
Raman spectroscopy is a spectroscopic technique typically used to determine vibrational modes of molecules, although rotational and other low-frequency modes of systems may also be observed. Raman spectroscopy is commonly used in chemistry to provide a structural fingerprint by which molecules can be identified.
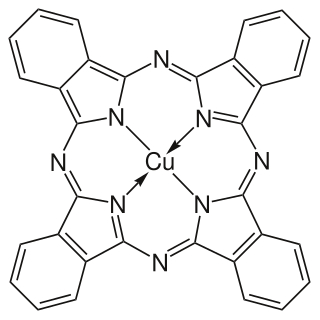
Copper phthalocyanine (CuPc), also called phthalocyanine blue, phthalo blue and many other names, is a bright, crystalline, synthetic blue pigment from the group of dyes based on phthalocyanines. Its brilliant blue is frequently used in paints and dyes. It is highly valued for its superior properties such as light fastness, tinting strength, covering power and resistance to the effects of alkalis and acids. It has the appearance of a blue powder, insoluble in most solvents including water.

In chemistry, charge-transfer (CT) complex, or electron donor-acceptor complex, describes a type of supramolecular assembly of two or more molecules or ions. The assembly consists of two molecules that self-attract through electrostatic forces, i.e., one has at least partial negative charge and the partner has partial positive charge, referred to respectively as the electron acceptor and electron donor. In some cases, the degree of charge transfer is "complete", such that the CT complex can be classified as a salt. In other cases, the charge-transfer association is weak, and the interaction can be disrupted easily by polar solvents.

Resonance Raman spectroscopy is a variant of Raman spectroscopy in which the incident photon energy is close in energy to an electronic transition of a compound or material under examination. This similarity in energy (resonance) leads to greatly increased intensity of the Raman scattering of certain vibrational modes, compared to ordinary Raman spectroscopy.

Quinacridone is an organic compound used as a pigment. Numerous derivatives constitute the quinacridone pigment family, which finds extensive use in industrial colorant applications such as robust outdoor paints, inkjet printer ink, tattoo inks, artists' watercolor paints, and color laser printer toner. As pigments, the quinacridones are insoluble. The development of this family of pigments supplanted the alizarin dyes.

The cyanate ion is an anion with the chemical formula OCN−. It is a resonance of three forms: [O−−C≡N] (61%) ↔ [O=C=N−] (30%) ↔ [O+≡C−N2−] (4%).

Azo dyes are organic compounds bearing the functional group R−N=N−R′, in which R and R′ are usually aryl and substituted aryl groups. They are a commercially important family of azo compounds, i.e. compounds containing the C−N=N−C linkage. Azo dyes are synthetic dyes and do not occur naturally. Most azo dyes contain only one azo group but there are some that contain two or three azo groups, called "diazo dyes" and "triazo dyes" respectively. Azo dyes comprise 60–70% of all dyes used in food and textile industries. Azo dyes are widely used to treat textiles, leather articles, and some foods. Chemically related derivatives of azo dyes include azo pigments, which are insoluble in water and other solvents.

Copper(II) acetate, also referred to as cupric acetate, is the chemical compound with the formula Cu(OAc)2 where AcO− is acetate (CH
3CO−
2). The hydrated derivative, Cu2(OAc)4(H2O)2, which contains one molecule of water for each copper atom, is available commercially. Anhydrous copper(II) acetate is a dark green crystalline solid, whereas Cu2(OAc)4(H2O)2 is more bluish-green. Since ancient times, copper acetates of some form have been used as fungicides and green pigments. Today, copper acetates are used as reagents for the synthesis of various inorganic and organic compounds. Copper acetate, like all copper compounds, emits a blue-green glow in a flame.
In crystallography, polymorphism is the phenomenon where a compound or element can crystallize into more than one crystal structure.

2-Pyridone is an organic compound with the formula C
5H
4NH(O). It is a colourless solid. It is well known to form hydrogen bonded dimers and it is also a classic case of a compound that exists as tautomers.
There are three sets of Indium halides, the trihalides, the monohalides, and several intermediate halides. In the monohalides the oxidation state of indium is +1 and their proper names are indium(I) fluoride, indium(I) chloride, indium(I) bromide and indium(I) iodide.

Tattoo inks consist of pigments combined with a carrier, used in the process of tattooing to create a tattoo in the skin. These inks are also used for permanent makeup, a form of tattoo.

Disiloxane has the chemical formula Si
2H
6O. It is the simplest known siloxane with hydrogen only R groups. The molecule contains six equivalent Si−H bonds and two equivalent Si−O bonds. Disiloxane exists as a colorless, pungent gas under standard conditions. However, it is generally safe for human use as evidence in its widespread use in cosmetics. It is also commonly known as disilyl ether, disilyl oxide, and perhydrodisiloxane

Dicopper chloride trihydroxide is the compound with chemical formula Cu2(OH)3Cl. It is often referred to as tribasic copper chloride (TBCC), copper trihydroxyl chloride or copper hydroxychloride. This greenish substance is encountered as the minerals atacamite, paratacamite, and botallackite. Similar materials are assigned to green solids formed upon corrosion of various copper objectss.

Monofluorophosphate is an anion with the formula PO3F2−, which is a phosphate group with one oxygen atom substituted with a fluoride atom. The charge of the ion is −2. The ion resembles sulfate in size, shape and charge, and can thus form compounds with the same structure as sulfates. These include Tutton's salts and langbeinites. The most well-known compound of monofluorophosphate is sodium monofluorophosphate, commonly used in toothpaste.

The cyanonickelates are a class of chemical compound containing anions consisting of nickel atoms, and cyanide groups. The most important of these are the tetracyanonickelates containing four cyanide groups per nickel. The tetracyanonickelates contain the [Ni(CN)4]2− anion. This can exist in solution or in solid salts. The ion has cyanide groups arranged in a square around the central nickel ion. The symmetry of the ion is D4h. The distance from the nickel atom to the carbon is 1.87 Å, and the carbon-nitrogen distance is 1.16 Å. In their crystals, the tetracyanonickelate(II) anions are often arranged in a columnar structure (e.g. in K2[Ni(CN)4]). Tetracyanonickelate(II) can be oxidised electrochemically in solution to yield tetracyanonickelate(III) [Ni(CN)4]−. [Ni(CN)4]− is unstable and Ni(III) oxidises the cyanide to cyanate OCN−. Tetracyanonickelate(III) can add two more cyanide groups to form hexacyanonickelate(III).
The phosphate sulfates are mixed anion compounds containing both phosphate and sulfate ions. Related compounds include the arsenate sulfates, phosphate selenates, and arsenate selenates.

Toluidine red is an organic compound with the formula C10H6(OH)(N2C6H3 CH3). A dark red solid, the compound is classified as a azo dye consisting of a 2-naphthol group linked to a 2-nitro-4-methylphenyl substituent. Toluidine red is a traditional pigment, found in oil paints. Although once popular, it suffers as a pigment owing to "insufficient lightfastness and bleeding when incorporated into a paint system."

Pigment Orange 34 is an organic compound and an azo compound. It is a commercial orange pigment, i.e. an insoluble colorant. It is also classified as a diarylide pigment, being derived from 3,3'-dichlorobenzidine. It is closely related to Pigment Orange 13, wherein the two tolyl groups are replaced by phenyl groups.

Pigment Yellow 74 is an azo dye and classified as an arylide yellow. It is an intensely yellow-green solid..

















