
In antenna theory, a phased array usually means an electronically scanned array, a computer-controlled array of antennas which creates a beam of radio waves that can be electronically steered to point in different directions without moving the antennas. The general theory of an electromagnetic phased array also finds applications in ultrasonic and medical imaging application and in optics optical phased array.
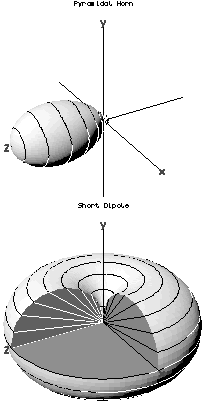
In the field of antenna design the term radiation pattern refers to the directional (angular) dependence of the strength of the radio waves from the antenna or other source.

In electronics and telecommunications, a radio transmitter or just transmitter is an electronic device which produces radio waves with an antenna with the purpose of signal transmission up to a radio receiver. The transmitter itself generates a radio frequency alternating current, which is applied to the antenna. When excited by this alternating current, the antenna radiates radio waves.

Very low frequency or VLF is the ITU designation for radio frequencies (RF) in the range of 3–30 kHz, corresponding to wavelengths from 100 to 10 km, respectively. The band is also known as the myriameter band or myriameter wave as the wavelengths range from one to ten myriameters. Due to its limited bandwidth, audio (voice) transmission is highly impractical in this band, and therefore only low data rate coded signals are used. The VLF band is used for a few radio navigation services, government time radio stations and for secure military communication. Since VLF waves can penetrate at least 40 meters (131 ft) into saltwater, they are used for military communication with submarines.
Low frequency (LF) is the ITU designation for radio frequencies (RF) in the range of 30–300 kHz. Since its wavelengths range from 10–1 km, respectively, it is also known as the kilometre band or kilometre waves.

Medium frequency (MF) is the ITU designation for radio frequencies (RF) in the range of 300 kilohertz (kHz) to 3 megahertz (MHz). Part of this band is the medium wave (MW) AM broadcast band. The MF band is also known as the hectometer band as the wavelengths range from ten to one hectometers. Frequencies immediately below MF are denoted as low frequency (LF), while the first band of higher frequencies is known as high frequency (HF). MF is mostly used for AM radio broadcasting, navigational radio beacons, maritime ship-to-shore communication, and transoceanic air traffic control.

In radio engineering, an antenna or aerial is an electronic device that converts an alternating electric current into radio waves, or radio waves into an electric current. It is the interface between radio waves propagating through space and electric currents moving in metal conductors, used with a transmitter or receiver. In transmission, a radio transmitter supplies an electric current to the antenna's terminals, and the antenna radiates the energy from the current as electromagnetic waves. In reception, an antenna intercepts some of the power of a radio wave in order to produce an electric current at its terminals, that is applied to a receiver to be amplified. Antennas are essential components of all radio equipment.

A parabolic antenna is an antenna that uses a parabolic reflector, a curved surface with the cross-sectional shape of a parabola, to direct the radio waves. The most common form is shaped like a dish and is popularly called a dish antenna or parabolic dish. The main advantage of a parabolic antenna is that it has high directivity. It functions similarly to a searchlight or flashlight reflector to direct radio waves in a narrow beam, or receive radio waves from one particular direction only. Parabolic antennas have some of the highest gains, meaning that they can produce the narrowest beamwidths, of any antenna type. In order to achieve narrow beamwidths, the parabolic reflector must be much larger than the wavelength of the radio waves used, so parabolic antennas are used in the high frequency part of the radio spectrum, at UHF and microwave (SHF) frequencies, at which the wavelengths are small enough that conveniently sized reflectors can be used.

A periscope is an instrument for observation over, around or through an object, obstacle or condition that prevents direct line-of-sight observation from an observer's current position.

A directional antenna or beam antenna is an antenna which radiates or receives greater radio wave power in specific directions. Directional antennas can radiate radio waves in beams, when greater concentration of radiation in a certain direction is desired, or in receiving antennas receive radio waves from one specific direction only. This can increase the power transmitted to receivers in that direction, or reduce interference from unwanted sources. This contrasts with omnidirectional antennas such as dipole antennas which radiate radio waves over a wide angle, or receive from a wide angle.

Grimeton Radio Station in southern Sweden, close to Varberg in Halland, is an early longwave transatlantic wireless telegraphy station built in 1922–1924, that has been preserved as a historical site. From the 1920s through the 1940s it was used to transmit telegram traffic by Morse code to North America and other countries, and during World War II was Sweden's only telecommunication link with the rest of the world. It is the only remaining example of an early pre-electronic radio transmitter technology called an Alexanderson alternator. It was added to the UNESCO World Heritage List in 2004, with the statement: "Grimeton Radio Station, Varberg is an exceptionally well preserved example of a type of telecommunication centre, representing the technological achievements by the early 1920s, as well as documenting the further development over some three decades." The radio station is also an anchor site for the European Route of Industrial Heritage. The transmitter is still in operational condition, and each year on a day called Alexanderson Day is started up and transmits brief Morse code test transmissions, which can be received all over Europe.

A loop antenna is a radio antenna consisting of a loop or coil of wire, tubing, or other electrical conductor, that for transmitting is usually fed by a balanced power source or for receiving feeds a balanced load. Within this physical description there are two distinct types:
The Friis transmission formula is used in telecommunications engineering, equating the power at the terminals of a receive antenna as the product of power density of the incident wave and the effective aperture of the receiving antenna under idealized conditions given another antenna some distance away transmitting a known amount of power. The formula was presented first by Danish-American radio engineer Harald T. Friis in 1946. The formula is sometimes referenced as the Friis transmission equation.

A radio repeater is a combination of a radio receiver and a radio transmitter that receives a signal and retransmits it, so that two-way radio signals can cover longer distances. A repeater sited at a high elevation can allow two mobile stations, otherwise out of line-of-sight propagation range of each other, to communicate. Repeaters are found in professional, commercial, and government mobile radio systems and also in amateur radio.

In radio, multiple-input and multiple-output (MIMO) is a method for multiplying the capacity of a radio link using multiple transmission and receiving antennas to exploit multipath propagation. MIMO has become an essential element of wireless communication standards including IEEE 802.11n, IEEE 802.11ac, HSPA+ (3G), WiMAX, and Long Term Evolution (LTE). More recently, MIMO has been applied to power-line communication for three-wire installations as part of the ITU G.hn standard and of the HomePlug AV2 specification.

Radio is the technology of communicating using radio waves. Radio waves are electromagnetic waves of frequency between 3 hertz (Hz) and 300 gigahertz (GHz). They are generated by an electronic device called a transmitter connected to an antenna which radiates oscillating electrical energy, often characterized as a wave. They can be received by other antennas connected to a radio receiver, this is the fundamental principle of radio communication. In addition to communication, radio is used for radar, radio navigation, remote control, remote sensing, and other applications.
Naval Radio Transmitter Facility Aguada is a tall guyed radio mast erected by the United States Navy. It is used as a facility of the US Navy for ashore and U.S. and NATO ships, planes, and submarines operating at sea in areas of broadcast coverage near Aguada, Puerto Rico at 18°23′55″N67°10′38″W by using radio waves in the very low frequency range.

German submarine U-1308 was the last Type VIIC/41 submarine to be laid down, launched and commissioned by Nazi Germany's Kriegsmarine during World War II. The Oberkommando der Marine or OKM,, had decided near the end of World War II to put all of its resources into building newer types of Unterseeboot, such as the types XXI and XXIII. U-1308 was part of a batch of eight U-boats ordered on 1 August 1942 to be built at Flensburger Schiffbau-Gesellschaft, Flensburg. She was laid down on 16 February 1944 and launched on 22 November. The eight boats were commissioned over a 12-month period between February 1944 and 17 January 1945.

Polarization-division multiplexing (PDM) is a physical layer method for multiplexing signals carried on electromagnetic waves, allowing two channels of information to be transmitted on the same carrier frequency by using waves of two orthogonal polarization states. It is used in microwave links such as satellite television downlinks to double the bandwidth by using two orthogonally polarized feed antennas in satellite dishes. It is also used in fiber optic communication by transmitting separate left and right circularly polarized light beams through the same optical fiber.















