For example, the chlorofluorocarbons have been shown to lead to ozone depletion. Methyl bromide is a controversial fumigant. Only haloalkanes that contain chlorine, bromine, and iodine are a threat to the ozone layer, but fluorinated volatile haloalkanes in theory may have activity as greenhouse gases. Methyl iodide, a naturally occurring substance, however, does not have ozone-depleting properties and the United States Environmental Protection Agency has designated the compound a non-ozone layer depleter. For more information, see Halomethane. Haloalkane or alkyl halides are the compounds which have the general formula "RX" where R is an alkyl or substituted alkyl group and X is a halogen.

Dichloromethane is an organochlorine compound with the formula CH2Cl2. This colorless, volatile liquid with a chloroform-like, sweet odor is widely used as a solvent. Although it is not miscible with water, it is slightly polar, and miscible with many organic solvents.
Dichlorodifluoromethane (R-12) is a colorless gas usually sold under the brand name Freon-12, and a chlorofluorocarbon halomethane (CFC) used as a refrigerant and aerosol spray propellant. In compliance with the Montreal Protocol, its manufacture was banned in developed countries in 1996, and in developing countries in 2010 out of concerns about its damaging effect on the ozone layer. Its only allowed usage is as a fire retardant in submarines and aircraft. It is soluble in many organic solvents. R-12 cylinders are colored white.
Trichlorofluoromethane, also called freon-11, CFC-11, or R-11, is a chlorofluorocarbon (CFC). It is a colorless, faintly ethereal, and sweetish-smelling liquid that boils around room temperature. CFC-11 is a Class 1 ozone-depleting substance which damages Earth's protective stratospheric ozone layer. Also R-11 is not flammable at ambient temperature and pressure but it can become very combustible if heated and ignited by a strong ignition source.

Organotin chemistry is the scientific study of the synthesis and properties of organotin compounds or stannanes, which are organometallic compounds containing tin–carbon bonds. The first organotin compound was diethyltin diiodide, discovered by Edward Frankland in 1849. The area grew rapidly in the 1900s, especially after the discovery of the Grignard reagents, which are useful for producing Sn–C bonds. The area remains rich with many applications in industry and continuing activity in the research laboratory.

Azobisisobutyronitrile (abbreviated AIBN) is an organic compound with the formula [(CH3)2C(CN)]2N2. This white powder is soluble in alcohols and common organic solvents but is insoluble in water. It is often used as a foamer in plastics and rubber and as a radical initiator.
![<span class="mw-page-title-main">Polymethylhydrosiloxane</span> Organic polymer with the repeating formula [CH3(H)SiO]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/b/b2/Polymethylhydrosiloxane.png/320px-Polymethylhydrosiloxane.png)
Polymethylhydrosiloxane (PMHS) is a polymer with the general structure [−CH3(H)Si−O−]. It is used in organic chemistry as a mild and stable reducing agent easily transferring hydrides to metal centers and a number of other reducible functional groups. A variety of related materials are available under the following CAS registry numbers 9004-73-3, 16066-09-4, 63148-57-2, 178873-19-3. These include the tetramer, copolymers of dimethylsiloxane and methylhydrosiloxane, and trimethylsilyl terminated materials.
The Dowd–Beckwith ring-expansion reaction is an organic reaction in which a cyclic carbonyl is expanded by up to 4 carbons in a free radical ring expansion reaction through an α-alkylhalo substituent. The radical initiator system is based on AIBN and tributyltin hydride. The cyclic β-keto ester can be obtained through a Dieckmann condensation. The original reaction consisted of a nucleophilic aliphatic substitution of the enolate of ethyl cyclohexanone-2-carboxylate with 1,4-diiodobutane and sodium hydride followed by ring expansion to ethyl cyclodecanone-6-carboxylate. A side-reaction is organic reduction of the iodoalkane.
Organofluorine chemistry describes the chemistry of organofluorine compounds, organic compounds that contain a carbon–fluorine bond. Organofluorine compounds find diverse applications ranging from oil and water repellents to pharmaceuticals, refrigerants, and reagents in catalysis. In addition to these applications, some organofluorine compounds are pollutants because of their contributions to ozone depletion, global warming, bioaccumulation, and toxicity. The area of organofluorine chemistry often requires special techniques associated with the handling of fluorinating agents.
The reduction of nitro compounds are chemical reactions of wide interest in organic chemistry. The conversion can be effected by many reagents. The nitro group was one of the first functional groups to be reduced. Alkyl and aryl nitro compounds behave differently. Most useful is the reduction of aryl nitro compounds.
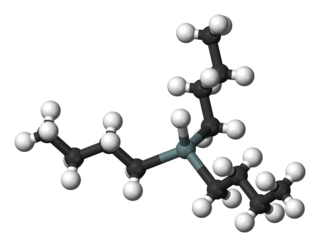
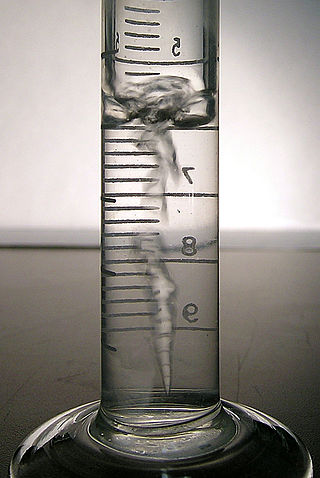
Tributyltin hydride is an organotin compound with the formula (C4H9)3SnH. It is a colorless liquid that is soluble in organic solvents. The compound is used as a source of hydrogen atoms in organic synthesis.
Total petroleum hydrocarbons (TPH) is a term used for any mixture of hydrocarbons that are found in crude oil. There are several hundred of these compounds, but not all occur in any one sample. Crude oil is used to make petroleum products, which can contaminate the environment. Because there are so many different chemicals in crude oil and in other petroleum products, it is not practical to measure each one separately. However, it is useful to measure the total amount of TPH at a site. Chemicals that occur in TPH include hexane, benzene, toluene, xylenes, naphthalene, and fluorene, other constituents of gasoline, jet fuels, mineral oils, and of other petroleum products. Petroleum hydrocarbon ranges are monitored at various levels depending on the state and testing site.

Bromofluoromethane is a mixed gaseous halomethane soluble in alcohol and very soluble in chloroform.

Tropospheric ozone depletion events are phenomena that reduce the concentration of ozone in the earth's troposphere. Ozone (O3) is a trace gas which has been of concern because of its unique dual role in different layers of the lower atmosphere. Apart from absorbing UV-B radiation and converting solar energy into heat in the stratosphere, ozone in the troposphere provides greenhouse effect and controls the oxidation capacity of the atmosphere.
An aryl radical in organic chemistry is a reactive intermediate and an arene compound incorporating one free radical carbon atom as part of the ring structure. As such it is the radical counterpart of the arenium ion. The parent compound is the phenyl radical C
6H•
5. Aryl radicals are intermediates in certain organic reactions.
The Markó–Lam deoxygenation is an organic chemistry reaction where the hydroxy functional group in an organic compound is replaced by a hydrogen atom to give an alkyl group. The Markó-Lam reaction is a variant of the Bouveault–Blanc reduction and an alternative to the classical Barton–McCombie deoxygenation. It is named for the Belgian chemists István Markó and Kevin Lam.
Triphenyltin compounds are organotin compounds with the general formula (C6H5)3SnX. They contain the triphenyltin group, (C6H5)3Sn, or Ph3Sn, which consists of an atom of tin bonded to three phenyl groups. Examples of triphenyltins include:

Tributyltin chloride is an organotin compound with the formula (C4H9)3SnCl. It is a colorless liquid that is soluble in organic solvents.
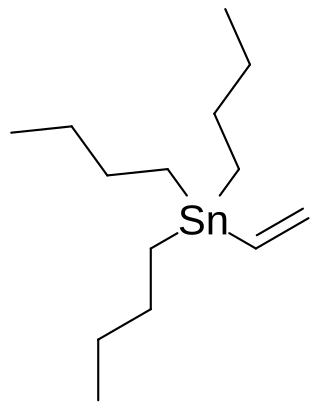
Vinyl tributyltin is an organotin compound with the formula Bu3SnCH=CH2 (Bu = butyl). It is a white, air-stable solid. It is used as a source of vinyl anion equivalent in Stille coupling reactions. As a source of vinyltin reagents, early work used vinyl trimethyltin, but trimethyltin compounds are avoided nowadays owing to their toxicity.








![<span class="mw-page-title-main">Polymethylhydrosiloxane</span> Organic polymer with the repeating formula [CH3(H)SiO]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/b/b2/Polymethylhydrosiloxane.png/320px-Polymethylhydrosiloxane.png)




