
Adhesive, also known as glue, cement, mucilage, or paste, is any non-metallic substance applied to one or both surfaces of two separate items that binds them together and resists their separation.
Coal tar is a thick dark liquid which is a by-product of the production of coke and coal gas from coal. It is a type of creosote. It has both medical and industrial uses. Medicinally it is a topical medication applied to skin to treat psoriasis and seborrheic dermatitis (dandruff). It may be used in combination with ultraviolet light therapy. Industrially it is a railroad tie preservative and used in the surfacing of roads. Coal tar was listed as a known human carcinogen in the first Report on Carcinogens from the U.S. Federal Government.

A dye is a colored substance that chemically bonds to the substrate to which it is being applied. This distinguishes dyes from pigments which do not chemically bind to the material they color. Dye is generally applied in an aqueous solution and may require a mordant to improve the fastness of the dye on the fiber.

Indigo dye is an organic compound with a distinctive blue color. Indigo is a natural dye extracted from the leaves of some plants of the Indigofera genus, in particular Indigofera tinctoria; dye-bearing Indigofera plants were commonly grown and used throughout the world, in Asia in particular, as an important crop, with the production of indigo dyestuff economically important due to the historical rarity of other blue dyestuffs

The chemical industry comprises the companies that develop and produce industrial, specialty and other chemicals. Central to the modern world economy, it converts raw materials into industrial and consumer products. The plastics industry contains some overlap, as some chemical companies produce plastics as well as chemicals.

Acridine is an organic compound and a nitrogen heterocycle with the formula C13H9N. Acridines are substituted derivatives of the parent ring. It is a planar molecule that is structurally related to anthracene with one of the central CH groups replaced by nitrogen. Like the related molecules pyridine and quinoline, acridine is mildly basic. It is an almost colorless solid, which crystallizes in needles. There are few commercial applications of acridines; at one time acridine dyes were popular, but they are now relegated to niche applications, such as with acridine orange. The name is a reference to the acrid odour and acrid skin-irritating effect of the compound.

Creosote is a category of carbonaceous chemicals formed by the distillation of various tars and pyrolysis of plant-derived material, such as wood, or fossil fuel. They are typically used as preservatives or antiseptics.

Sir William Henry Perkin was a British chemist and entrepreneur best known for his serendipitous discovery of the first commercial synthetic organic dye, mauveine, made from aniline. Though he failed in trying to synthesise quinine for the treatment of malaria, he became successful in the field of dyes after his first discovery at the age of 18.

Naphthalene is an organic compound with formula C
10H
8. It is the simplest polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon, and is a white crystalline solid with a characteristic odor that is detectable at concentrations as low as 0.08 ppm by mass. As an aromatic hydrocarbon, naphthalene's structure consists of a fused pair of benzene rings. It is the main ingredient of traditional mothballs.

Pitch is a viscoelastic polymer which can be natural or manufactured, derived from petroleum, coal tar, or plants. Various forms of pitch may also be called tar, bitumen, or asphalt. Pitch produced from plants is also known as resin. Some products made from plant resin are also known as rosin.

August Wilhelm von Hofmann was a German chemist who made considerable contributions to organic chemistry. His research on aniline helped lay the basis of the aniline-dye industry, and his research on coal tar laid the groundwork for his student Charles Mansfield's practical methods for extracting benzene and toluene and converting them into nitro compounds and amines. Hofmann's discoveries include formaldehyde, hydrazobenzene, the isonitriles, and allyl alcohol. He prepared three ethylamines and tetraethylammonium compounds and established their structural relationship to ammonia.

Tar is a dark brown or black viscous liquid of hydrocarbons and free carbon, obtained from a wide variety of organic materials through destructive distillation. Tar can be produced from coal, wood, petroleum, or peat.

Kotaro Shimomura was a Japanese chemical engineer known for many famous inventions. He coined the term for chemical engineering, kagaku-kōgaku (化学工学), in Japanese in 1909.

Carl Ludwig von Reichenbach was a German chemist, geologist, metallurgist, naturalist, industrialist and philosopher, and a member of the Prussian Academy of Sciences. He is best known for his discoveries of several chemical products of economic importance, extracted from tar, such as eupione, waxy paraffin, pittacal and phenol. He also dedicated himself in his last years to research an unproved field of energy combining electricity, magnetism and heat, emanating from all living things, which he called the Odic force.
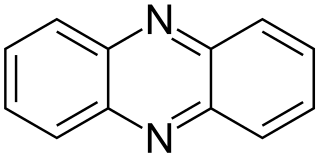
Phenazine is an organic compound with the formula (C6H4)2N2. It is a dibenzo annulated pyrazine, and the parent substance of many dyestuffs, such as the toluylene red, indulines, and safranines (and the closely related eurhodines). Phenazine crystallizes in yellow needles, which are only sparingly soluble in alcohol. Sulfuric acid dissolves it, forming a deep-red solution.
Picamar is a colorless, hydrocarbon oil extracted from the creosote of beechwood tar with a peculiar odor and bitter taste. It consists of derivatives of pyrogallol. It was discovered by German chemist Carl Reichenbach in the 1830s. Picamar can be used to lubricate machinery.

Natural dyes are dyes or colorants derived from plants, invertebrates, or minerals. The majority of natural dyes are vegetable dyes from plant sources—roots, berries, bark, leaves, and wood—and other biological sources such as fungi.

Friedrich Engelhorn was a German industrialist and founder of BASF in Ludwigshafen.
Azuline is a coal-tar blue dye that became popular for colouring silk in 1861. It was one of the first synthetic dyes. The name was a combination of "azure" and "aniline". A variant of the name was "Azurine". The word was introduced as a colour term about the same time as "mauve" and "magenta", but it has not survived in the English language.

A colorant is any substance that changes the spectral transmittance or reflectance of a material. Synthetic colorants are those created in a laboratory or industrial setting. The production and improvement of colorants was a driver of the early synthetic chemical industry, in fact many of today's largest chemical producers started as dye-works in the late 19th or early 20th centuries, including Bayer AG(1863). Synthetics are extremely attractive for industrial and aesthetic purposes as they have they often achieve higher intensity and color fastness than comparable natural pigments and dyes used since ancient times. Market viable large scale production of dyes occurred nearly simultaneously in the early major producing countries Britain (1857), France (1858), Germany (1858), and Switzerland (1859), and expansion of associated chemical industries followed. The mid-nineteenth century through WWII saw an incredible expansion of the variety and scale of manufacture of synthetic colorants. Synthetic colorants quickly became ubiquitous in everyday life, from clothing to food. This stems from the invention of industrial research and development laboratories in the 1870s, and the new awareness of empirical chemical formulas as targets for synthesis by academic chemists. The dye industry became one of the first instances where directed scientific research lead to new products, and the first where this occurred regularly.
Kaufmann, GB - Pittacal—the first synthetic dyestuff. J. Chem. Edu., 753, 1977.

















