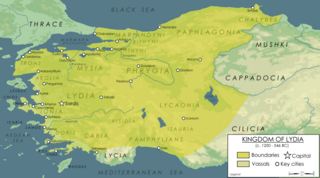
Lydia was an Iron Age kingdom of western Asia Minor located generally east of ancient Ionia in the modern western Turkish provinces of Uşak, Manisa and inland Izmir. The ethnic group inhabiting this kingdom are known as the Lydians, and their language, known as Lydian, was a member of the Anatolian branch of the Indo-European language family. The capital of Lydia was Sardis.

Tindari, ancient Tyndaris or Tyndarion, is a small town, frazione in the comune of Patti and a Latin Catholic titular see.

Cleopatra VII Thea Philopator was Queen of the Ptolemaic Kingdom of Egypt from 51 to 30 BC, and its last active ruler. A member of the Ptolemaic dynasty, she was a descendant of its founder Ptolemy I Soter, a Macedonian Greek general and companion of Alexander the Great. After the death of Cleopatra, Egypt became a province of the Roman Empire, marking the end of the last Hellenistic-period state in the Mediterranean and of the age that had lasted since the reign of Alexander. Her first language was Koine Greek, and she was the only known Ptolemaic ruler to learn the Egyptian language.

Ptolemy of Mauretania was the last Roman client king and ruler of Mauretania for Rome. He was the son of Juba II, the king of Numidia and a member of the Berber Massyles tribe, as well as a descendant of the Ptolemaic dynasty via his mother Cleopatra Selene II.

Berenice II Euergetis was queen regnant of Cyrenaica from 258 to 246 BCE and co-regent queen of Ptolemaic Egypt from 246 to 222 BCE as the wife of Ptolemy III.

Taormina is a comune (municipality) in the Metropolitan City of Messina, on the east coast of the island of Sicily, Italy. Taormina has been a tourist destination since the 19th century. Its beaches on the Ionian sea, including that of Isola Bella, are accessible via an aerial tramway built in 1992, and via highways from Messina in the north and Catania in the south. On 26–27 May 2017 Taormina hosted the 43rd G7 summit.

Basileus is a Greek term and title that has signified various types of monarchs in history. In the English-speaking world it is perhaps most widely understood to mean "monarch", referring to either a "king" or an "emperor" and also by bishops of the Eastern Orthodox Church and Eastern Catholic Churches. The title was used by sovereigns and other persons of authority in ancient Greece, the Byzantine emperors, and the kings of modern Greece.

Enna, known from the Middle Ages until 1926 as Castrogiovanni, is a city and comune located roughly at the center of Sicily, southern Italy, in the province of Enna, towering above the surrounding countryside. It has earned the nicknames belvedere and ombelico ("navel") of Sicily.

Phraates V, also known by the diminutive version of his name, Phraataces, was the King of Kings of the Parthian Empire from 2 BC to 4 AD. He was the younger son of Phraates IV and Musa, who ruled with him.

Musa, also known as Thea Musa, was a ruling queen of the Parthian Empire from 2 BC to 4 AD. Originally an Italian slave-girl, she was given as a gift to the Parthian monarch Phraates IV by the Roman Emperor Augustus. She quickly became queen and a favourite of Phraates IV, giving birth to Phraataces. In 2 BC, she had Phraates IV poisoned and made herself, along with Phraates V, the co-rulers of the empire. Their reign was short-lived; they were forced to flee to Rome after being deposed by the Parthian nobility, who crowned Orodes III as king.

Rajuvula was an Indo-Scythian Great Satrap (Mahākṣatrapa), one of the "Northern Satraps" who ruled in the area of Mathura in the northern Indian Subcontinent in the years around 10 CE. The Mathura lion capital was consecrated under the reign of Rajuvula. In central India, the Indo-Scythians had conquered the area of Mathura from Indian kings around 60 BCE. Some of their satraps were Hagamasha and Hagana, who were in turn followed by Rajuvula.
Mithridates IV of Pontus, sometimes known by his full name Mithridates Philopator Philadelphus, was a prince and sixth ruler of the Kingdom of Pontus.

Naxos or Naxus was an ancient Greek city of Magna Graecia, presently situated in modern Giardini Naxos near Taormina on the east coast of Sicily.

Netum or Neetum, was a considerable ancient town in the south of Sicily, near the sources of the little river Asinarus, and about 34 km southwest of Syracuse. Its current site is at the località of Noto Antica, in the modern comune of Noto.
Pythodoris of Pontus was a Roman client queen of Pontus, the Bosporan Kingdom, Cilicia, and Cappadocia.
Dynamis, nicknamed Philoromaios, was a Roman client queen of the Bosporan Kingdom during the Late Roman Republic and part of the reign of Augustus, the first Roman Emperor. Dynamis is an ancient Greek name which means the “powerful one”. She was a monarch of Iranian and Greek Macedonian ancestry. She was the daughter of King Pharnaces II of Pontus and his Sarmatian wife. She had an older brother called Darius and a younger brother called Arsaces. Her paternal grandparents had been the monarchs of the Kingdom of Pontus, Mithridates VI of Pontus and his first wife Laodice, who was also his sister. Dynamis married three times. Her husbands were Asander, a certain Scribonius and Polemon I of Pontus. According to Rostovtzeff, she also had a fourth husband, Aspurgos.

The ancient theatre of Taormina is an ancient Greek theatre in Taormina, Sicily, built in the third century BC.

The Greek theatre of Syracuse lies on the south slopes of the Temenite hill, overlooking the modern city of Syracuse in southeastern Sicily, Italy. It was first built in the 5th century BC, rebuilt in the 3rd century BC and renovated again in the Roman period. Today, it is a part of the Unesco World Heritage Site of "Syracuse and the Rocky Necropolis of Pantalica".
Apollonos Hieron was an ancient city of Lydia.

Taormina dates to around 396 BC after Dionysius I of Syracuse destroyed nearby Naxos in 403 BC and the Siculi formed a new settlement on the nearby Mount Taurus which gradually grew up into the city of Tauromenium.
















