
Superoxide dismutase (SOD, EC 1.15.1.1) is an enzyme that alternately catalyzes the dismutation (or partitioning) of the superoxide (O−
2) radical into ordinary molecular oxygen (O2) and hydrogen peroxide (H
2O
2). Superoxide is produced as a by-product of oxygen metabolism and, if not regulated, causes many types of cell damage. Hydrogen peroxide is also damaging and is degraded by other enzymes such as catalase. Thus, SOD is an important antioxidant defense in nearly all living cells exposed to oxygen. One exception is Lactobacillus plantarum and related lactobacilli, which use a different mechanism to prevent damage from reactive O−
2.

The zebu, sometimes known in the plural as indicine cattle, Camel cow or humped cattle, is a species or subspecies of domestic cattle originating in South Asia. Zebu, like many Sanga cattle breeds, differs from taurine cattle by a fatty hump on their shoulders, a large dewlap, and sometimes drooping ears. They are well adapted to withstanding high temperatures and are farmed throughout the tropics.

Red Bull is a brand of energy drinks created and owned by the Austrian company Red Bull GmbH. With a market share of 43%, it is the most popular energy drink brand as of 2020, and the third most valuable soft drink brand, behind Coca-Cola and Pepsi. Sinсe its launch in 1987, more than 100 billion cans of Red Bull have been sold worldwide, including over 12 billion in 2023.

Taurine, or 2-aminoethanesulfonic acid, is a non-proteinogenic amino sulfonic acid that is widely distributed in animal tissues. It is a major constituent of bile and can be found in the large intestine, and accounts for up to 0.1% of total human body weight.
In chemistry, a superoxide is a compound that contains the superoxide ion, which has the chemical formula O−2. The systematic name of the anion is dioxide(1−). The reactive oxygen ion superoxide is particularly important as the product of the one-electron reduction of dioxygen O2, which occurs widely in nature. Molecular oxygen (dioxygen) is a diradical containing two unpaired electrons, and superoxide results from the addition of an electron which fills one of the two degenerate molecular orbitals, leaving a charged ionic species with a single unpaired electron and a net negative charge of −1. Both dioxygen and the superoxide anion are free radicals that exhibit paramagnetism. Superoxide was historically also known as "hyperoxide".
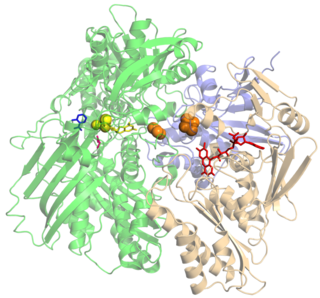
Xanthine oxidase is a form of xanthine oxidoreductase, a type of enzyme that generates reactive oxygen species. These enzymes catalyze the oxidation of hypoxanthine to xanthine and can further catalyze the oxidation of xanthine to uric acid. These enzymes play an important role in the catabolism of purines in some species, including humans.

The Brahman is an American breed of zebuine-taurine hybrid beef cattle. It was bred in the United States from 1885 from cattle originating in India, imported at various times from the United Kingdom, India, and Brazil. These were mainly Gir, Guzerá and Nelore stock, with some Indu-Brasil, Krishna Valley and Ongole. The Brahman has a high tolerance of heat, sunlight and humidity, and good resistance to parasites. It has been exported to many countries, particularly in the tropics; in Australia it is the most numerous breed of cattle. It has been used in the creation of numerous taurine-indicine hybrids, some of which – such as the Brangus and Brahmousin – are established as separate breeds.

Potassium superoxide is an inorganic compound with the formula KO2. It is a yellow paramagnetic solid that decomposes in moist air. It is a rare example of a stable salt of the superoxide anion. It is used as a CO2 scrubber, H2O dehumidifier, and O2 generator in rebreathers, spacecraft, submarines, and spacesuits.

Sodium superoxide is the inorganic compound with the formula NaO2. This yellow-orange solid is a salt of the superoxide anion. It is an intermediate in the oxidation of sodium by oxygen.
NADPH oxidase is a membrane-bound enzyme complex that faces the extracellular space. It can be found in the plasma membrane as well as in the membranes of phagosomes used by neutrophil white blood cells to engulf microorganisms. Human isoforms of the catalytic component of the complex include NOX1, NOX2, NOX3, NOX4, NOX5, DUOX1, and DUOX2.

The hydroperoxyl radical, also known as the hydrogen superoxide, is the protonated form of superoxide with the chemical formula HO2, also written HOO•. This species plays an important role in the atmosphere and as a reactive oxygen species in cell biology.
Mother is an energy drink that originated in Australia and New Zealand by Coca-Cola. Introduced in late 2006 after Coca-Cola's failed attempt to purchase Red Bull, it competes with the two leading energy drinks on the market, V and Red Bull, in the $151 million industry.

Superoxide dismutase [Cu-Zn] also known as superoxide dismutase 1 or hSod1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the SOD1 gene, located on chromosome 21. SOD1 is one of three human superoxide dismutases. It is implicated in apoptosis, familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and Parkinson's disease.
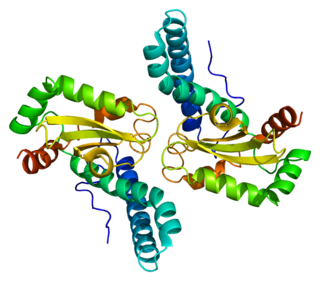
Superoxide dismutase 2, mitochondrial (SOD2), also known as manganese-dependent superoxide dismutase (MnSOD), is an enzyme which in humans is encoded by the SOD2 gene on chromosome 6. A related pseudogene has been identified on chromosome 1. Alternative splicing of this gene results in multiple transcript variants. This gene is a member of the iron/manganese superoxide dismutase family. It encodes a mitochondrial protein that forms a homotetramer and binds one manganese ion per subunit. This protein binds to the superoxide byproducts of oxidative phosphorylation and converts them to hydrogen peroxide and diatomic oxygen. Mutations in this gene have been associated with idiopathic cardiomyopathy (IDC), premature aging, sporadic motor neuron disease, and cancer.

Extracellular superoxide dismutase [Cu-Zn] is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the SOD3 gene.
In enzymology, a sulfoacetaldehyde acetyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Sodium- and chloride-dependent taurine transporter is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC6A6 gene.

NADPH oxidase organizer 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the NOXO1 gene.
In general, cognitive support diets are formulated to include nutrients that have a known role in brain development, function and/or maintenance, with the goal of improving and preserving mental processes such as attentiveness, short-term and long-term memory, learning, and problem solving. Currently, there is very little conclusive research available regarding cat cognition as standardized tests for evaluating cognitive ability are less established and less reliable than cognitive testing apparatus used in other mammalian species, like dogs. Much of what is known about feline cognition has been inferred from a combination of owner-reported behaviour, brain necropsies, and comparative cognitive neurology of related animal models. Cognition claims appear primarily on kitten diets which include elevated levels of nutrients associated with optimal brain development, although there are now diets available for senior cats that include nutrients to help slow the progression of age-related changes and prevent cognitive decline. Cognition diets for cats contain a greater portion of omega-3 fatty acids, especially docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) as well as eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), and usually feature a variety of antioxidants and other supporting nutrients thought to have positive effects on cognition.

Caesium superoxide is a chemical compound with the chemical formula CsO2. It consists of caesium cations Cs+ and superoxide anions O−2. It is an orange solid.















