
Green building refers to both a structure and the application of processes that are environmentally responsible and resource-efficient throughout a building's life-cycle: from planning to design, construction, operation, maintenance, renovation, and demolition. This requires close cooperation of the contractor, the architects, the engineers, and the client at all project stages. The Green Building practice expands and complements the classical building design concerns of economy, utility, durability, and comfort. Green building also refers to saving resources to the maximum extent, including energy saving, land saving, water saving, material saving, etc., during the whole life cycle of the building, protecting the environment and reducing pollution, providing people with healthy, comfortable and efficient use of space, and being in harmony with nature Buildings that live in harmony. Green building technology focuses on low consumption, high efficiency, economy, environmental protection, integration and optimization.’
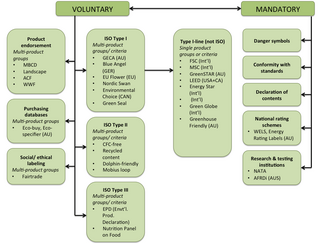
Ecolabels and Green Stickers are labeling systems for food and consumer products. The use of ecolabels is voluntary, whereas green stickers are mandated by law; for example, in North America major appliances and automobiles use Energy Star. They are a form of sustainability measurement directed at consumers, intended to make it easy to take environmental concerns into account when shopping. Some labels quantify pollution or energy consumption by way of index scores or units of measurement, while others assert compliance with a set of practices or minimum requirements for sustainability or reduction of harm to the environment. Many ecolabels are focused on minimising the negative ecological impacts of primary production or resource extraction in a given sector or commodity through a set of good practices that are captured in a sustainability standard. Through a verification process, usually referred to as "certification", a farm, forest, fishery, or mine can show that it complies with a standard and earn the right to sell its products as certified through the supply chain, often resulting in a consumer-facing ecolabel.

Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design (LEED) is a green building certification program used worldwide. Developed by the non-profit U.S. Green Building Council (USGBC), it includes a set of rating systems for the design, construction, operation, and maintenance of green buildings, homes, and neighborhoods, which aims to help building owners and operators be environmentally responsible and use resources efficiently.

The U.S. Green Building Council (USGBC), co-founded by Mike Italiano, David Gottfried and Rick Fedrizzi in 1993, is a private 501(c)3, membership-based non-profit organization that promotes sustainability in building design, construction, and operation. USGBC is best known for its development of the Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design (LEED) green building rating systems and its annual Greenbuild International Conference and Expo, the world’s largest conference and expo dedicated to green building. USGBC was one of eight national councils that helped found the World Green Building Council (WorldGBC). The current president and CEO is Peter Templeton.

The Canada Green Building Council (CaGBC) was created in 2003 to further the expansion of green building in Canada. Prior to the formation of the Council, Canada had participated in the United States Green Building Council (USGBC) through British Columbia's membership in the USGBC's Cascadia Chapter.
Design impact measures are measures used to qualify projects for various environmental rating systems and to guide both design and regulatory decisions from beginning to end. Some systems, like the greenhouse gas inventory, are required globally for all business decisions. Some are project-specific, like the LEED point rating system which is used only for its own ratings, and its qualifications do not correspond to much beyond physical measurements. Others like the Athena life-cycle impact assessment tool attempt to add up all the kinds of measurable impacts of all parts of a building throughout its life and are quite rigorous and complex.
Green Star is a voluntary sustainability rating system for buildings in Australia. It was launched in 2003 by the Green Building Council of Australia (GBCA).
Enermodal Engineering was an engineering consulting firm that specialized in the creation of green buildings and communities. It provided LEED services for larger-scale green buildings in Canada. Enermodal designed several low-energy building projects in Canada and the USA. In 2010, Enermodal was acquired by MMM, which subsequently was acquired by WSP (2016).
This article provides examples of green building programs in the United States. These programs span the public, private, and non-profit sectors, and all have the goal of increasing energy efficiency and the sustainability of the built environment.
Green rating or certification is used to indicate the level of environmental friendliness for real estate properties.
BREEAM, first published by the Building Research Establishment (BRE) in 1990, is the world's longest established method of assessing, rating, and certifying the sustainability of buildings. More than 550,000 buildings have been 'BREEAM-certified' and over two million are registered for certification in more than 50 countries worldwide. BREEAM also has a tool which focuses on neighbourhood development.
Environmentally sustainable design is the philosophy of designing physical objects, the built environment, and services to comply with the principles of ecological sustainability and also aimed at improving the health and comfortability of occupants in a building. Sustainable design seeks to reduce negative impacts on the environment, the health and well-being of building occupants, thereby improving building performance. The basic objectives of sustainability are to reduce the consumption of non-renewable resources, minimize waste, and create healthy, productive environments.
LEED for Neighborhood Development (LEED-ND), where "LEED" stands for Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design, is a United States-based rating system that integrates the principles of smart growth, urbanism, and green building into a national system for neighborhood design. LEED certification provides independent, third-party verification that a development's location and design meet accepted high levels of environmentally responsible, sustainable development.
Qatar Sustainability Assessment System (QSAS) is a green building certification system developed for the State of Qatar. The primary objective of Qatar Sustainability Assessment System [QSAS] is to create a sustainable built environment that minimizes ecological impact while addressing the specific regional needs and environment of Qatar.
The World Green Building Council (WorldGBC) is a non-profit organisation and global network of national Green Building Councils (GBCs). It has member councils in over 70 countries worldwide, which collectively have 49,000 members.
Bangladesh is one of the most vulnerable nations in the world due to climate change. As the ninth most populous country and twelfth most densely populated countries in the world, its rising population and limited land space have put tremendous strains on the urban ecosystem. The capital of Dhaka itself underwent severe transformations in recent years to catch up the increased rate of urbanisation. This change was paralleled by a boom in the real estate, construction and housing industry. According to United Nations Population Fund (UNFPA), Dhaka is one of the most polluted cities in the world.
Green Building Initiative (GBI) is a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization that owns and administers the Green Globes green building assessment and certification in the United States and Canada. It was established in 2004 and is headquartered in Portland, Oregon.
Net Park is a 38-story green and sustainable corporate tower located in Bonifacio Global City, Metro Manila, Philippines. It is part of the office space portfolio of the Net Group, a developer who pioneered the concept of IT office building in the Philippines. The building will be part of the Net Metropolis 5th Ave, a mixed-use development considered as the nation’s first certified green project in Taguig.
The Global Sustainability Assessment System (GSAS) [Originally QSAS] is the first performance-based system in the Middle East and North Africa (MENA) region, developed for assessing and rating buildings and infrastructure for their sustainability impacts. In 2016, FIFA officially endorsed GSAS as the sustainability assessment system for Qatar's eight stadiums set to host the 2022 FIFA World Cup. The primary objective of GSAS is to create a sustainable built environment that minimizes ecological impact and reduces resources consumption while addressing the local needs and environmental conditions specific to the region. GSAS adopts an integrated lifecycle approach for the assessment of the built environment including design, construction and operation phases.

Green building certification systems are a set of rating systems and tools that are used to assess a building or a construction project's performance from a sustainability and environmental perspective. Such ratings aim to improve the overall quality of buildings and infrastructures, integrate a life cycle approach in its design and construction, and promote the fulfillment of the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals by the construction industry. Buildings that have been assessed and are deemed to meet a certain level of performance and quality, receive a certificate proving this achievement.





