
The Magdalena River is the main river of Colombia, flowing northward about 1,528 kilometres (949 mi) through the western half of the country. It takes its name from the biblical figure Mary Magdalene. It is navigable through much of its lower reaches, in spite of the shifting sand bars at the mouth of its delta, as far as Honda, at the downstream base of its rapids. It flows through the Magdalena River Valley.

George Albert Boulenger was a Belgian-British zoologist who described and gave scientific names to over 2,000 new animal species, chiefly fish, reptiles, and amphibians. Boulenger was also an active botanist during the last 30 years of his life, especially in the study of roses.

The Sierra Nevada de Santa Marta is an isolated mountain range in northern Colombia, separate from the Andes range that runs through the north of the country. Reaching an elevation of 5,700 m (18,700 ft) just 42 km (26 mi) from the Caribbean coast, the Sierra Nevada is the highest coastal range in the tropics, and one of the highest coastal ranges in the world, being 250 metres (820 ft) shorter than the Saint Elias Mountains in Canada. The Sierra Nevada encompasses about 17,000 km2 (6,600 sq mi) and serves as the source of 36 rivers. The range is in the Departments of Magdalena, Cesar and La Guajira.

Trichomycterus is a genus of fish in the family Trichomycteridae, the largest genus of its family with over 170 species currently described. This genus is native to freshwater habitats in Central and South America. These fish are generally small, usually about 5 to 15 cm (2–6 in) in standard length, although the largest, T. rivulatus, can reach more than twice this size. Species differ from one another primarily in body proportions, fin ray counts and colouration. Despite their relatively small size, some, such as T. punctulatus, support fisheries and are important in the local cuisine.

Pristella is a genus of fish in the family Characidae. It was formerly a monotypic taxon only containing Pristella maxillaris, but in 2019 a second species, Pristella ariporo, was described.

Hemiancistrus is a genus of suckermouth armored catfishes. These species are native to South America. The taxonomy of this genus is complex and unclear, and major work has to be done. Many of these fish are popular aquarium fish.

The Santa Marta parakeet is an Endangered species of bird in subfamily Arinae of the family Psittacidae, the African and New World parrots. It is endemic to Colombia.

The Santa Marta bush tyrant is a species of bird in the family Tyrannidae (tyrants). It is endemic to Colombia.

Pimelodella is a genus of three-barbeled catfishes.

The Ariporo River is a river in the eastern Casanare Department of Colombia. It is part of the Orinoco River basin.

Creagrutus is a genus of characins found mostly in South America, with one species C. affinis extending into Panama in Central America.
Imparfinis is a genus of three-barbeled catfishes native to South America, with a single species in Central America.
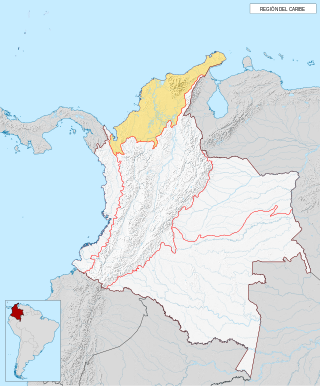
The Caribbean region is mostly lowland plains extending from the northern reaches of the Colombian Andes to the Caribbean Sea that are characterized by a variety of ecosystems including: humid forests, dry forests, savannas, wetlands and desert. The Sierra Nevada de Santa Marta rise from the plains to snow-capped peaks, separated from the Andes as an isolated area of high biodiversity and endemism. It contains one of the largest marshes in Colombia, the Ciénaga Grande de Santa Marta. The main river is the Magdalena which is fully navigable in the region and a major path for the flow of shipments to and from inland Colombia.

The Chibcha Terrane, named after Chibcha, is the largest of the geological provinces (terranes) of Colombia. The terrane, the oldest explored domains of which date to the Meso- to Neoproterozoic, is situated on the North Andes Plate. The megaregional Romeral Fault System forms the contact of the terrane with the Tahamí Terrane. The contact with the Caribbean and La Guajira Terranes is formed by the regional Bucaramanga-Santa Marta Fault. The northeastern boundary is formed by the regional Oca Fault, bounding the La Guajira Terrane. The terrane is emplaced over the Río Negro-Juruena Province of the Amazonian Craton along the megaregional Eastern Frontal Fault System.

Microglanis iheringi is a species of South American catfish described by Alcides Lourenço Gomes in 1945. The species belongs to the genus Microglanis, a group of catfishes that are native to South America and which are distributed widely throughout the region. M. iheringi is endemic to the Orinoco river basin and populations are present in parts of Colombia and Venezuela. One estimate places the total population at more than 10,000 individuals.
Pristella ariporo is a freshwater fish in the family Characidae of the order Characiformes. It is a tropical fish. It resides in the basin of the Orinoco in Colombia.
Pariolius pax is a species of three-barbeled catfish found only in small creeks and tributaries of the upper Orinoco River basin. This species grows to a length of 3.2 centimetres (1.3 in) SL and inhabits sand and gravel bottoms of creeks of relatively fast flowing water as well as sluggish waters of the same streams where aquatic vegetation is lacking. It feeds mainly on Trichoptera larvae.
Pariolius maldonadoi is a species of three-barbeled catfish was found in the small creeks and tributaries of the Upper Orinoco and Negro Rivers in Colombia. This species grows to a length of 3.2 centimetres (1.3 in) SL and inhabits sand and gravel bottoms of creeks of relatively fast flowing water as well as sluggish waters of the same streams where aquatic vegetation is lacking. It feeds mainly on Trichoptera larvae.
Cetopsorhamdia hidalgoi is a species of three-barbeled catfishes native to the upper Amazon in Peru.
Cetopsorhamdia molinae is a species of three-barbeled catfishes found in the Magdalena, Orinoco, and Tocantins River basins in South America. This species reaches a length of 3.6 cm (1.4 in).













