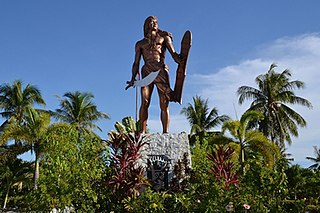The Battle of Mactan was fought on a beach in Mactan Island between Spanish forces led by the Portuguese explorer Ferdinand Magellan along with local allies, and Lapulapu, the chieftain of the island, on the early morning hours of April 27, 1521. Magellan, a Portuguese-born commander serving the Spanish Empire who led an expedition that ultimately circumnavigated the world for the first time, commanded a small Spanish contingent in an effort to subdue Mactan under the Spanish crown. The sheer number of Lapulapu's forces, compounded with issues associated with the location and the armor, ultimately resulted in a disastrous defeat to the Europeans and the death of Magellan. Surviving members of Magellan's crew continued the expedition under the command of Juan Sebastian de Elcano, who completed the journey in September 1522.

Cebu City, officially the City of Cebu, is a 1st class highly urbanized city in the Central Visayas region of the Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 964,169 people, making it the sixth-most populated city in the nation and the most populous in the Visayas and in Central Visayas Region.

Lapulapu or Lapu-Lapu, whose name was first recorded as Çilapulapu, was a datu (chief) of Mactan, an island now part of the Philippines. Lapulapu is known for the 1521 Battle of Mactan, where he and his men defeated Spanish forces led by Portuguese explorer Ferdinand Magellan and his native allies Rajah Humabon and Datu Zula. Magellan's death in battle ended his voyage of circumnavigation and delayed the Spanish occupation of the islands by over forty years until the expedition of Miguel López de Legazpi in 1564.

Intramuros is the 0.67-square-kilometer (0.26 sq mi) historic walled area within the city of Manila, the capital of the Philippines. It is administered by the Intramuros Administration with the help of the city government of Manila.

Fort San Pedro is a military defense structure in Cebu, Philippines, built by the Spanish under the command of Miguel López de Legazpi, first governor of the Captaincy General of the Philippines. It is located in the area now called Plaza Independencia, in the pier area of the city. The original fort was made of wood and built after the arrival of Legazpi and his expedition. In the early 17th century a stone fort was built to repel Muslim raiders. Today's structure dates from 1738 and is the oldest triangular bastion fort in the country. It served as the nucleus of the first Spanish settlement in the Philippines. During the Philippine Revolution at the end of the 19th century, it was attacked and taken by Filipino revolutionaries, who used it as a stronghold.

Magellan's Cross Pavilion is a stone kiosk in Cebu City, Philippines. The structure is situated on Plaza Sugbo beside the Basilica del Santo Niño. It houses a Christian cross that was planted by explorers of the Spanish expedition of the first circumnavigation of the world, led by Ferdinand Magellan, upon arriving in Cebu in the Philippines on April 21, 1521.

Dapitan, officially the City of Dapitan, is a 3rd class component city in the province of Zamboanga del Norte, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 85,202 people.

Naga, officially the City of Naga, or the Pilgrim City of Naga, is a 1st class independent component city in the Bicol Region. According to the 2020 census, Naga has a population of 209,170 people. The most populous in Camarines Sur and the second most populous following Legazpi in Albay.

The architecture of the Philippines reflects the historical and cultural traditions in the country. Most prominent historic structures in the archipelago are influenced by Austronesian and American architectures.
Rajah Humabon later baptized as Don Carlos Valderrama, was one of the recorded chiefs in Cebu who encountered Ferdinand Magellan in the 16th century. Humabon ruled at the time of the arrival of Portuguese-born Spanish explorer Ferdinand Magellan in the Philippines in 1521. Humabon, his wife, and his subjects were the first known Christian converts in the Philippines. However, since there were no Catholic priests in Cebu from 1521 to 1565, this Christianity was not practised until the return of the Spaniards to Cebu. There is no official record of Humabon's existence before the Spanish contact. The existing information was written by Magellan's Italian voyage chronicler, Antonio Pigafetta on Humabon and the indigenous Philippine peoples that existed prior to Spanish colonization. Rajah Humabon is cited as the reason for why Magellan fought in the Battle of Mactan, as the latter wanted to earn the trust of Humabon by helping him subdue his opponent Lapulapu, one of the chiefs of Mactan. Despite being referred to as "king" in the journal of Antonio Pigafetta, he was not one like in the manner of a monarch in centralized societies, it is plausible that the title was mistakenly applied because according to succeeding chroniclers, there were no kingdoms in the pre-colonial Philippines.

The National Historical Commission of the Philippines (NHCP) and its predecessor agencies install historical markers in the Philippines and overseas to signify important and historic events, persons, sites, structures, and institutions. The commemorative plaques are permanent signs installed by the NHCP in publicly visible locations on buildings, monuments, or in special locations. The NHCP also allows local municipalities and cities to install markers of figures and events of local significance, although these markers are barred from using the seal of the Republic of the Philippines.

The first documented Catholic Mass in the Philippines was held on March 31, 1521, Easter Sunday. It was conducted by Father Pedro de Valderrama of Ferdinand Magellan's expedition along the shores of what was referred to in the journals of Antonio Pigafetta as "Mazaua".
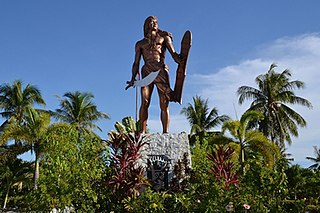
Mactan Shrine, also known as Liberty Shrine or Lapulapu Monument, is a memorial park on the island of Mactan in Lapu-Lapu City, Philippines. It hosts two monuments, namely the Magellan Monument, which is dedicated to Portuguese explorer Ferdinand Magellan and the Lapu Lapu Monument, a bronze statue which commemorates Lapu Lapu, a native leader who defeated Spanish soldiers led by Magellan in the 1521 Battle of Mactan.

The 2021 Quincentennial Commemorations in the Philippines was a series of observances organized to mark the 500th anniversary of various events in the Philippines, notably the introduction of Christianity in the Philippines, the role of the country in the Magellan–Elcano circumnavigation, and the victory of Lapulapu in the Battle of Mactan.
The Lapulapu Memorial Shrine and Museum is a proposed museum and monument to Lapulapu to be built at Mactan Shrine in Lapu-Lapu City, Philippines.

The Blockade of Cebu was a failed Portuguese naval action against the Spanish colony in the present-day city of Cebu, Philippines in 1568. The Portuguese fleet under captain-general Gonzalo Pereira blockaded Cebu in an effort to starve and expel the Spanish. However, the Spanish colony proved to be resistant to the blockade and the Portuguese fleet eventually suffered from typhoid fever. Pereira then decided to lift the blockade and sail the fleet to the Maluku Islands.

Plaza Sugbu, formerly known as Plaza Rizal, is a public square in Cebu City, Philippines. The square connects the Magellan's Cross kiosk and the Cebu City Hall. The square was inaugurated in 2008 by Philippine president Gloria Arroyo.