Related Research Articles

Treponema is a genus of spiral-shaped bacteria. The major treponeme species of human pathogens is Treponema pallidum, whose subspecies are responsible for diseases such as syphilis, bejel, and yaws. Treponema carateum is the cause of pinta. Treponema paraluiscuniculi is associated with syphilis in rabbits. Treponema succinifaciens has been found in the gut microbiome of traditional rural human populations.

Ursolic acid, is a pentacyclic triterpenoid identified in the epicuticular waxes of apples as early as 1920 and widely found in the peels of fruits, as well as in herbs and spices like rosemary and thyme.

Taste receptors for bitter substances (T2Rs/TAS2Rs) belong to the family of G-protein coupled receptors and are related to class A-like GPCRs. There are 25 known T2Rs in humans responsible for bitter taste perception.

MAX-interacting protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MXI1 gene.

Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 3 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CDKN3 gene.
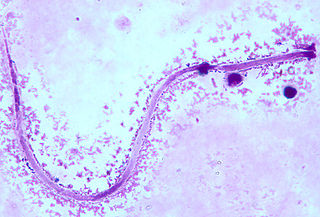
Mansonella is a genus of parasitic nematodes. It includes three species that are responsible for the disease mansonelliasis: Mansonella ozzardi, M. perstans, and M. streptocerca. A potential fourth species has been identified in Gabon in 2015 and proposed as a new species Mansonella sp. "DEUX". Whole-genome sequences from Mansonella perstans, Mansonella ozzardi, and the newly proposed species Mansonella sp. "DEUX" have been assembled.
Peptoniphilus is a genus of bacteria in the phylum Bacillota (Bacteria).
Anaerococcus is a genus of bacteria. Its type species is Anaerococcus prevotii. These bacteria are Gram-positive and strictly anaerobic. The genus Anaerococcus was proposed in 2001. Its genome was sequenced in August 2009. The genus Anaerococcus is one of six genera classified within the group GPAC. These six genera are found in the human body as part of the commensal human microbiota.
The Untermassfeld fossil site is a palaeontological site in Thuringia, Germany. Excavated continuously since its discovery in 1978, it has produced many fossils dating to the late Early Pleistocene or Epivillafranchian geologic period, approximately 1.2 – 0.9 million years before present (BP). Claims that hominins were also present at the site have sparked a major controversy.
"Brachybacterium massiliense" is a species of Gram positive bacterium. It was first isolated from a stool sample of 38-month-old healthy girl from Senegal. The species was first proposed in 2017, and the name is derived from Massilia, the Roman name for Marseille, the location of the laboratory where B. massiliense was first isolated.
Sediminibacillus is a genus of bacteria from the family of Bacillaceae. Sediminibacillus species are halophilic bacteria and found in salty human stools and marine sponges. Sediminibacillus species are identified from Plakortis dariae sponge of the Saint Martin's island of the Bay of Bengal, Bangladesh.
Mobilicoccus massiliensis is a Gram-positive, facultatively anaerobic non-spore-forming and motile bacterium from the genus of Mobilicoccus which has been isolated from feces of a human boy with kwashiorkor.
Ileibacterium massiliense is a bacterium from the genus of Ileibacterium which has been isolated from the ileum of a human.
Treponema succinifaciens is an anaerobic spirochete bacterium first discovered in the intestines of swine in 1981. The helical cells of T. succinifaciens grow to 16 μm in length and often form chains of cells when cultured. T. succinifaciens is gram-negative and non spore-forming.
Peptoniphilus coxii is a bacterium from the genus Peptoniphilus which has been isolated from human infections.
Peptoniphilus lacydonensis is a Gram-positive, anaerobic and microaerophilic bacterium from the genus Peptoniphilus which has been isolated from a patient with chronic refractory sinusitis.
Virgibacillus ndiopensis is a halophilic bacterium from the genus of Virgibacillus.
Weeksella massiliensis is a bacterium from the genus of Weeksella. Weeksella massiliensis has been isolated from the urine from a man with acute cystitis Weeksella massiliensis is a human pathogen.
Parabacteroides massiliensis is a bacterium from the genus of Parabacteroides which has been isolated from human faeces.
Leptospira wolffii is a gram negative aerobic bacterium in the spirochaete phylum. The species named after Dutch bacteriologist Jan Willem Wolff.
References
- 1 2 3 "Peptoniphilus urinimassiliensis". www.uniprot.org.
- ↑ Brahimi, S; Cadoret, F; Founier, PE; Moal, V; Raoult, D (March 2017). "Peptoniphilus urinimassiliensis sp. nov., a new bacterial species isolated from a human urine sample after de novo kidney transplantation". New Microbes and New Infections. 16: 49–50. doi:10.1016/j.nmni.2017.01.001. PMC 5294733 . PMID 28203376. (This paper currently has an expression of concern, see doi:10.1016/j.nmni.2024.101376, PMID 38799976, Retraction Watch )