
A screwdriver is a tool, manual or powered, used for turning screws.

A drill is a tool used for making round holes or driving fasteners. It is fitted with a bit, either a drill or driver chuck. Hand-operated types are dramatically decreasing in popularity and cordless battery-powered ones proliferating due to increased efficiency and ease of use.

Taps and dies are tools used to create screw threads, which is called threading. Many are cutting tools; others are forming tools. A tap is used to cut or form the female portion of the mating pair. A die is used to cut or form the male portion of the mating pair. The process of cutting or forming threads using a tap is called tapping, whereas the process using a die is called threading.

In the philosophy of thermal and statistical physics, the Brownian ratchet or Feynman–Smoluchowski ratchet is an apparent perpetual motion machine of the second kind, first analysed in 1912 as a thought experiment by Polish physicist Marian Smoluchowski. It was popularised by American Nobel laureate physicist Richard Feynman in a physics lecture at the California Institute of Technology on May 11, 1962, during his Messenger Lectures series The Character of Physical Law in Cornell University in 1964 and in his text The Feynman Lectures on Physics as an illustration of the laws of thermodynamics. The simple machine, consisting of a tiny paddle wheel and a ratchet, appears to be an example of a Maxwell's demon, able to extract mechanical work from random fluctuations (heat) in a system at thermal equilibrium, in violation of the second law of thermodynamics. Detailed analysis by Feynman and others showed why it cannot actually do this.

Drill bits are cutting tools used in a drill to remove material to create holes, almost always of circular cross-section. Drill bits come in many sizes and shapes and can create different kinds of holes in many different materials. In order to create holes drill bits are usually attached to a drill, which powers them to cut through the workpiece, typically by rotation. The drill will grasp the upper end of a bit called the shank in the chuck.
A reamer is a type of rotary cutting tool used in metalworking. Precision reamers are designed to enlarge the size of a previously formed hole by a small amount but with a high degree of accuracy to leave smooth sides. There are also non-precision reamers which are used for more basic enlargement of holes or for removing burrs. The process of enlarging the hole is called reaming. There are many different types of reamer and they may be designed for use as a hand tool or in a machine tool, such as a milling machine or drill press.
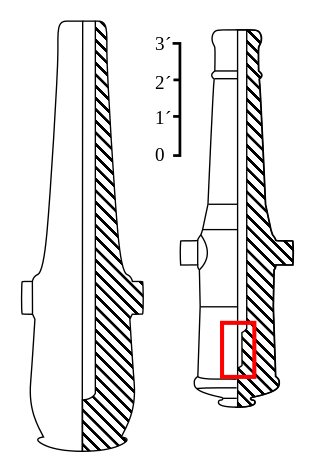
The Rodman gun is any of a series of American Civil War–era columbiads designed by Union artilleryman Thomas Jackson Rodman (1815–1871). The guns were designed to fire both shot and shell. These heavy guns were intended to be mounted in seacoast fortifications. They were built in 8-inch, 10-inch, 13-inch, 15-inch, and 20-inch bore. Other than size, the guns were all nearly identical in design, with a curving bottle shape, large flat cascabels with ratchets or sockets for the elevating mechanism. Rodman guns were true guns that did not have a howitzer-like powder chamber, as did many earlier columbiads. Rodman guns differed from all previous artillery because they were hollow cast, a new technology that Rodman developed that resulted in cast-iron guns that were much stronger than their predecessors.

Ratchet & Clank is a platform video game developed by Insomniac Games and published by Sony Computer Entertainment for the PlayStation 2 in 2002. It is the first game in the Ratchet & Clank series.
The shank is the end of a drill bit grasped by the chuck of a drill. The cutting edges of the drill bit contact the workpiece, and are connected via the shaft with the shank, which fits into the chuck. In many cases a general-purpose arrangement is used, such as a bit with cylindrical shaft and shank in a three-jaw chuck which grips a cylindrical shank tightly. Different shank and chuck combination can deliver improved performance, such as allowing higher torque, greater centering accuracy, or moving the bit independently of the chuck, with a hammer action.

In botany, an awn is either a hair- or bristle-like appendage on a larger structure, or in the case of the Asteraceae, a stiff needle-like element of the pappus.

A brace is a hand tool used with a bit to drill holes, usually in wood. Pressure is applied to the top while the handle is rotated. If the bit's lead and cutting spurs are both in good working order, the user should not have to apply any pressure other than for balance: the lead will pull the bit through the wood. Bits used to come in a variety of types but the more commonly used Ridgeway and Irwin-pattern bits also rely on a tip called a snail, which is a tapered threaded screw that pulls the bit forward.

Bevel gears are gears where the axes of the two shafts intersect and the tooth-bearing faces of the gears themselves are conically shaped. Bevel gears are most often mounted on shafts that are 90 degrees apart, but can be designed to work at other angles as well. The pitch surface of bevel gears is a cone, known as a pitch cone. Bevel gears change the axis of rotation of rotational power delivery and are widely used in mechanical settings.

A Persian, Persian roll or Pershing is a fried sweet roll or doughnut with a spiral shape similar to a cinnamon bun. It may be covered with a sugar glaze, iced or frosted, or sprinkled with sugar or cinnamon sugar.

Ratchet & Clank is a series of action-adventure platform and third-person shooter video games created and developed by Insomniac Games and published by Sony Interactive Entertainment for PlayStation consoles, such as PlayStation 2, PlayStation 3, PlayStation 4, and PlayStation 5, with the exclusion of Size Matters and Secret Agent Clank, which were developed by High Impact Games for the PlayStation Portable. The series was exclusive to Sony platforms until Rift Apart received a Windows port in 2023. Despite this however, the intellectual property is still owned by Sony Interactive Entertainment. An animated feature film adaptation was released on April 29, 2016.

Ratchet & Clank Future: A Crack in Time is a 2009 platform game developed by Insomniac Games and published by Sony Computer Entertainment for the PlayStation 3. It is the seventh main installment in the Ratchet & Clank series and the third in its Future saga. The game was released for the PlayStation 3 in North America on October 27, 2009, in Australia on November 5, 2009 and in Europe on November 6, 2009.

A pullback motor is a simple clockwork motor used in toy cars. A patent for them was granted to Bertrand 'Fred' Francis in 1952 as a keyless clockwork motor.

Milling is the process of machining using rotary cutters to remove material by advancing a cutter into a workpiece. This may be done by varying directions on one or several axes, cutter head speed, and pressure. Milling covers a wide variety of different operations and machines, on scales from small individual parts to large, heavy-duty gang milling operations. It is one of the most commonly used processes for machining custom parts to precise tolerances.
The North Brothers Manufacturing Company was an American manufacturer based in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania that specialized in the making of hand tools, small appliances and some specialized power tools. They were family owned and operated for over 60 years before being acquired by the Stanley Works in 1946. They are probably most well known for their line of tools, particularly the "Yankee" brand of ratcheting screwdrivers.

The trade name "Yankee" screwdriver was first marketed by North Brothers Manufacturing Company in ≈16 April 1895, with the No. ≠130 spiral ratchet screwdriver. Yankee soon became and still is a well-known name in automatic spiral ratchet screwdrivers, with several other models, and model improvements patented by North Bros. over a 40-year period.
Ratchet feminism emerged in the United States from hip hop culture in the early 2000s, largely as a critique of, and a response to, respectability politics. It is distinct from black feminism, womanism, and hip hop feminism. Ratchet feminism coopts the derogatory term (ratchet). Other terms used to describe this concept include ratchet womanism as used by Georgia Tech professor Joycelyn Wilson or ratchet radicalism used by Rutgers professor Brittney Cooper. Ratchet is an identity embraced by many millennials and Gen Z black women and girls. The idea of ratchetness as empowering, or of ratchet feminism, has been articulated by artists and celebrities like Nicki Minaj, City Girls, Amber Rose, and Junglepussy, scholars like Brittney Cooper and Mikki Kendall, and through events like Amber Rose's SlutWalk. Many view ratchet feminism as a form of female empowerment that doesn't adhere to respectability politics.
















