
A fossil is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in amber, hair, petrified wood and DNA remnants. The totality of fossils is known as the fossil record.

Stromatolites or stromatoliths are layered sedimentary formations (microbialite) that are created mainly by photosynthetic microorganisms such as cyanobacteria, sulfate-reducing bacteria, and Pseudomonadota. These microorganisms produce adhesive compounds that cement sand and other rocky materials to form mineral "microbial mats". In turn, these mats build up layer by layer, growing gradually over time.
The Pilbara is a large, dry, thinly populated region in the north of Western Australia. It is known for its Aboriginal peoples; its ancient landscapes; the red earth; and its vast mineral deposits, in particular iron ore. It is also a global biodiversity hotspot for subterranean fauna.

The geology of the Grand Canyon area includes one of the most complete and studied sequences of rock on Earth. The nearly 40 major sedimentary rock layers exposed in the Grand Canyon and in the Grand Canyon National Park area range in age from about 200 million to nearly 2 billion years old. Most were deposited in warm, shallow seas and near ancient, long-gone sea shores in western North America. Both marine and terrestrial sediments are represented, including lithified sand dunes from an extinct desert. There are at least 14 known unconformities in the geologic record found in the Grand Canyon.

Marble Bar is a town and rock formation in the Pilbara region of north-western Western Australia. It was the social centre of European settlers in the Pilbara region during the early 1900s, predating the construction of other towns now established.

The Paleoarchean, also spelled Palaeoarchaean, is a geologic era within the Archean Eon. The name derives from Greek "Palaios" ancient. It spans the period of time 3,600 to 3,200 million years ago. The era is defined chronometrically and is not referenced to a specific level of a rock section on Earth. The earliest confirmed evidence of life comes from this era, and Vaalbara, one of Earth's earliest supercontinents, may have formed during this era.

The geology of Australia includes virtually all known rock types, spanning a geological time period of over 3.8 billion years, including some of the oldest rocks on earth. Australia is a continent situated on the Indo-Australian Plate.

The Hamelin Pool Marine Nature Reserve is a protected marine nature reserve located in the UNESCO World Heritage–listed Shark Bay in the Gascoyne region of Western Australia. The 127,000-hectare (310,000-acre) nature reserve boasts the most diverse and abundant examples of living marine stromatolites in the world, monuments to life on Earth over 3,500 million years BP.

Vaalbara is a hypothetical Archean supercontinent consisting of the Kaapvaal Craton and the Pilbara Craton. E. S. Cheney derived the name from the last four letters of each craton's name. The two cratons consist of continental crust dating from 2.7 to 3.6 Ga, which would make Vaalbara one of Earth's earliest supercontinents.

The Pilbara Craton is an old and stable part of the continental lithosphere located in the Pilbara region of Western Australia.

The Bitter Springs Group, also known as the Bitter Springs Formation is a Precambrian fossil locality in Australia, which preserves stromatolites and microorganisms in silica. Its preservational mode ceased in the late Neoproterozoic with the advent of silicifying organisms.
Alcheringa: An Australasian Journal of Palaeontology is a quarterly peer-reviewed scientific journal covering all aspects of palaeontology and its ramifications into the Earth and biological sciences, especially the disciplines of taxonomy, biostratigraphy, micropalaeontology, vertebrate palaeontology, palaeobotany, palynology, palaeobiology, palaeoanatomy, palaeoecology, biostratinomy, biogeography, chronobiology, biogeochemistry and palichnology. It is the official journal of the Association of Australasian Palaeontologists and is published by Taylor & Francis.
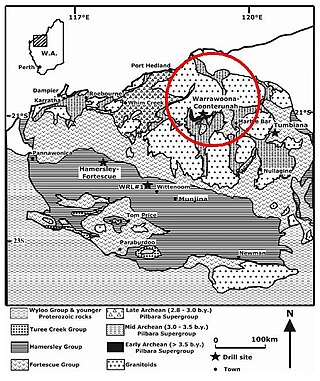
The Warrawoona Group is a geological unit in Western Australia containing putative fossils of cyanobacteria cells. Dated 3.465 Ga, these microstructures, found in Archean chert, are considered to be the oldest known geological record of life on Earth.
This timeline of natural history summarizes significant geological and biological events from the formation of the Earth to the arrival of modern humans. Times are listed in millions of years, or megaanni (Ma).

The Barberton Greenstone Belt of eastern South Africa contains some of the most widely accepted fossil evidence for Archean life. These cell-sized prokaryote fossils are seen in the Barberton fossil record in rocks as old as 3.5 billion years. The Barberton Greenstone Belt is an excellent place to study the Archean Earth due to exposed sedimentary and metasedimentary rocks.
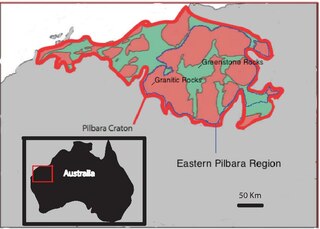
The Eastern Pilbara Craton is the eastern portion of the Pilbara Craton located in Western Australia. This region contains variably metamorphosed mafic and ultramafic greenstone belt rocks, intrusive granitic dome structures, and volcanic sedimentary rocks. These greenstone belts worldwide are thought to be the remnants of ancient volcanic belts, and are subject to much debate in today's scientific community. Areas such as Isua and Barberton which have similar lithologies and ages as Pilbara have been argued to be subduction accretion arcs, while others suggest that they are the result of vertical tectonics. This debate is crucial to investigating when/how plate tectonics began on Earth. The Pilbara Craton along with the Kaapvaal Craton are the only remaining areas of the Earth with pristine 3.6–2.5 Ga crust. The extremely old and rare nature of this crustal region makes it a valuable resource in the understanding of the evolution of the Archean Earth.

The earliest known life forms on Earth may be as old as 4.1 billion years old according to biologically fractionated graphite inside a single zircon grain in the Jack Hills range of Australia. The earliest evidence of life found in a stratigraphic unit, not just a single mineral grain, is the 3.7 Ga metasedimentary rocks containing graphite from the Isua Supracrustal Belt in Greenland. The earliest direct known life on land may be stromatolites which have been found in 3.480-billion-year-old geyserite uncovered in the Dresser Formation of the Pilbara Craton of Western Australia. Various microfossils of microorganisms have been found in 3.4 Ga rocks, including 3.465-billion-year-old Apex chert rocks from the same Australian craton region, and in 3.42 Ga hydrothermal vent precipitates from Barberton, South Africa. Much later in the geologic record, likely starting in 1.73 Ga, preserved molecular compounds of biologic origin are indicative of aerobic life. Therefore, the earliest time for the origin of life on Earth is at least 3.5 billion years ago, possibly as early as 4.1 billion years ago — not long after the oceans formed 4.5 billion years ago and after the formation of the Earth 4.54 billion years ago.
The Dresser Formation is a Paleoarchean geologic formation that outcrops as a generally circular ring of hills the North Pole Dome area of the East Pilbara Terrane of the Pilbara Craton of Western Australia. This formation is one of many formations that comprise the Warrawoona Group, which is the lowermost of four groups that comprise the Pilbara Supergroup. The Dresser Formation is part of the Panorama greenstone belt that surrounds and outcrops around the intrusive North Pole Monzogranite. Dresser Formation consists of metamorphosed, blue, black, and white bedded chert; pillow basalt; carbonate rocks; minor felsic volcaniclastic sandstone and conglomerate; hydrothermal barite; evaporites; and stromatolites. The lowermost of three stratigraphic units that comprise the Dresser Formation contains some of the Earth's earliest commonly accepted evidence of life such as morphologically diverse stromatolites, microbially induced sedimentary structures, putative organic microfossils, and biologically fractionated carbon and sulfur isotopic data.
Kulparia is a genus of fossil stromatolite-forming cyanobacteria from the late Neoproterozoic era. It is named after the town of Kulpara in South Australia, where the type specimen was found nearby.













