
Potassium oxide (K2O) is an ionic compound of potassium and oxygen. It is a base. This pale yellow solid, the simplest oxide of potassium, is a rarely encountered, highly reactive compound. Some materials of commerce, such as fertilizers and cements, are assayed assuming the percent composition that would be equivalent to the chemical compound mixture K2O.
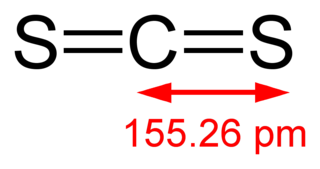
Carbon disulfide, also spelled as carbon disulphide, is a colorless volatile liquid with the formula CS2. The compound is used frequently as a building block in organic chemistry as well as an industrial and chemical non-polar solvent. It has an "ether-like" odor, but commercial samples are typically contaminated with foul-smelling impurities.

Anthracene is a solid polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) of formula C14H10, consisting of three fused benzene rings. It is a component of coal tar. Anthracene is used in the production of the red dye alizarin and other dyes. Anthracene is colorless but exhibits a blue (400–500 nm peak) fluorescence under ultraviolet radiation.
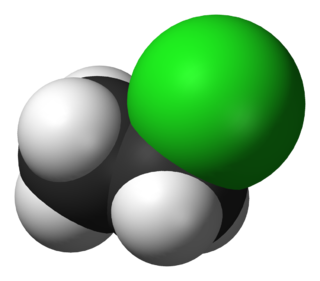
Chloroethane, commonly known as ethyl chloride, is a chemical compound with chemical formula CH3CH2Cl, once widely used in producing tetraethyllead, a gasoline additive. It is a colorless, flammable gas or refrigerated liquid with a faintly sweet odor.
Myristic acid (IUPAC name: tetradecanoic acid) is a common saturated fatty acid with the molecular formula CH3(CH2)12COOH. Its salts and esters are commonly referred to as myristates or tetradecanoates. It is named after the binomial name for nutmeg (Myristica fragrans), from which it was first isolated in 1841 by Lyon Playfair.
This page provides supplementary chemical data on acetic acid.
This page provides supplementary chemical data on acetone.
This page provides supplementary chemical data on ethanol. Except where noted otherwise, data relate to standard ambient temperature and pressure.
This page provides supplementary chemical data on methanol.
Dioxygen difluoride is a compound of fluorine and oxygen with the molecular formula O2F2. It can exist as an orange-colored solid which melts into a red liquid at −163 °C (110 K). It is an extremely strong oxidant and decomposes into oxygen and fluorine even at −160 °C (113 K) at a rate of 4% per day: its lifetime at room temperature is thus extremely short. Dioxygen difluoride reacts vigorously with nearly every chemical it encounters – even ordinary ice – leading to its onomatopoeic nickname "FOOF" (a play on its chemical structure and its explosive tendencies).
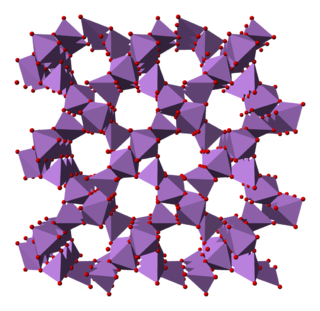
Arsenic pentoxide is the inorganic compound with the formula As2O5. This glassy, white, deliquescent solid is relatively unstable, consistent with the rarity of the As(V) oxidation state. More common, and far more important commercially, is arsenic(III) oxide (As2O3). All arsenic compounds are highly toxic and thus find only limited commercial applications.

Cadmium oxide is an inorganic compound with the formula CdO. It is one of the main precursors to other cadmium compounds. It crystallizes in a cubic rocksalt lattice like sodium chloride, with octahedral cation and anion centers. It occurs naturally as the rare mineral monteponite. Cadmium oxide can be found as a colorless amorphous powder or as brown or red crystals. Cadmium oxide is an n-type semiconductor with a band gap of 2.18 eV at room temperature.

Antimony pentachloride is a chemical compound with the formula SbCl5. It is a colourless oil, but typical samples are yellowish due to impurities. Owing to its tendency to hydrolyse to hydrochloric acid, SbCl5 is a highly corrosive substance and must be stored in glass or PTFE containers.
The table below provides information on the variation of solubility of different substances in water with temperature, at one atmosphere pressure. Units of solubility are given in grams per 100 millilitres of water, unless shown otherwise. The substances are listed in alphabetical order.

ChemSpider is a database of chemicals. ChemSpider is owned by the Royal Society of Chemistry.
Tridecylic acid, or tridecanoic acid, is a 13-carbon saturated fatty acid with the chemical formula CH3(CH2)11COOH.
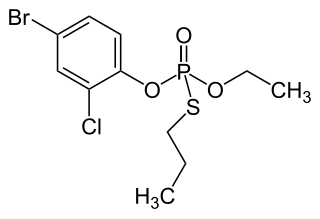
Profenofos is an organophosphate insecticide. It is a liquid with a pale yellow to amber color and a garlic-like odor. It was first registered in the United States in 1982. As of 2015, it was not approved in the European Union.

Benzyl iodide is an organic compound with the chemical formula C
7H
7I. The compound consists of a benzene ring with an attached iodidemethyl group. The substance is an alkyl halide and is a constitutional isomer of the iodotoluenes.
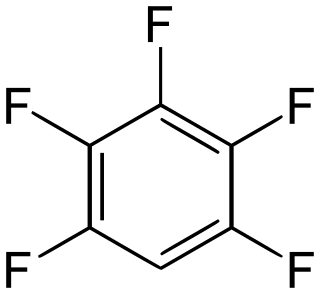
Pentafluorobenzene is an organofluoride compound with the molecular formula C
6HF
5. The compound consists of a benzene ring substituted with five fluorine atoms. The substance is a colorless liquid with a boiling point similar to that of benzene. It is prepared by defluorination of highly fluorinated cyclohexanes over hot nickel or iron. Another method involved dehydrofluorination of polyfluorinated cyclohexane using hot aqueous solution of KOH.
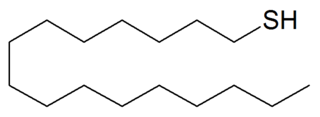
1-Hexadecanethiol is a chemical compound from the group of thiols. Its chemical formula is C
16H
34S.












