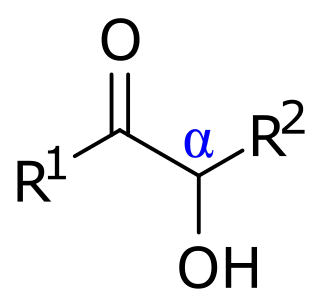In organic chemistry, phenols, sometimes called phenolics, are a class of chemical compounds consisting of one or more hydroxyl groups (−OH) bonded directly to an aromatic hydrocarbon group. The simplest is phenol, C
6H
5OH. Phenolic compounds are classified as simple phenols or polyphenols based on the number of phenol units in the molecule.
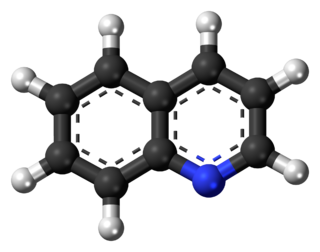
Quinoline is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound with the chemical formula C9H7N. It is a colorless hygroscopic liquid with a strong odor. Aged samples, especially if exposed to light, become yellow and later brown. Quinoline is only slightly soluble in cold water but dissolves readily in hot water and most organic solvents. Quinoline itself has few applications, but many of its derivatives are useful in diverse applications. A prominent example is quinine, an alkaloid found in plants. Over 200 biologically active quinoline and quinazoline alkaloids are identified. 4-Hydroxy-2-alkylquinolines (HAQs) are involved in antibiotic resistance.

The aldol reaction is a reaction in organic chemistry that combines two carbonyl compounds to form a new β-hydroxy carbonyl compound. Its simplest form might involve the nucleophilic addition of an enolized ketone to another:

Isatin, also known as tribulin, is an organic compound derived from indole with formula C8H5NO2. The compound was first obtained by Otto Linné Erdman and Auguste Laurent in 1840 as a product from the oxidation of indigo dye by nitric acid and chromic acids.
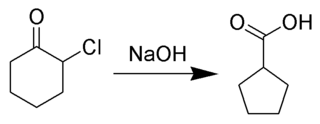
The Favorskii rearrangement is principally a rearrangement of cyclopropanones and α-halo ketones that leads to carboxylic acid derivatives. In the case of cyclic α-halo ketones, the Favorskii rearrangement constitutes a ring contraction. This rearrangement takes place in the presence of a base, sometimes hydroxide, to yield a carboxylic acid, but usually either an alkoxide base or an amine to yield an ester or an amide, respectively. α,α'-Dihaloketones eliminate HX under the reaction conditions to give α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds.Note that trihalomethyl ketone substrates will result in haloform and carboxylate formation via the haloform reaction instead.
The Friedländer synthesis is a chemical reaction of 2-aminobenzaldehydes with ketones to form quinoline derivatives. It is named after German chemist Paul Friedländer (1857–1923).
The Niementowski quinoline synthesis is the chemical reaction of anthranilic acids and ketones to form γ-hydroxyquinoline derivatives.
The Stollé synthesis is a series of chemical reactions that produce oxindoles from anilines and α-haloacid chlorides.
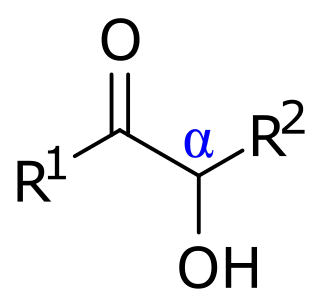
In organic chemistry, acyloins or α-hydroxy ketones are a class of organic compounds of the general form R−C(=O)−CR'(OH)−R", composed of a hydroxy group adjacent to a ketone group. The name acyloin is derived from the fact that they are formally derived from reductive coupling of carboxylic acyl groups. They are one of the two main classes of hydroxy ketones, distinguished by the position of the hydroxy group relative to the ketone; in this form, the hydroxy is on the alpha carbon, explaining the secondary name of α-hydroxy ketone.

The Doebner–Miller reaction is the organic reaction of an aniline with α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds to form quinolines.

The Wolff rearrangement is a reaction in organic chemistry in which an α-diazocarbonyl compound is converted into a ketene by loss of dinitrogen with accompanying 1,2-rearrangement. The Wolff rearrangement yields a ketene as an intermediate product, which can undergo nucleophilic attack with weakly acidic nucleophiles such as water, alcohols, and amines, to generate carboxylic acid derivatives or undergo [2+2] cycloaddition reactions to form four-membered rings. The mechanism of the Wolff rearrangement has been the subject of debate since its first use. No single mechanism sufficiently describes the reaction, and there are often competing concerted and carbene-mediated pathways; for simplicity, only the textbook, concerted mechanism is shown below. The reaction was discovered by Ludwig Wolff in 1902. The Wolff rearrangement has great synthetic utility due to the accessibility of α-diazocarbonyl compounds, variety of reactions from the ketene intermediate, and stereochemical retention of the migrating group. However, the Wolff rearrangement has limitations due to the highly reactive nature of α-diazocarbonyl compounds, which can undergo a variety of competing reactions.

In organic chemistry, cyclopropanation refers to any chemical process which generates cyclopropane rings. It is an important process in modern chemistry as many useful compounds bear this motif; for example pyrethroid insecticides and a number of quinolone antibiotics. However, the high ring strain present in cyclopropanes makes them challenging to produce and generally requires the use of highly reactive species, such as carbenes, ylids and carbanions. Many of the reactions proceed in a cheletropic manner.
The Bucherer reaction in organic chemistry is the reversible conversion of a naphthol to a naphthylamine in the presence of ammonia and sodium bisulfite. The reaction is widely used in the synthesis of dye precursors aminonaphthalenesulfonic acids.
The Balz–Schiemann reaction is a chemical reaction in which a primary aromatic amine is transformed to an aryl fluoride via a diazonium tetrafluoroborate intermediate. This reaction is a traditional route to fluorobenzene and some related derivatives, including 4-fluorobenzoic acid.
The Combes quinoline synthesis is a chemical reaction, which was first reported by Combes in 1888. Further studies and reviews of the Combes quinoline synthesis and its variations have been published by Alyamkina et al., Bergstrom and Franklin, Born, and Johnson and Mathews.
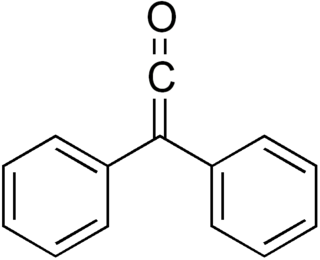
Diphenylketene is a chemical substance of the ketene family. Diphenylketene, like most stable disubstituted ketenes, is a red-orange oil at room temperature and pressure. Due to the successive double bonds in the ketene structure R1R2C=C=O, diphenyl ketene is a heterocumulene. The most important reaction of diphenyl ketene is the [2+2] cycloaddition at C-C, C-N, C-O, and C-S multiple bonds.

In organic chemistry, organocatalysis is a form of catalysis in which the rate of a chemical reaction is increased by an organic catalyst. This "organocatalyst" consists of carbon, hydrogen, sulfur and other nonmetal elements found in organic compounds. Because of their similarity in composition and description, they are often mistaken as a misnomer for enzymes due to their comparable effects on reaction rates and forms of catalysis involved.

The Doebner reaction is the chemical reaction of an aniline with an aldehyde and pyruvic acid to form quinoline-4-carboxylic acids.

Indole is an organic compound with the formula C6H4CCNH3. Indole is classified as an aromatic heterocycle. It has a bicyclic structure, consisting of a six-membered benzene ring fused to a five-membered pyrrole ring. Indoles are derivatives of indole where one or more of the hydrogen atoms have been replaced by substituent groups. Indoles are widely distributed in nature, most notably as amino acid tryptophan and neurotransmitter serotonin.
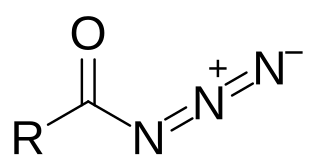
Acyl azides are carboxylic acid derivatives with the general formula RCON3. These compounds, which are a subclass of organic azides, are generally colorless.