
The octet rule is a chemical rule of thumb that reflects the theory that main-group elements tend to bond in such a way that each atom has eight electrons in its valence shell, giving it the same electronic configuration as a noble gas. The rule is especially applicable to carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, and the halogens; although more generally the rule is applicable for the s-block and p-block of the periodic table. Other rules exist for other elements, such as the duplet rule for hydrogen and helium, and the 18-electron rule for transition metals.

A chemical structure of a molecule is a spatial arrangement of its atoms and their chemical bonds. Its determination includes a chemist's specifying the molecular geometry and, when feasible and necessary, the electronic structure of the target molecule or other solid. Molecular geometry refers to the spatial arrangement of atoms in a molecule and the chemical bonds that hold the atoms together and can be represented using structural formulae and by molecular models; complete electronic structure descriptions include specifying the occupation of a molecule's molecular orbitals. Structure determination can be applied to a range of targets from very simple molecules to very complex ones.
In chemistry, a hypervalent molecule is a molecule that contains one or more main group elements apparently bearing more than eight electrons in their valence shells. Phosphorus pentachloride, sulfur hexafluoride, chlorine trifluoride, the chlorite ion in chlorous acid and the triiodide ion are examples of hypervalent molecules.

Valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR) theory is a model used in chemistry to predict the geometry of individual molecules from the number of electron pairs surrounding their central atoms. It is also named the Gillespie-Nyholm theory after its two main developers, Ronald Gillespie and Ronald Nyholm.
In chemistry, an interhalogen compound is a molecule which contains two or more different halogen atoms and no atoms of elements from any other group.
In chemistry, the valence or valency of an atom is a measure of its combining capacity with other atoms when it forms chemical compounds or molecules. Valence is generally understood to be the number of chemical bonds that each atom of a given chemical element typically forms. Double bonds are considered to be two bonds, triple bonds to be three, quadruple bonds to be four, quintuple bonds to be five and sextuple bonds to be six. In most compounds, the valence of hydrogen is 1, of oxygen is 2, of nitrogen is 3, and of carbon is 4. Valence is not to be confused with the related concepts of the coordination number, the oxidation state, or the number of valence electrons for a given atom.

Phosphorus pentachloride is the chemical compound with the formula PCl5. It is one of the most important phosphorus chlorides/oxychlorides, others being PCl3 and POCl3. PCl5 finds use as a chlorinating reagent. It is a colourless, water-sensitive solid, although commercial samples can be yellowish and contaminated with hydrogen chloride.
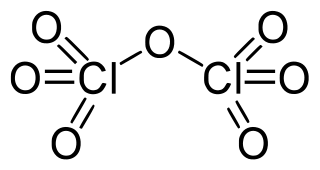
Dichlorine heptoxide is the chemical compound with the formula Cl2O7. This chlorine oxide is the anhydride of perchloric acid. It is produced by the careful distillation of perchloric acid in the presence of the dehydrating agent phosphorus pentoxide:

In chemistry, a trigonal bipyramid formation is a molecular geometry with one atom at the center and 5 more atoms at the corners of a triangular bipyramid. This is one geometry for which the bond angles surrounding the central atom are not identical, because there is no geometrical arrangement with five terminal atoms in equivalent positions. Examples of this molecular geometry are phosphorus pentafluoride, and phosphorus pentachloride in the gas phase.
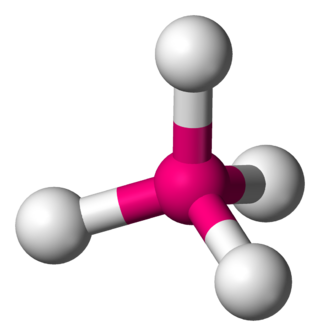
In a tetrahedral molecular geometry, a central atom is located at the center with four substituents that are located at the corners of a tetrahedron. The bond angles are cos−1(−1⁄3) = 109.4712206...° ≈ 109.5° when all four substituents are the same, as in methane as well as its heavier analogues. Methane and other perfectly symmetrical tetrahedral molecules belong to point group Td, but most tetrahedral molecules have lower symmetry. Tetrahedral molecules can be chiral.

Thiophosphoryl chloride is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula PSCl3. It is a colorless pungent smelling liquid that fumes in air. It is synthesized from phosphorus chloride and used to thiophosphorylate organic compounds, such as to produce insecticides.

In chemistry, isomers are molecules or polyatomic ions with identical molecular formula – that is, the same number of atoms of each element – but distinct arrangements of atoms in space. Isomerism refers to the existence or possibility of isomers.

Thionyl tetrafluoride, also known as sulfur tetrafluoride oxide, is an inorganic compound with the formula SOF4. It is a colorless gas.
Boron monofluoride or fluoroborylene is a chemical compound with the formula BF, one atom of boron and one of fluorine. It is an unstable gas, but it is a stable ligand on transition metals, in the same way as carbon monoxide. It is a subhalide, containing fewer than the normal number of fluorine atoms, compared with boron trifluoride. It can also be called a borylene, as it contains boron with two unshared electrons. BF is isoelectronic with carbon monoxide and dinitrogen; each molecule has 14 electrons.
In chemistry, molecular oxohalides (oxyhalides) are a group of chemical compounds in which both oxygen and halogen atoms are attached to another chemical element A in a single molecule. They have the general formula AOmXn, where X is a halogen. Known oxohalides have fluorine (F), chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br), and/or iodine (I) in their molecules. The element A may be a main group element, a transition element, a rare earth element or an actinide. The term oxohalide, or oxyhalide, may also refer to minerals and other crystalline substances with the same overall chemical formula, but having an ionic structure.

Thiophosphoryl fluoride is an inorganic molecular gas with formula PSF3 containing phosphorus, sulfur and fluorine. It spontaneously ignites in air and burns with a cool flame. The discoverers were able to have flames around their hands without discomfort, and called it "probably one of the coldest flames known". The gas was discovered in 1888.
Fluorine forms a great variety of chemical compounds, within which it always adopts an oxidation state of −1. With other atoms, fluorine forms either polar covalent bonds or ionic bonds. Most frequently, covalent bonds involving fluorine atoms are single bonds, although at least two examples of a higher order bond exist. Fluoride may act as a bridging ligand between two metals in some complex molecules. Molecules containing fluorine may also exhibit hydrogen bonding. Fluorine's chemistry includes inorganic compounds formed with hydrogen, metals, nonmetals, and even noble gases; as well as a diverse set of organic compounds. For many elements the highest known oxidation state can be achieved in a fluoride. For some elements this is achieved exclusively in a fluoride, for others exclusively in an oxide; and for still others the highest oxidation states of oxides and fluorides are always equal.
Chlorotrifluorosilane is an inorganic gaseous compound with formula SiClF3 composed of silicon, fluorine and chlorine. It is a silane that substitutes hydrogen with fluorine and chlorine atoms.

Chlorine oxide trifluoride or chlorine trifluoride oxide is a corrosive liquid molecular compound with formula ClOF3. It was developed secretly as a rocket fuel oxidiser.

Phosphorus monoxide is an unstable radical inorganic compound with molecular formula PO.













