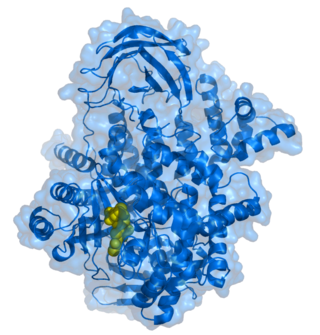
Phosphoinositide 3-kinases (PI3Ks), also called phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases, are a family of enzymes involved in cellular functions such as cell growth, proliferation, differentiation, motility, survival and intracellular trafficking, which in turn are involved in cancer.
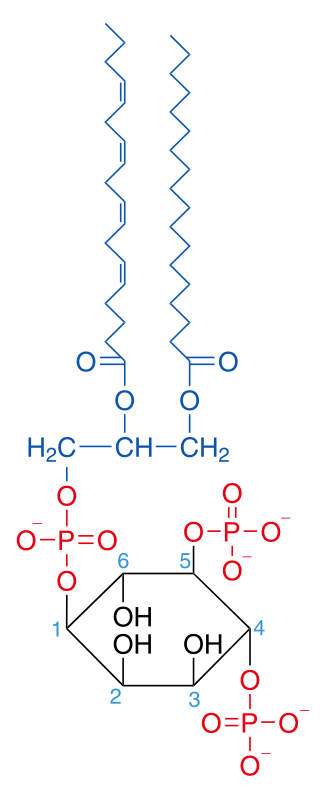
Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate or PtdIns(4,5)P2, also known simply as PIP2 or PI(4,5)P2, is a minor phospholipid component of cell membranes. PtdIns(4,5)P2 is enriched at the plasma membrane where it is a substrate for a number of important signaling proteins. PIP2 also forms lipid clusters that sort proteins.

Phosphatidylinositol (3,4)-bisphosphate is a minor phospholipid component of cell membranes, yet an important second messenger. The generation of PtdIns(3,4)P2 at the plasma membrane activates a number of important cell signaling pathways.

Pleckstrin homology domain or (PHIP) is a protein domain of approximately 120 amino acids that occurs in a wide range of proteins involved in intracellular signaling or as constituents of the cytoskeleton.

Gelsolin is an actin-binding protein that is a key regulator of actin filament assembly and disassembly. Gelsolin is one of the most potent members of the actin-severing gelsolin/villin superfamily, as it severs with nearly 100% efficiency.
Phospholipase D (EC 3.1.4.4, lipophosphodiesterase II, lecithinase D, choline phosphatase, PLD; systematic name phosphatidylcholine phosphatidohydrolase) is an enzyme of the phospholipase superfamily that catalyses the following reaction

Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase regulatory subunit alpha is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PIK3R1 gene.

PTK2 protein tyrosine kinase 2 (PTK2), also known as focal adhesion kinase (FAK), is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the PTK2 gene. PTK2 is a focal adhesion-associated protein kinase involved in cellular adhesion and spreading processes. It has been shown that when FAK was blocked, breast cancer cells became less metastatic due to decreased mobility.

Ezrin also known as cytovillin or villin-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EZR gene.

ROCK1 is a protein serine/threonine kinase also known as rho-associated, coiled-coil-containing protein kinase 1. Other common names are ROKβ and P160ROCK. ROCK1 is a major downstream effector of the small GTPase RhoA and is a regulator of the actomyosin cytoskeleton which promotes contractile force generation. ROCK1 plays a role in cancer and in particular cell motility, metastasis, and angiogenesis.
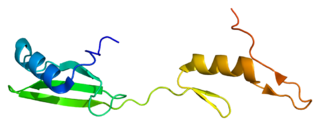
Cytoplasmic protein NCK1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NCK1 gene.

Tyrosine-protein kinase Tec is a tyrosine kinase that in humans is encoded by the TEC gene. Tec kinase is expressed in hematopoietic, liver, and kidney cells and plays an important role in T-helper cell processes. Tec kinase is the name-giving member of the Tec kinase family, a family of non-receptor protein-tyrosine kinases.

Pleckstrin homology domain-containing family O member 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PLEKHO1 gene.

Pleckstrin homology domain-containing family A member 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PLEKHA1 gene.

SH2B adapter protein 3 (SH2B3), also known as lymphocyte adapter protein (LNK), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SH2B3 gene on chromosome 12. SH2B3 is ubiquitously expressed in many tissues and cell types. LNK functions as a regulator in signaling pathways relating to hematopoiesis, inflammation, and cell migration. As a result, it is involved in blood diseases, autoimmune disorders, and vascular disease. The SH2B3 gene also contains one of 27 SNPs associated with increased risk of coronary artery disease.
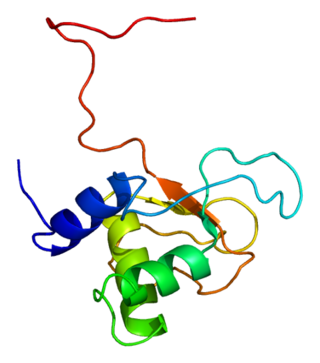
Pleckstrin-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PLEK2 gene. The PLEK2 gene is located on chromosome 14 in Homo sapiens and is flanked by TMEM229B to its right and ATP6V1D to its left.
The Akt signaling pathway or PI3K-Akt signaling pathway is a signal transduction pathway that promotes survival and growth in response to extracellular signals. Key proteins involved are PI3K and Akt.

In the field of biochemistry, PDPK1 refers to the protein 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1, an enzyme which is encoded by the PDPK1 gene in humans. It is implicated in the development and progression of melanomas.
A non-receptor tyrosine kinase (nRTK) is a cytosolic enzyme that is responsible for catalysing the transfer of a phosphate group from a nucleoside triphosphate donor, such as ATP, to tyrosine residues in proteins. Non-receptor tyrosine kinases are a subgroup of protein family tyrosine kinases, enzymes that can transfer the phosphate group from ATP to a tyrosine residue of a protein (phosphorylation). These enzymes regulate many cellular functions by switching on or switching off other enzymes in a cell.

Rho-associated protein kinase (ROCK) is a kinase belonging to the AGC family of serine-threonine specific protein kinases. It is involved mainly in regulating the shape and movement of cells by acting on the cytoskeleton.

















