
An electric current is a flow of charged particles, such as electrons or ions, moving through an electrical conductor or space. It is defined as the net rate of flow of electric charge through a surface. The moving particles are called charge carriers, which may be one of several types of particles, depending on the conductor. In electric circuits the charge carriers are often electrons moving through a wire. In semiconductors they can be electrons or holes. In an electrolyte the charge carriers are ions, while in plasma, an ionized gas, they are ions and electrons.
In physics, screening is the damping of electric fields caused by the presence of mobile charge carriers. It is an important part of the behavior of charge-carrying fluids, such as ionized gases, electrolytes, and charge carriers in electronic conductors . In a fluid, with a given permittivity ε, composed of electrically charged constituent particles, each pair of particles interact through the Coulomb force as

A corona discharge is an electrical discharge caused by the ionization of a fluid such as air surrounding a conductor carrying a high voltage. It represents a local region where the air has undergone electrical breakdown and become conductive, allowing charge to continuously leak off the conductor into the air. A corona discharge occurs at locations where the strength of the electric field around a conductor exceeds the dielectric strength of the air. It is often seen as a bluish glow in the air adjacent to pointed metal conductors carrying high voltages, and emits light by the same mechanism as a gas discharge lamp. Corona discharges can also happen in weather, such as thunderstorms, where objects like ship masts or airplane wings have a charge significantly different from the air around them.
Plasma diagnostics are a pool of methods, instruments, and experimental techniques used to measure properties of a plasma, such as plasma components' density, distribution function over energy (temperature), their spatial profiles and dynamics, which enable to derive plasma parameters.

A glow discharge is a plasma formed by the passage of electric current through a gas. It is often created by applying a voltage between two electrodes in a glass tube containing a low-pressure gas. When the voltage exceeds a value called the striking voltage, the gas ionization becomes self-sustaining, and the tube glows with a colored light. The color depends on the gas used.
In physics, the Saha ionization equation is an expression that relates the ionization state of a gas in thermal equilibrium to the temperature and pressure. The equation is a result of combining ideas of quantum mechanics and statistical mechanics and is used to explain the spectral classification of stars. The expression was developed by physicist Meghnad Saha in 1920.
A Coulomb collision is a binary elastic collision between two charged particles interacting through their own electric field. As with any inverse-square law, the resulting trajectories of the colliding particles is a hyperbolic Keplerian orbit. This type of collision is common in plasmas where the typical kinetic energy of the particles is too large to produce a significant deviation from the initial trajectories of the colliding particles, and the cumulative effect of many collisions is considered instead. The importance of Coulomb collisions was first pointed out by Lev Landau in 1936, who also derived the corresponding kinetic equation which is known as the Landau kinetic equation.
The Madison Symmetric Torus (MST) is a reversed field pinch (RFP) physics experiment with applications to both fusion energy research and astrophysical plasmas.
The diffusion of plasma across a magnetic field was conjectured to follow the Bohm diffusion scaling as indicated from the early plasma experiments of very lossy machines. This predicted that the rate of diffusion was linear with temperature and inversely linear with the strength of the confining magnetic field.

The degree of ionization refers to the proportion of neutral particles, such as those in a gas or aqueous solution, that are ionized. For electrolytes, it could be understood as a capacity of acid/base to ionize itself. A low degree of ionization is sometimes called partially ionized, and a high degree of ionization as fully ionized. However, the term fully ionized is also used to describe an ion that has no electrons left.

The mass-to-charge ratio (m/Q) is a physical quantity relating the mass (quantity of matter) and the electric charge of a given particle, expressed in units of kilograms per coulomb (kg/C). It is most widely used in the electrodynamics of charged particles, e.g. in electron optics and ion optics.
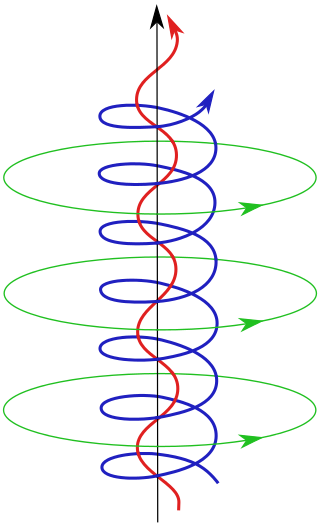
Plasma parameters define various characteristics of a plasma, an electrically conductive collection of charged particles that responds collectively to electromagnetic forces. Plasma typically takes the form of neutral gas-like clouds or charged ion beams, but may also include dust and grains. The behaviour of such particle systems can be studied statistically.
Neutral-beam injection (NBI) is one method used to heat plasma inside a fusion device consisting in a beam of high-energy neutral particles that can enter the magnetic confinement field. When these neutral particles are ionized by collision with the plasma particles, they are kept in the plasma by the confining magnetic field and can transfer most of their energy by further collisions with the plasma. By tangential injection in the torus, neutral beams also provide momentum to the plasma and current drive, one essential feature for long pulses of burning plasmas. Neutral-beam injection is a flexible and reliable technique, which has been the main heating system on a large variety of fusion devices. To date, all NBI systems were based on positive precursor ion beams. In the 1990s there has been impressive progress in negative ion sources and accelerators with the construction of multi-megawatt negative-ion-based NBI systems at LHD (H0, 180 keV) and JT-60U (D0, 500 keV). The NBI designed for ITER is a substantial challenge (D0, 1 MeV, 40 A) and a prototype is being constructed to optimize its performance in view of the ITER future operations. Other ways to heat plasma for nuclear fusion include RF heating, electron cyclotron resonance heating (ECRH), ion cyclotron resonance heating (ICRH), and lower hybrid resonance heating (LH).
The polywell is a design for a fusion reactor based on two ideas: heating ions by concentrating (-) charge to accelerate the ions and trapping a diamagnetic plasma inside a cusp field.
The electrothermal instability is a magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) instability appearing in magnetized non-thermal plasmas used in MHD converters. It was first theoretically discovered in 1962 and experimentally measured into a MHD generator in 1963 by Evgeny Velikhov.
"This paper shows that it is possible to assert sufficiently specifically that the ionization instability is the number one problem for the utilization of a plasma with hot electrons."

Plasma is one of four fundamental states of matter, characterized by the presence of a significant portion of charged particles in any combination of ions or electrons. It is the most abundant form of ordinary matter in the universe, mostly in stars, but also dominating the rarefied intracluster medium and intergalactic medium. Plasma can be artificially generated, for example, by heating a neutral gas or subjecting it to a strong electromagnetic field.

In electromagnetism, a streamer discharge, also known as filamentary discharge, is a type of transient electric discharge which forms at the surface of a conductive electrode carrying a high voltage in an insulating medium such as air. Streamers are luminous writhing branching sparks, plasma channels composed of ionized air molecules, which repeatedly strike out from the electrode into the air.
The index of physics articles is split into multiple pages due to its size.
A non-neutral plasma is a plasma whose net charge creates an electric field large enough to play an important or even dominant role in the plasma dynamics. The simplest non-neutral plasmas are plasmas consisting of a single charge species. Examples of single species non-neutral plasmas that have been created in laboratory experiments are plasmas consisting entirely of electrons, pure ion plasmas, positron plasmas, and antiproton plasmas.

Dynamics Explorer 2 was a NASA low-altitude mission, launched on 3 August 1981. It consisted of two satellites, DE-1 and DE-2, whose purpose was to investigate the interactions between plasmas in the magnetosphere and those in the ionosphere. The two satellites were launched together into polar coplanar orbits, which allowed them to simultaneously observe the upper and lower parts of the atmosphere.









