
The Battle of Gettysburg was fought July 1–3, 1863, in and around the town of Gettysburg, Pennsylvania, by Union and Confederate forces during the American Civil War. In the battle, Union Major General George Meade's Army of the Potomac defeated attacks by Confederate General Robert E. Lee's Army of Northern Virginia, halting Lee's invasion of the North. The battle involved the largest number of casualties of the entire war and is often described as the war's turning point due to the Union's decisive victory and concurrence with the Siege of Vicksburg.

John Fulton Reynolds was a career United States Army officer and a general in the American Civil War. One of the Union Army's most respected senior commanders, he played a key role in committing the Army of the Potomac to the Battle of Gettysburg and was killed at the start of the battle.
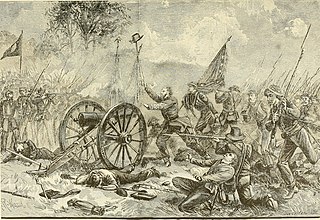
Pickett's Charge, also known as the Pickett–Pettigrew–Trimble Charge, was an infantry assault ordered by Confederate General Robert E. Lee against Major General George G. Meade's Union positions on the last day of the Battle of Gettysburg in the commonwealth of Pennsylvania during the Civil War. Confederate troops made a frontal assault towards the center of Union lines, ultimately being repulsed with heavy casualties. Suffering from a lack of preparation and problems from the onset, the attack was a costly mistake that decisively ended Lee's invasion of the north and forced a retreat back to Virginia.

Cemetery Hill is a landform on the Gettysburg Battlefield that was the scene of fighting each day of the Battle of Gettysburg. The northernmost part of the Army of the Potomac defensive "fish-hook" line, the hill is gently sloped and provided a site for American Civil War artillery.

Little Round Top is the smaller of two rocky hills south of Gettysburg, Pennsylvania—the companion to the adjacent, taller hill named Big Round Top. It was the site of an unsuccessful assault by Confederate troops against the Union left flank on July 2, 1863, the second day of the Battle of Gettysburg, during the American Civil War.

The Peach Orchard is a Gettysburg Battlefield site at the southeast corner of the north-south Emmitsburg Road intersection with the Wheatfield Road. The orchard is demarcated on the east and south by Birney Avenue, which provides access to various memorials regarding the "momentous attacks and counterattacks in…the orchard on the afternoon of July 2, 1863."

Gettysburg is a 1993 American epic war film about the Battle of Gettysburg in the American Civil War. Written and directed by Ronald F. Maxwell, the film was adapted from the 1974 historical novel The Killer Angels by Michael Shaara. It features an ensemble cast, including Tom Berenger as James Longstreet, Jeff Daniels as Joshua Chamberlain, Martin Sheen as Robert E. Lee, Stephen Lang as George Pickett, and Sam Elliott as John Buford.
The Battle of Thoroughfare Gap, also known as Chapman's Mill, took place on August 28, 1862, in Fauquier County and Prince William County, Virginia, as part of the Northern Virginia Campaign of the American Civil War. Confederate forces under Maj. Gen. James Longstreet successfully drove back Union forces under Brig. Gen. James B. Ricketts and Col. Percy Wyndham, allowing his corps to unite with that of Thomas J. "Stonewall" Jackson prior to the Second Battle of Bull Run.

The Battle of Aldie took place on June 17, 1863, in Loudoun County, Virginia, as part of the Gettysburg Campaign of the American Civil War.

Evander McIver Law was an author, teacher, and a Confederate general in the American Civil War.

Devil's Den is a boulder-strewn hill on the south end of Houck's Ridge at Gettysburg Battlefield, used by artillery and sharpshooters on the second day of the 1863 Battle of Gettysburg during the American Civil War. A tourist attraction since the memorial association era, several boulders are worn from foot traffic and the site includes numerous cannon, memorials, and walkways, including a bridge spanning two boulders.

Seminary Ridge is a dendritic ridge which was an area of Battle of Gettysburg engagements in July 1863 during the American Civil War (1861–1865), and of military installations during World War II (1941–1945).

Hiram Berdan was an American engineer, inventor, military officer, marksman, and guiding force behind and commanding colonel of the United States Volunteer Sharpshooter Regiments during the American Civil War. He was the inventor of the Berdan rifle, the Berdan centerfire primer and other weapons and accessories.

During the second day of the Battle of Gettysburg Confederate Gen. Robert E. Lee attempted to capitalize on his first day's accomplishments. His Army of Northern Virginia launched multiple attacks on the flanks of the Union Army of the Potomac, commanded by Maj. Gen. George G. Meade. The assaults were unsuccessful, and resulted in heavy casualties for both sides.

Rock Creek is an 18.9-mile-long (30.4 km) tributary of the Monocacy River in south-central Pennsylvania and serves as the border between Cumberland and Mount Joy townships. Rock Creek was used by the Underground Railroad and flows near several Gettysburg Battlefield sites, including Culp's Hill, the Benner Hill artillery location, and Barlow Knoll.

Micah Jenkins, was a Confederate general in the American Civil War, mortally wounded by friendly fire at the Battle of the Wilderness.
The 1st United States Sharpshooters were an infantry regiment that served in the Union Army during the American Civil War. During battle, the mission of the sharpshooter was to kill enemy targets of importance from long range.

A sharpshooter is one who is highly proficient at firing firearms or other projectile weapons accurately. Military units composed of sharpshooters were important factors in 19th-century combat. Along with "marksman" and "expert", "sharpshooter" is one of the three marksmanship badges awarded by the United States Army and the United States Marine Corps. The United States Navy and the United States Coast Guard use a ribbon with an attached "S" device to note a sharpshooter qualification.
Pitzer Woods is a Gettysburg Battlefield site used for Gettysburg Battlefield camps after the American Civil War such as the 1933–37 Camp Renaissance Civilian Conservation Corps camp.

The 1st Company Massachusetts Sharpshooters was a sharpshooter unit in the Union Army during the American Civil War.

















