Coordinates: 59°08′58″N35°16′54″E / 59.14944°N 35.28167°E

A geographic coordinate system is a coordinate system that enables every location on Earth to be specified by a set of numbers, letters or symbols. The coordinates are often chosen such that one of the numbers represents a vertical position and two or three of the numbers represent a horizontal position; alternatively, a geographic position may be expressed in a combined three-dimensional Cartesian vector. A common choice of coordinates is latitude, longitude and elevation. To specify a location on a plane requires a map projection.
| Pes Russian: Песь | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Country | Russia |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Main source | Lake Rakitinskoye |
| River mouth | Chagodoshcha |
| Length | 145 km (90 mi) [1] |
| Discharge |
|
| Basin features | |
| Basin size | 2,730 square kilometres (1,050 sq mi) [1] |

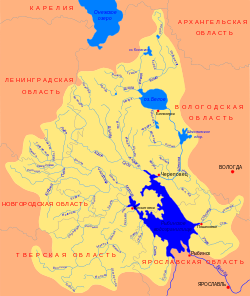
The Pes (Russian : Песь) is a river in Khvoyninsky District of Novgorod Oblast and in Chagodoshchensky District of Vologda Oblast in Russia. It is a right tributary of the Chagodoshcha River. It is 145 kilometres (90 mi) long, and the area of its basin 2,730 square kilometres (1,050 sq mi). The principal tributary of the Pes is the Rattsa River (left). The urban-type settlements of Khvoynaya and Sazonovo are located on the banks of the Pes.

Russian is an East Slavic language, which is official in the Russian Federation, Belarus, Kazakhstan and Kyrgyzstan, as well as being widely used throughout Eastern Europe, the Baltic states, the Caucasus and Central Asia. It was the de facto language of the Soviet Union until its dissolution on 25 December 1991. Although nearly three decades have passed since the breakup of the Soviet Union, Russian is used in official capacity or in public life in all the post-Soviet nation-states, as well as in Israel and Mongolia.

Khvoyninsky District is an administrative and municipal district (raion), one of the twenty-one in Novgorod Oblast, Russia. It is located in the northeast of the oblast and borders with Boksitogorsky District of Leningrad Oblast in the north, Chagodoshchensky District of Vologda Oblast in the northeast, Pestovsky District in the southeast, Moshenskoy District in the south, Borovichsky District in the southwest, and with Lyubytinsky District in the west. The area of the district is 3,200 square kilometers (1,200 sq mi). Its administrative center is the urban locality of Khvoynaya. Population: 15,552 (2010 Census); 17,173 ; 19,649 (1989 Census). The population of Khvoynaya accounts for 41.1% of the district's total population.

Novgorod Oblast is a federal subject of Russia. Its administrative center is the city of Veliky Novgorod. Some of the oldest Russian cities, including Veliky Novgorod and Staraya Russa, are located in the oblast. The historic monuments of Veliky Novgorod and surroundings have been declared a UNESCO World Heritage Site. Population: 634,111.
The source of the Pes is Lake Rakitinskoye in the west of Khvoyninsky District. The Medveda is the principal tributary of Lake Rakitinskoye. The Pes flows in the eastern direction, passes the settlement of Khvoynaya, accepts the Kushavera from the right, enters Vologda Oblast, and turns northeast. In the settlement of Sazonovo, it accepts the Rattsa from the left. The mouth of the Pes is close to the urban-type settlement of Chagoda.
Chagoda is an urban locality and the administrative center of Chagodoshchensky District of Vologda Oblast, Russia, situated on the Chagodoshcha River 326 kilometers (203 mi) from Vologda. Municipally, it is incorporated as Chagoda Urban Settlement, one of the two urban settlements in the district. Population: 6,920 (2010 Census); 7,432 (2002 Census); 8,171 (1989 Census).
The river basin of the Pes comprises the major part (western and central) of Khvoyninsky District, some areas in the east of Lyubytinsky District of Novgorod Oblast, and the southwest of Chagodoshchensky district. In particular, it includes many lakes located in the southwest of Khvoyninsky District.

Lyubytinsky District is an administrative and municipal district (raion), one of the twenty-one in Novgorod Oblast, Russia. It is located in the northeast of the oblast and borders with Tikhvinsky District of Leningrad Oblast in the north, Boksitogorsky District of Leningrad Oblast in the northeast, Khvoyninsky District in the east, Borovichsky District in the southeast, Okulovsky District in the southwest, Malovishersky District in the west, and with Kirishsky District of Leningrad Oblast in the northwest. The area of the district is 4,500 square kilometers (1,700 sq mi). Its administrative center is the urban locality of Lyubytino. Population: 9,744 (2010 Census); 12,432 ; 15,263 (1989 Census). The population of Lyubytino accounts for 28.8% of the district's total population.
Until the 1990s, the Pes was used for timber rafting. [1]

Timber rafting is a log transportation method in which logs are tied together into rafts and drifted or pulled across a water body or down a river. It is arguably the second cheapest method of transportation of timber, next after log driving. Both methods may be referred to as timber floating.